What causes plants to have nutrient deficiencies? Nutrient deficiency may occur due to one or more of the following reasons: The soil or growth medium is deficient in the required nutrient. The soil is not sufficiently moist to allow the roots to take up and transport the nutrients. Many micronutrients are used by plants to process other nutrients or work together with other nutrients, so a deficiency of one may look like another (for instance, molybdenum is required by legumes to complete the nitrogen fixation process).

Plant Nutrient Deficiency Leaf Illustrations and Charts Reference Guide
When a plant lacks a sufficient amount of an essential nutrient required for growth, you will see signs of nutrient deficiency. Plants need a mix of nutrients to grow and remain healthy [ 1 ]. For high-yield crops, you especially need to keep a close eye to ensure they are getting what they need to thrive properly. Nutrient deficiency occurs when a plant lacks sufficient quantity of an essential nutrient required for growth. Without sufficient essential nutrients, plants will not grow well and show various symptoms to express the deficiency. Learn more about nutrient deficiency as you stay at home during this period. Essential Nutrients Shanyn Hosier. Plants need the right combination of nutrients to live, grow and reproduce. When plants suffer from malnutrition, they show symptoms of being unhealthy. This publication provides information on the pattern of symptoms and the treatments for plant nutrient deficiencies. View Publication - AZ1106. Boron deficiency in plants Copper deficiency in plants Manganese deficiency in plants Molybdenum deficiency in plants Measuring pH, EC and temperature regularly can help prevent nutrient deficiencies - here's how What are nutrient deficiencies? All plants need nutrients so that they can grow and achieve optimal plant health.

best_cannabis_deficiency_visual_chart 420 Magazine
Plant Nutrition Deficiency Database (NutDef) Diagnose your plant with this Decision Tree; List of Photos Indexed by Deficient Element & Scientific Name of Plant Common Nutrient Deficiency In Plants Boron (B) Calcium (Ca) Copper (Cu) Iron (Fe) Magnesium (Mg) Manganese (Mn) Molybdenum (Mo) Nitrogen (N) Phosphorus (P) Potassium (K) Silicon (Si) Sulfur (S) Zinc (Zn) Final Thoughts On Nutrient Deficiency In Plants As a novice grower, its really important for you to learn all about nutrient deficiency in plants. The purpose of this publication is to inform Extension agents, consultants, and farmers about plant essential nutrients, benefits, and deficiency symptoms. This publication provides a whole plant picture with deficiency symptoms for each nutrient and the location of those symptoms on the plant. Written by Lakesh K. Sharma, J. Mabry McCray, and Kelly Morgan, and published by the UF/IFAS. Crops need phosphorus to build proteins, buds, seeds, and blooms. A typical signal of phosphorus nutrient deficiency in plants is bronzish, purplish, or reddish coloring in the lower parts of mature foliage. Sometimes, severe starvation results in brownish dotting and necrosis. P deficiency in grain crops (e.g., wheat) results in poor tillering.

Types of plant deficiencies r/coolguides
Nutrient deficiencies can be identified in field through visual observations. However, additional analysis, either plant or soil testing is often necessary to confirm nutrient stress. The following is a quick-reference flow chart that can be used in field to identify potential nutrient deficiencies. Each nutrient has unique deficiency symptoms. Cu is essential in several plant enzyme systems in-volved in photosynthesis. Cu is part of the chloroplast protein plastocyanin, which forms part of the electron transport chain. Cu may have a role in the synthesis and/or stability of chlorophyll and other plant pigments. Deficiency symptoms (p.
Plants lacking nitrogen will show yellowing on older, lower leaves; too much nitrogen can cause excessive leafy growth and delayed fruiting. Plants lacking phosphorus may show stunted growth or a reddish-purple tint in leaf tissue. A potassium deficiency can cause browning of leaf tissue along the leaf edges, starting with lower, older leaves. The diagnosis of nutrient deficincies can be a key to optimizing plant growth. However, this technique is very subjective and requires careful observation. Plants respond to nutrient deficient conditions in several different ways. Growers must become familiar with these on a crop-by-crop basis. Photographs and record keeping can be very useful.
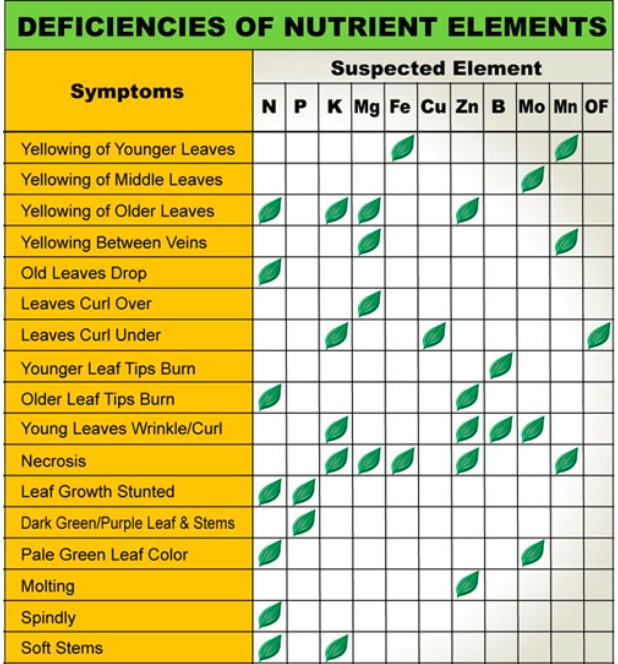
Leaf Illustrations and Charts to Help Diagnose Plant Nutrient Deficiencies
A plant deficiencies chart is a visual resource that displays various nutrient deficiency symptoms in plants. It helps gardeners and farmers identify which essential nutrients are lacking in their plants based on the specific symptoms exhibited, aiding in targeted treatment. Micronutrient Deficiency Chart. Below is a chart of micronutrient deficiencies and their symptoms: Symptoms. Nutrient. Notes. Poor stem and root growth. Terminal (end) buds may die. Witches' brooms sometimes. Plants need a variety of nutrients to stay healthy, and sometimes a plant can suffer from a nutrient deficiency or overload, causing.



