Drugs Emotions Takeaway The size of your pupils varies throughout the day, but most people's pupils fall within a particular size range. Average pupil size We'll look at when and why. Associated Conditions Pupil Size and LASIK Normal pupil size ranges between 1/16 to 5/16 of an inch (2.0 to 8.0 millimeters), depending on the lighting. The size of your pupil can tell your healthcare provider quite a bit about your health. It's an important key to unlocking possible medical conditions you might not otherwise know about.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/illo-what-can-my-pupil-eye-size-tell-me-about-my-health-342186-59b1afd322fa3a0011f43d91.png)
Pupil Size and Your Health
The normal pupil size in adults varies from 2 to 4 mm in diameter in bright light to 4 to 8 mm in the dark. The pupils are generally equal in size. They constrict to direct illumination (direct response) and to illumination of the opposite eye (consensual response). The pupil dilates in the dark. mechanical pathological Physiological anisocoria: This is when the pupils are naturally different sizes. It is the most common type of anisocoria, and the difference between the pupil sizes. Refers to the asymmetric sizes of pupils Physiologic anisocoria can is very common and a normal variant in up to 20% of the population. The variation should be no more than 1mm and both eyes should react to light normally. mydriasis ). Pupillary abnormalities can be caused by a variety of conditions. Overview Isocoria pupils pupil [1] 2-4 mm 4-8 mm Fixed pupil pupillary convergence Afferent neural pathway (afferent limb) eye central nervous system Isolated unilateral afferent pupillary defect (e.g. optic neuritis) → pupils are isocoric eye pupils eye pupillary
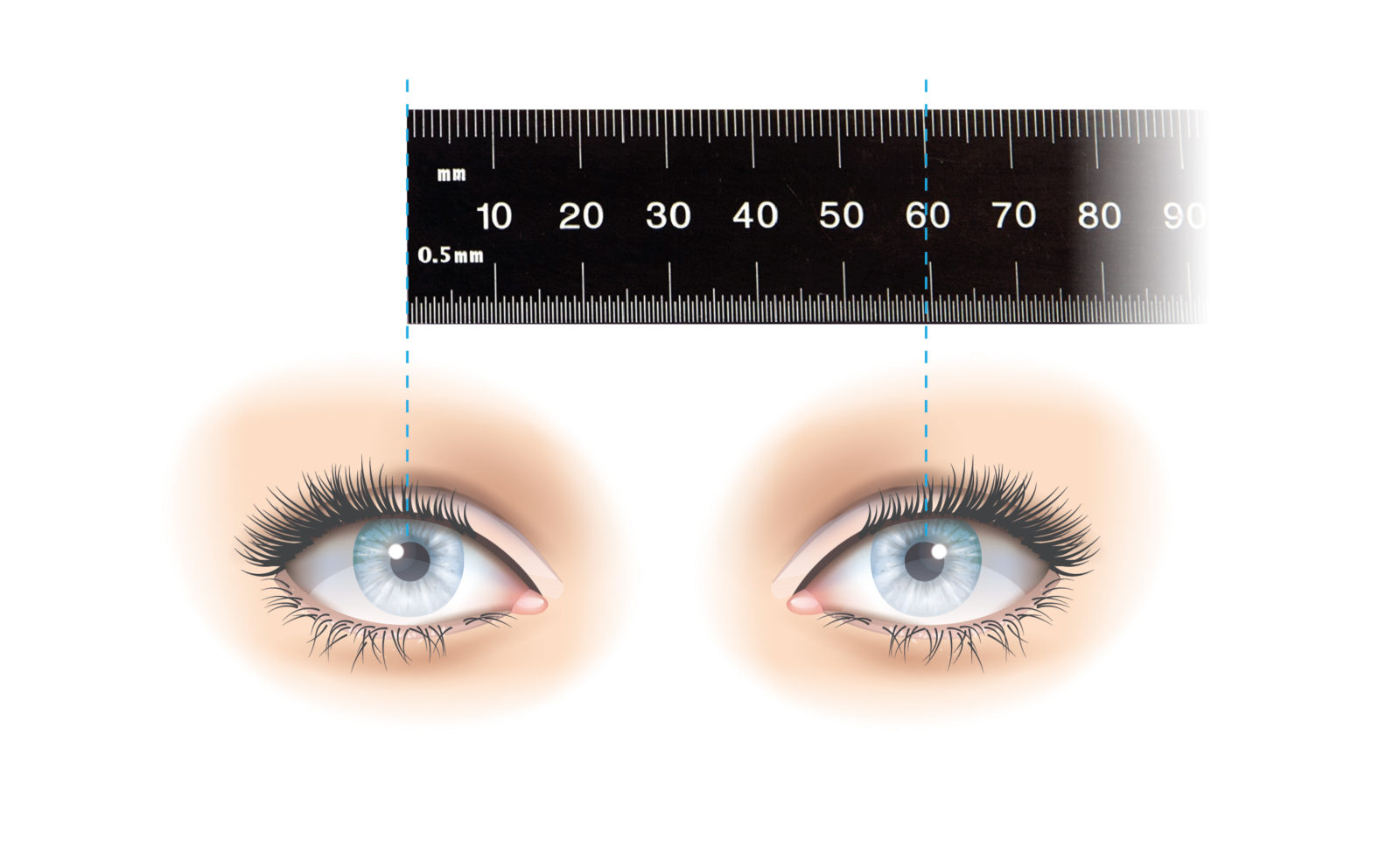
How to measure your Pupillary Distance (PD) Adlens
Normal pupil size generally ranges from 2.0 to 4.0 millimeters (mm) in bright light, and 4.0 to 8.0 mm in the dark. To some degree, pupil size tends to get smaller with age. In one study of 500 Americans ages 18 to 34 years, average pupil sizes in three different lighting conditions were found to be: 3.35 mm in direct light Function What does the pupil do? Your pupil lets light into your eye as the muscles of your iris change its shape. The lens in your eye focuses light that passes through your pupil. Light then goes to the back of your eye and hits your retina. Your retina turns light into electrical signals. 4) Test for relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD)/Marcus Gunn Pupil. Method: Use a bright handheld light in a dim room. Shine the light in one of the patient's eyes and observe for a reaction. After ~3 seconds, rapidly swing the light to the opposite pupil and observe the reaction. After ~3 seconds, swing back to the first eye and observe. Optimal pupil size and modulation depend on a delicate balance among the image quality of objects at varying degrees of defocus, LOAs, HOAs, ocular forward light scatter, and retinal contrast sensitivity—the last profoundly affected by photon noise in dim light. Under varying lighting conditions and retinal illumination, the optimal pupil.
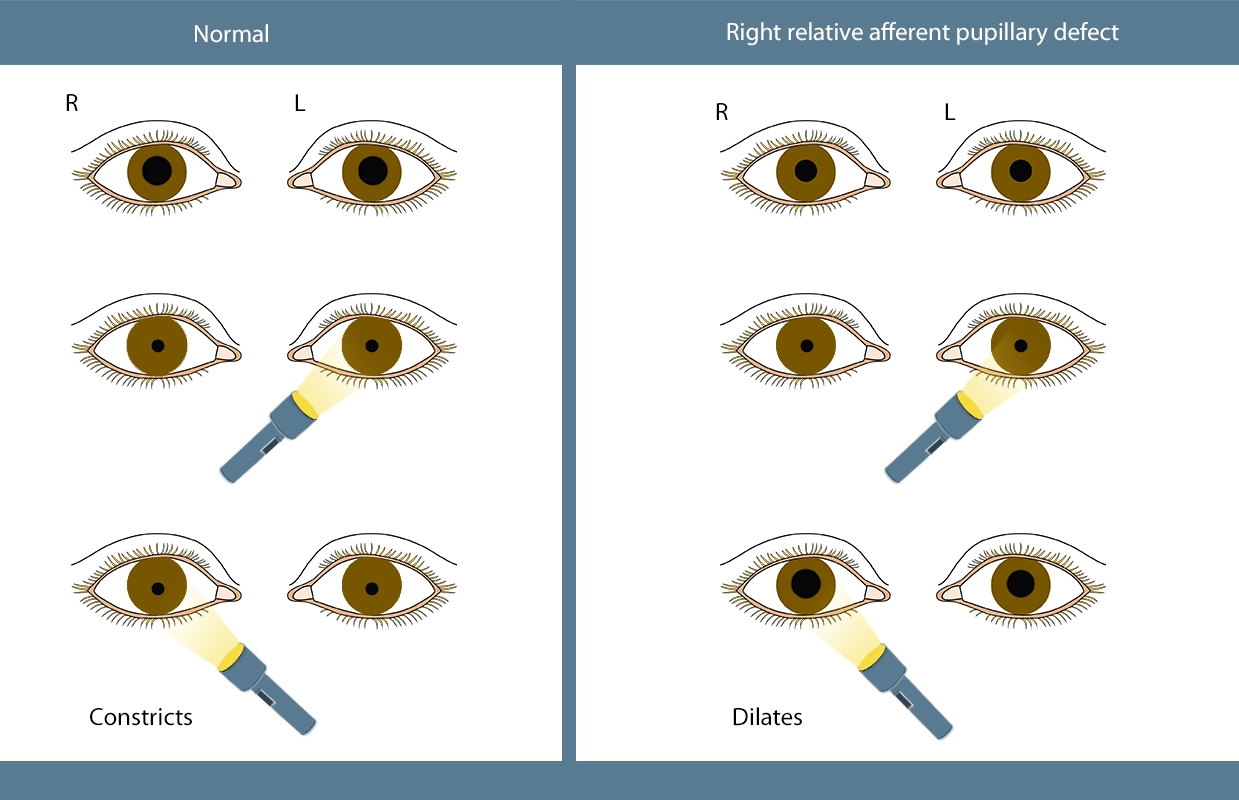
The Definitive Guide to Evaluating Pupillary Reaction How to Measure
An average pupil size chart may include measurements ranging from 2 to 8 millimeters in diameter. It's also important to note that certain medical conditions or medications may affect pupil size, leading to abnormal variations. These variations may require medical attention and evaluation from a healthcare professional. Dilated pupils are one sign that someone has used illegal drugs, such as: Cocaine. Amphetamines. LSD. Ecstasy. These drugs affect the muscle that widens the pupil, slowing how it reacts to light.
The pupil is the hole in the centre of the iris that allows light to enter the eye and reach the retina. Inspect the patient's pupils for abnormalities. Pupil size . Normal pupil size varies between individuals and depends on lighting conditions (i.e. smaller in bright light, larger in the dark). The pupil sizes chart is a visual representation of the range of pupil sizes and their corresponding measurements. It helps healthcare professionals and researchers assess and interpret the size of a person's pupils in different lighting conditions. The chart typically includes measurements in millimeters and may also indicate the corresponding.
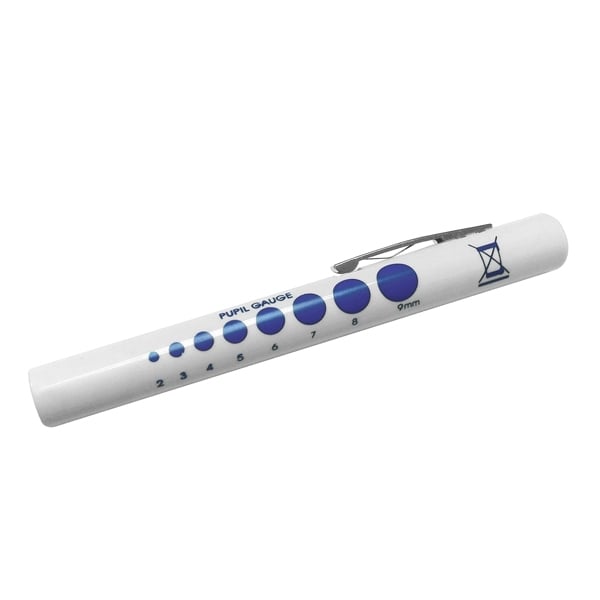
Pupil Size Chart A Guide for Nursing Students
Pupil Size Compare size with pupil scale Record size of each pupil Record reaction to light Record as "c" if unable to open eye due to trauma or swelling. Document a lack of consensual reaction (opposite pupil fails to constrict when light is shone in eye) in health care record. Pupil Reaction Hold eyelid open Move small bright light side The pupil is black circle in the center of the iris. With the ability to adjust to brightness, it controls the amount of light that passes through to the retina. The pupil will dilate to let more light in, or constrict to let less in. When light is too bright, your pupils will become smaller to protect the retina from damaging itself.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/illo-what-can-my-pupil-eye-size-tell-me-about-my-health-342186-59b1afd322fa3a0011f43d91.png)



