plant cell, the basic unit of all plants.Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane. Plant cells are eukaryotic cells, that are found in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae which means they have a membrane-bound nucleus. They have a variety of membrane-bound cell organelles that perform various specific functions to maintain the normal functioning of the plant cell. Table of Contents

Plant Cell Parts and Structure
7,261 5,292 Let us have a detailed look at the plant cell, its structure, and the functions of different plant cell organelles. Plant Cell Definition "Plant cells are eukaryotic cells with a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out certain specific functions." Table of Contents What is a Plant Cell? Plant cells comprise several organelles, each with unique functions vital to the cell's operation: Cell Wall: The cell wall is a rigid layer that provides support, protection, and shape to the cell. It consists mainly of cellulose. Plasma Membrane: This is a semi-permeable membrane that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Figure 10.1.5 10.1. 5: A micrograph of a cell nucleus. The nucleolus (A) is a condensed region within the nucleus (B) where ribosomes are synthesized. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (C). Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (D) is composed of many layers of folded membrane. Plant and animal cells are both eukaryotic cells, meaning they possess a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. They share many common features, such as a cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, and more. However, they have some apparent differences.
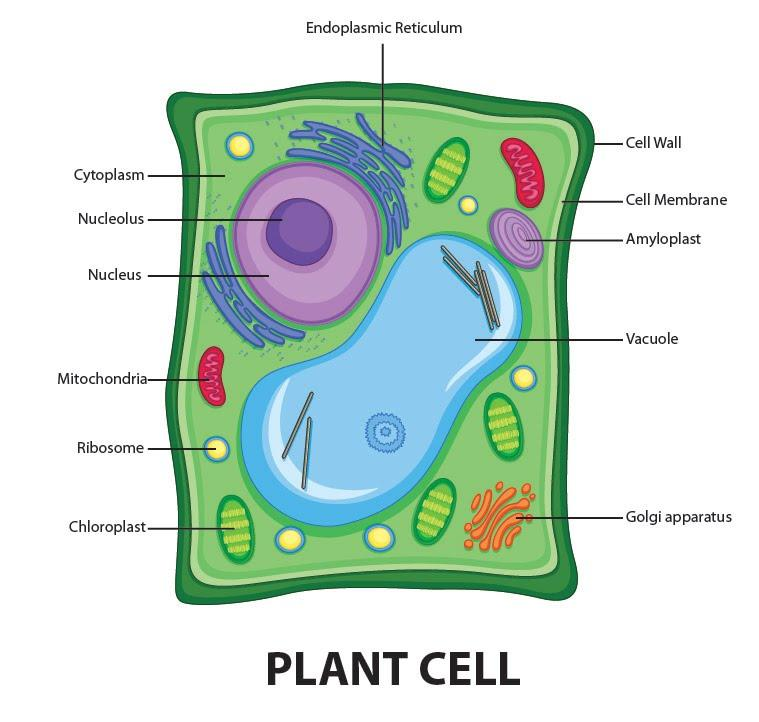
Draw a welllabelled diagram of a plant cell.
3. DNA, the heredity information of cells, which can be found in a nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the a nucleoid region of prokaryotic cell. 4. ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures composed of ribosomes and proteins. These structures can be found on the image of the plant cell (Figure 3.1.2.1 3.1.2. 1 ). Structure of a plant cell. Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae.Their distinctive features include primary cell walls containing cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin, the presence of plastids with the capability to perform photosynthesis and store starch, a large vacuole that regulates turgor pressure, the absence of flagella or. Label the parts of a plant cell. List the types of tissues in a plant and describe where they are located and the specialized cells that make up each of these tissues. Summarize the key functions of those tissues. Plant cell Watch this video about plant cell parts (7:47) les 7 cell parts Watch on Plant Cell Structure and Parts Explained With a Labeled Diagram - Biology Wise Plant Cell Structure and Parts Explained With a Labeled Diagram We know plants from time immemorial and they are a part of our day-to-day life, either directly or indirectly, but do we actually know what does a plant cell structure look like?

Diagrammatic representation of a generalized plant cell depicting the
Plant cells are the basic unit and building blocks of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are cells that have a distinct nucleus and other cellular organelles enclosed within a membrane and thus are eukaryotic in origin. A model of a typical plant cell is found to be rectangular in shape, ranging in size from 10 to 100 µm. A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles - Biology Wise A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles We are aware that all life stems from a single cell, and that the cell is the most basic unit of all living organisms.
Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common. A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where many of the chemical. The parenchyma cells are the most common cell type and are found in the vascular bundles, leaves, and epidermis of the plant. Some common examples of parenchyma cells are guard cells, chlorenchyma cells (involved in photosynthesis). iii. Collenchyma Cells: Collenchyma tissues are made of collenchyma cells. They also do not have a secondary cell.

Plant Cell Diagram Labeled Class 9 Labeled Functions and Diagram
This will teach you how to draw plant cell diagram easily. This is a step-by-step dr. #plantcell #howtodraw #adimushowThis is an easy drawing of a plant cell. Plant cells have chloroplasts and a cell wall, but animal cells do not. The plant cell wall is outside the cell membrane, and it provides structure for the cell. Cell diagrams showing a typical animal cell and plant cell. Image created with Biorender.com. Questions Tips & Thanks Sort by: Top Voted lillianjohnson a year ago




