Looking for Bird Parts? Find it all on eBay with Fast and Free Shipping. No matter what you love, you'll find it here. Search Bird Parts and more. What Are the Parts of a Bird? Birds are a remarkable group of animals, known for their ability to take flight and their unique features that distinguish them from other creatures. What sets a bird apart and defines its identity?
basicpartsofabird Bird Academy • The Cornell Lab
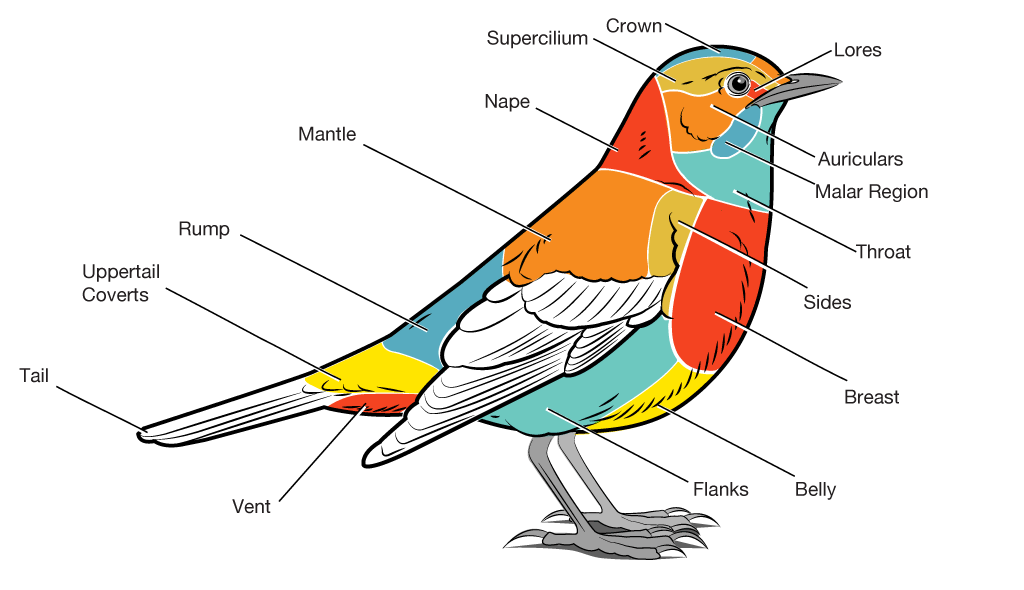
How much do you know about bird anatomy? Test yourself with an interactive reference guide to all the important anatomical systems in a bird. Belly: area below the breast and reaching to the vent. These feathers overlap the bases of the undertail coverts. Cere: the fleshy, often brightly coloured, structure at the base of the bill. Chin: ventral leathering below the bill ending where throat begins. Crest: the tuft of elongated feathers on the head of some species. patella tarsometatarsus digits tibia ( tibiotarsus) fibula ( tibiotarsus) femur ischium ( innominate) pubis (innominate) ilium (innominate) caudal vertebrae pygostyle synsacrum scapula dorsal vertebrae humerus ulna radius Carpometacarpus Parts of a Bird Bird Parts List Forehead Beak Chin Eye Throat Wing Thigh Tarsus Foot Undertail feathers Tail Uppertail feathers Rump Back Nape Crown Bird Anatomy Image Parts of a Bird Names with Pictures and Examples Learn these bird body parts names to increase your vocabulary about animal body parts in English.

Parts of a BIRD Vocabulary English Study Here
The nervous system is large relative to the bird's size. The most developed part of the brain of birds is the one that controls the flight-related functions, while the cerebellum coordinates movement and the cerebrum controls behaviour patterns, navigation, mating and nest building. They are actually modified front legs. Birds move their wings using muscles in the chest. These muscles are quite large, making up as much as 35 percent of a bird's body weight. Feathers help birds fly and also provide insulation and serve other purposes. Birds actually have two basic types of feathers: flight feathers and down feathers. Flying birds have evolved skeletons in which part of the bone is replaced by air spaces, an adaptation for reducing weight. The crop, an enlarged part of the esophagus used for temporary food storage, enables birds to feed while in flight. The wings and bill are part of a bird's skeleton. The bill is composed of two bones. The upper beak, also known as the premaxillary bone, and the lower jaw, also known as the mandibular bone. Anatomical differences. Birds have several anatomical differences from other animals. For example, unlike most mammals, birds have: Birds don't have a.

English Vocabulary Birds and Parts of a Bird ESL Buzz
The mantle, rump, uppertail coverts, and folded wings are loosely referred to as the back or upper parts. The rump is generally under the folded wings of a perched bird. The wing feathers are discussed in detail in a separate article. Mantle: Area below the nape. Parts of a Bird: Flight Feathers The colors, lengths, and shapes of a bird's wing and tail feathers are variable, but the configuration and positioning are remarkably similar across all species.
What are birds? Test your knowledge of birds with this quiz. Play Let's go • • • • • Question 1 of 5 What kind of animal is an eagle? a bird a mammal a fish • • • • • Question 2 of 5 Which. Abdomen: The abdomen or belly of a bird extends from the bottom of the chest to the undertail coverts. The colors and markings on the abdomen may vary from the chest and flanks, making it a good feature to check for identification. Flanks: The flanks (sides) of a bird are located between the underside of the wings and the abdomen.

Basic Bird Anatomy World of Birds
Ornithologists talk about parts of a bird by dividing its body into topographical regions. The main divisions are beak (or bill), head, back, throat, breast, wings, tail, and legs.. Birds' wings are another great place to pick up clues to a bird's identity. In a few groups, including warblers and vireos, wing markings can give you a. Ovary and testes: the reproductive organs in birds that produce eggs and sperm. Crop: an enlarged part of the esophagus that serves as a food storage area. Haunches: the thick muscles located at the base of the tail that power the bird's flight. Pectoral muscles: the large muscles in the chest that power the bird's wings during flight.




