This membrane has about the consistency of.salad oil 1 . The first time I read that factoid, I didn't find it very reassuring! Salad oil seems like an awfully fragile boundary to place between a cell and the rest of the world. Luckily, the plasma membrane turns out to be very well-suited to its job, salad oil texture and all. The plasma membrane of a cell is a network of lipids and proteins that forms the boundary between a cell's contents and the outside of the cell. It is also simply called the cell membrane. The main function of the plasma membrane is to protect the cell from its surrounding environment.
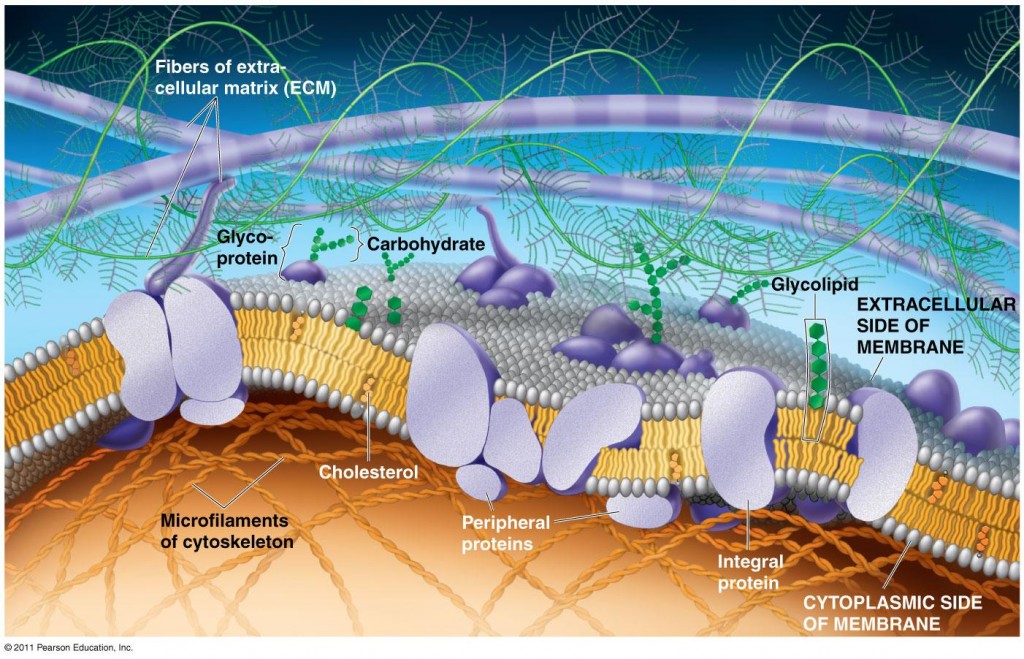
The Plasma Membrane Structure Anatomy & Physiology
Like all other cellular membranes, the plasma membrane consists of both lipids and proteins. The fundamental structure of the membrane is the phospholipid bilayer, which forms a stable barrier between two aqueous compartments. In the case of the plasma membrane, these compartments are the inside and the outside of the cell. IB Biology 2.4.1: Drawing a plasma membrane jasondenys 1.7K subscribers 392 82K views 11 years ago For students doing IB Biology. Follow along and draw the plasma membrane. Music:. Key Points. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids ( phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrates. The plasma membrane protects intracellular components from the extracellular environment. The plasma membrane mediates cellular processes by regulating the materials that enter and exit the cell. The cell membrane is primarily made up of three things: 1. Phospholipids 2. Cholesterol 3. Proteins 1) Phospholipids There are two important parts of a phospholipid: the head and the two tails. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water ( hydrophilic ).
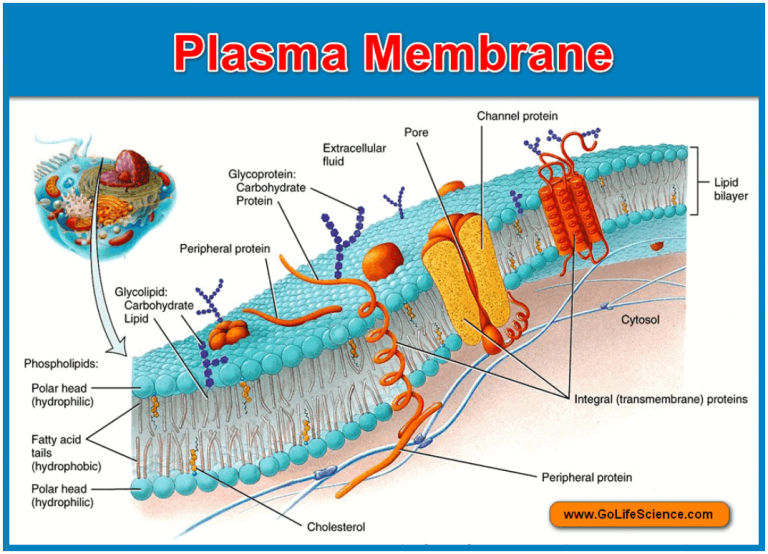
Plasma membrane Basic structure, composition and Function
The plasma membrane is the border between the interior and exterior of a cell. As such, it controls passage of various molecules—including sugars, amino acids, ions, and water—into and out of the cell. How easily these molecules can cross the membrane depends on their size and polarity. Here we'll describe general features of membranes, using the plasma membrane as our example. A. The Phospholipid Bilayer. Gorter and Grendel predicted the bilayer membrane structure as early as 1925. They knew that red blood cells (erythrocytes) have no nucleus or other organelles, and thus have only a plasma membrane. Figure 3.4.1 3.4. 1: Animal cell model. The plasma membrane is a structure that forms a barrier between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment outside the cell. Without the plasma membrane, there would be no cell. The membrane also protects and supports the cell and controls everything that enters and leaves it. IB Biology video on topic 2.4.1 for SL and HL, explaining how to draw the plasma membrane and labelling its components.
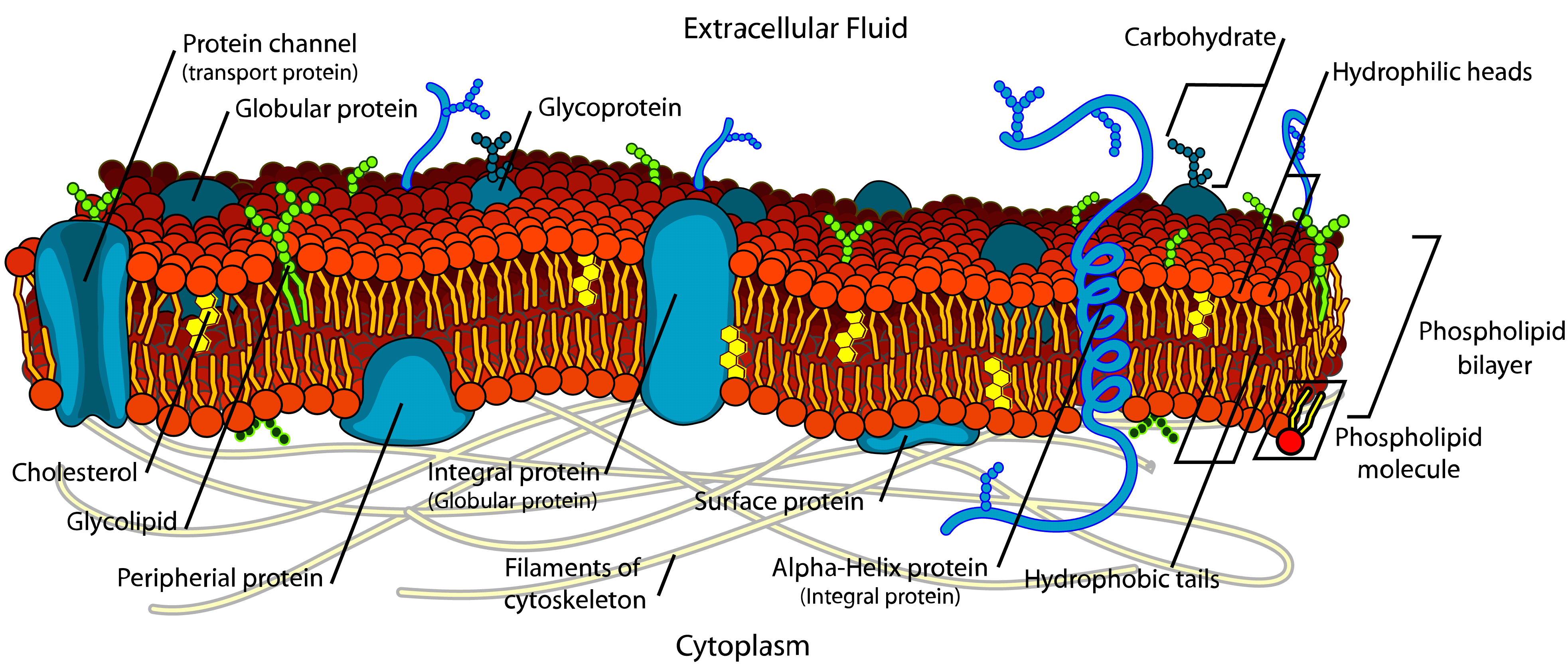
Function of the Plasma Membrane Biology Review (Video)
Just as the outer layer of your skin separates your body from its environment, the cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) separates the inner contents of a cell from its exterior environment. This cell membrane provides a protective barrier around the cell and regulates which materials can pass in or out. On the Web: cell membrane, thin membrane that surrounds every living cell, delimiting the cell from the environment around it. Enclosed by this cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane) are the cell's constituents, often large, water-soluble, highly charged molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and substances.
Structure of the Plasma Membrane (Fluid-Mosaic) Components of the Plasma Membrane Phospholipids - Form a bilayer with phosphate heads facing outwards and fatty acid tails facing inwards Cholesterol - Found in animal cell membranes and functions to improve stability and reduce fluidity The plasma membrane (also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane) is a biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids, proteins and carbohydrate. The plasma membrane is impermeable to ions and most water-soluble molecules. They cross the membrane only through.
/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
A Phospholipid Bilayer. The plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol. The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called aphospholipid bilayer.As shown in Figure below, each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails.The head "loves" water (hydrophilic) and the tails "hate" water (hydrophobic). What does the plasma membrane do? View a plasma membrane definition, plasma membrane function, and plasma membrane structure. Updated: 11/21/2023 Table of Contents Plasma Membrane:.



/plasma_membrane-58a617c53df78c345b5efb37.jpg)
