Congenital heart defects. Faulty heart chambers or valves at birth can directly affect the functionality of the heart. Other heart conditions. Viral infections such as COVID-19 may cause inflammation of the cardiac muscles known as myocarditis. 1. Initiating Interventions for Decrease in Cardiac Output 2. Monitoring Diagnostic Procedures and Laboratory Studies 3. Administering Medication and Providing Pharmacological Interventions 4. Maintaining or Improving Respiratory Function 5. Managing Fluid Volume and Electrolyte Imbalance 6. Providing Perioperative Nursing Care 7.
Congestive Heart Failure CHF Nursing Diagnosis Care Plan
Written by Maegan Wagner, BSN, RN, CCM Heart failure (HF), sometimes referred to as Congestive Heart Failure (CHF), occurs when the heart can't supply blood effectively to the rest of the body. The left ventricle of the heart is larger and is responsible for most of the pumping action. Most patients with heart failure have symptoms due to impaired left ventricular myocardial function. Patients usually present with dyspnea, fatigue, decreased exercise tolerance, and fluid retention, seen as pulmonary and peripheral edema. [1] Upon physical assessment his breathing is shallow and labored, respiratory rate is 30 breaths per minute, heart rate 115 beats per minute, oxygen saturation 83% on room air, blood pressure 179/98 mm Hg, he has +4 pitting edema in bilateral lower extremities, and crackles are heard in his lung fields throughout. Updated on May 19, 2022 By Marianne Belleza, R.N. Learn about the nursing care management of patients with heart failure. What is Heart Failure? Heart failure, also known as congestive heart failure, is recognized as a clinical syndrome characterized by signs and symptoms of fluid overload or of inadequate tissue perfusion.

congestive_heart_failure_differential_diagnosis_map Nursing notes
Congestive heart failure (CHF), as defined by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) and the American Heart Association (AHA), is "a complex clinical syndrome that results from any structural or functional impairment of ventricular filling or ejection of blood." This page contains the complete congestive heart failure nursing lecture e.g. (definition, pathophysiology,& more) ,nursing exam and nursing care plan. Outline Objective for Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) What is Congestive Heart Failure? Imagine your heart is like a pump in a garden watering system. In Congestive Heart Failure, this pump isn't working as well as it should. It doesn't mean the heart has stopped working, but it's struggling to pump blood efficiently. Management. Nursing Diagnosis & Care Plan. Congestive heart failure (CHF), otherwise known simply as heart failure (HF) is the medical term that describes the heart's inability to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow and meet the body's metabolic needs. This ineffective pumping leads to congestion of the venous circuit on both the.
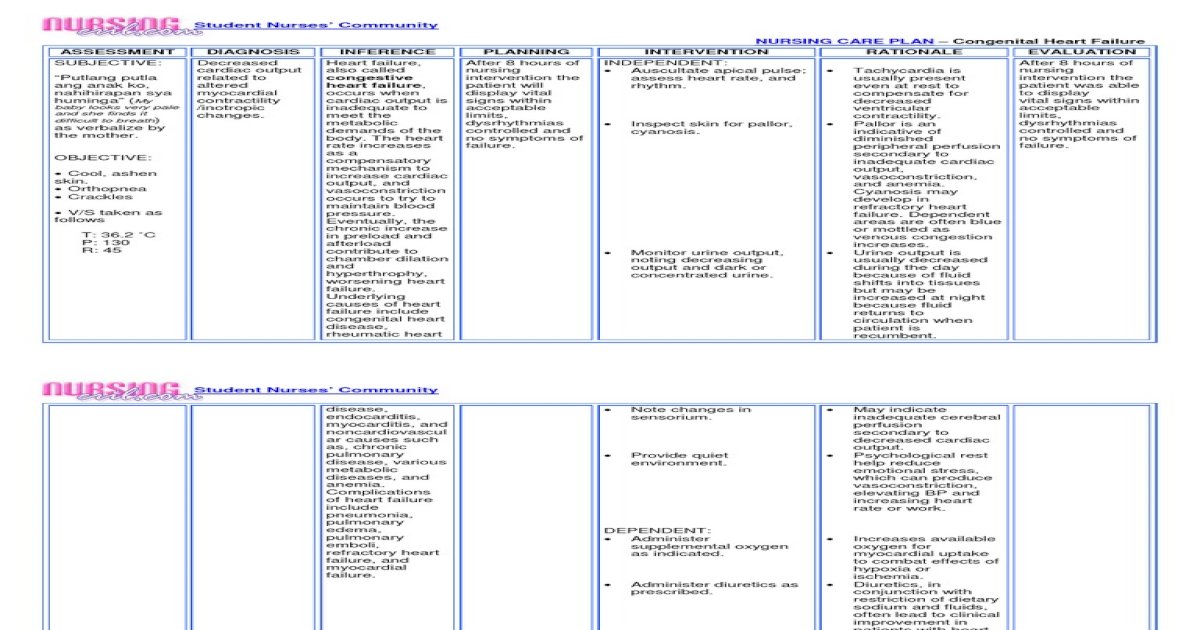
Nursing Care Plan Congestive Heart Failure [PDF Document]
Congestive heart failure causes substantial patient morbidity and mortality in the United States. Symptoms and physical findings can be helpful in diagnosis but have limited sensitivity and specificity. Objective measurement of ventricular function is essential in virtually all patients in whom a diagnosis of heart failure is suspected. Reversible causes of heart failure must be sought. Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a severe condition that can be difficult to manage and requires comprehensive care. Without an effective nursing care plan, CHF patients may not receive the care they need to improve their quality of life. This can lead to further complications and even death.
Introduction. Heart failure is a common and complex clinical syndrome that results from any functional or structural heart disorder, impairing ventricular filling or ejection of blood to the systemic circulation to meet the body's needs. Heart failure can be caused by several different diseases. Most patients with heart failure have symptoms. Diagnosis. To diagnose heart failure, your health care provider examines you and asks questions about your symptoms and medical history. Your provider checks to see if you have risk factors for heart failure, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease or diabetes. Your care provider listens to your lungs and heart with a device called.
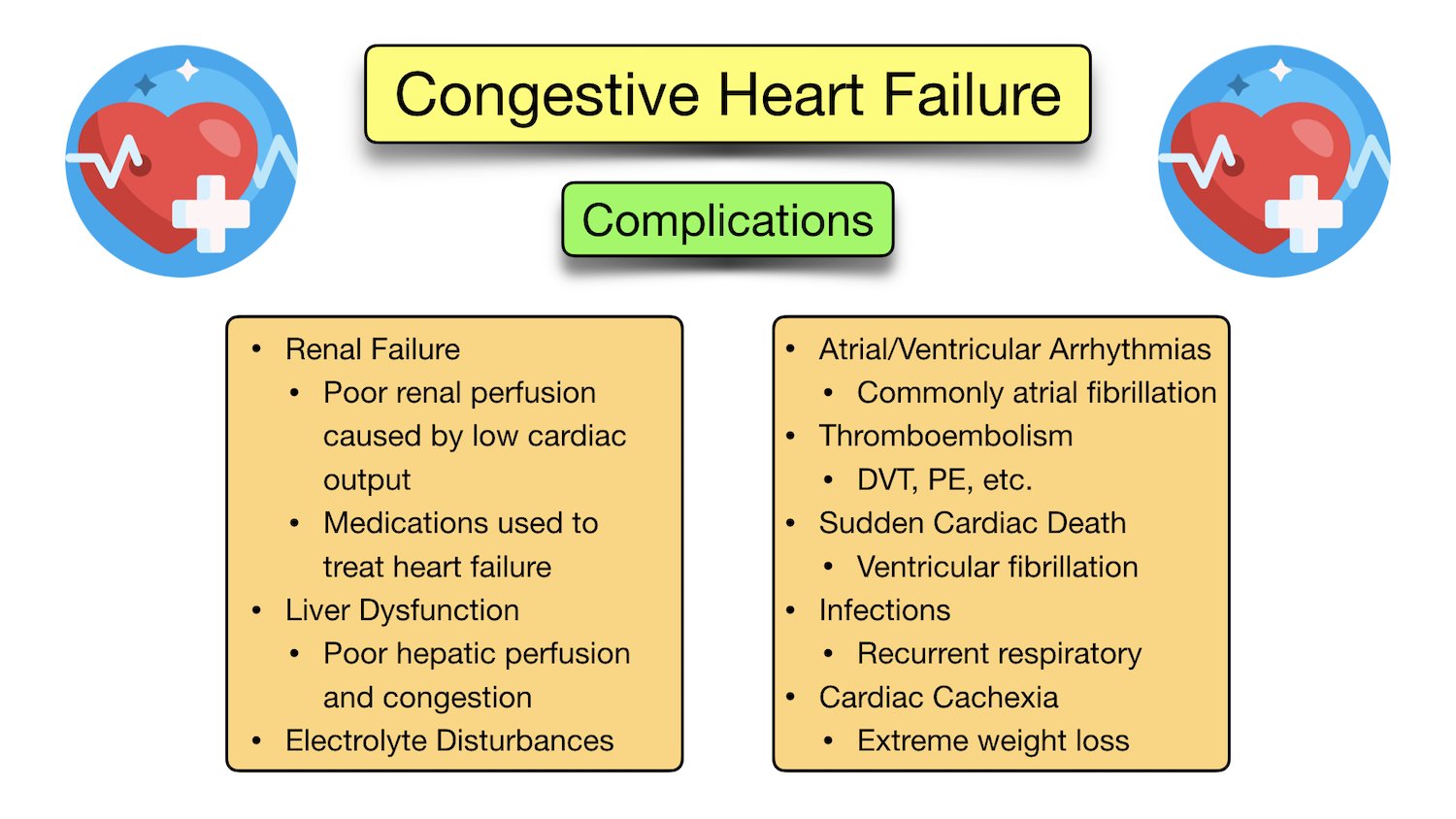
Congestive Heart Failure Symptoms, Stages, Treatment, Diagnosis
To accomplish this aim, 53 terms were identified in the focus axis of the International Classification for Nursing Practice (ICNP®), which guided the construction of these statements using the guidelines of the International Council of Nurses and ISO 18. 104. Lets take a look at a concept map for congestive heart failure or CHF! So in this lesson we will take a look at the components of a concept map including contributing factors, medications, lab work and the significance, patient education, and associated nursing diagnoses with interventions and evaluations! Ok so here is a basic example of a.




