Here are some common examples: A soda is a saturated solution of carbon dioxide in water. This is why, when the pressure is released, carbon dioxide gas forms bubbles. Adding chocolate powder to milk so that it stops dissolving forms a saturated solution. Everyday Examples of Saturated Solutions There are saturated solution examples all around you! Take a walk through your kitchen, bathroom or backyard to find saturated solutions in your everyday life. Saturated Solution Examples in the Home Have you ever added too much chocolate powder to your chocolate milk?

Saturated Solution Definition in Chemistry
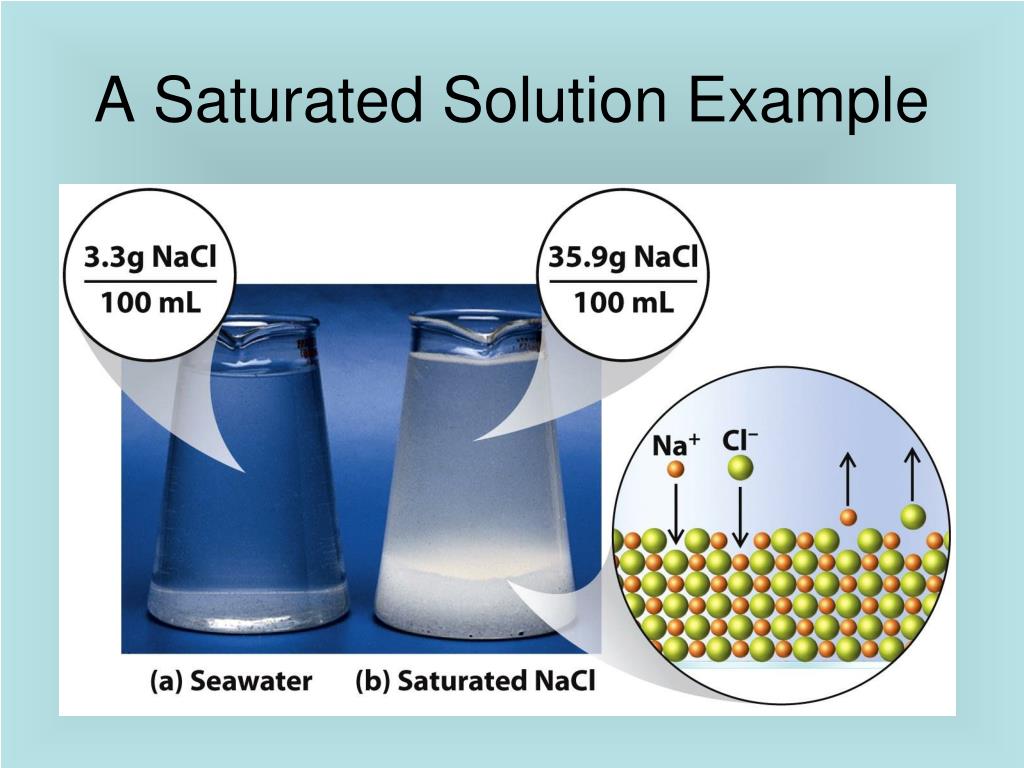
Everyday Examples of Saturated Solution Beverages are one of the most widely used and loved saturated solutions. In these drinks, water is a solvent and carbon is bombarded as a solute until the point of saturation is reached. In the kitchen, many cooking recipes involves dissolving of salt, sugar and other household ingredients into the water. Using the value just stated, a saturated aqueous solution of NaCl, for example, contains 35.9 g of NaCl per 100 mL of water at 20°C. We can prepare a homogeneous saturated solution by adding excess solute (in this case, greater than 35.9 g of NaCl) to the solvent (water), stirring until the maximum possible amount of solute has dissolved, and. Remove Solvent If you have an unsaturated solution, make it saturated by removing solvent. The easiest method is evaporation. Increase air circulation or temporarily raise the temperature of the solution and drive off solvent. Trickier methods involve removing excess solvent via chemical reactions. A saturated solution is one containing as much solute —the solid being dissolved in the liquid—as possible without forming a precipitate, or leftover solid. This is the maximum concentration of solute. How to Make a Saturated Solution Here are three ways to make a saturated solution : Add solute to a liquid until no more will dissolve.

Examples of Saturated Solution YourDictionary
An unsaturated solution is a solution that contains less than the maximum amount of solute that is capable of being dissolved. The figure below illustrates the above process and shows the distinction between unsaturated and saturated. Figure 16.3.1 16.3. 1: When 30.0g 30.0 g of NaCl NaCl is added to 100mL 100 mL, it all dissolves, forming an. For example, if you prepare a saturated solution of sugar in hot water and then cool the solution, it becomes supersaturated when the temperature changes. Disturbing the solution or adding a nucleation point (like a seed crystal or even a scratch on the container) induces crystal growth. Examples of Saturated Solutions 1. Figure 7.10.1 7.10. 1 : An unsaturated solution and an exactly-saturated solution, respectively. These solutions can, however, be differentiated through the addition of more solute. Because an unsaturated solution does not contain the maximum of amount of solute that can dissolve in the quantity of solvent that is present, additional solute. Example 1: Saturated Solution Example 1: Above is illustrated an example of a saturated solution. In Figure 1.1-1.3, there is a constant amount of water in all the beakers. Figure 1.1 shows the start of the saturation process, in which the solid solute begins to dissolve ( represented by red arrows ).
PPT Chapter 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4638445
Examples of Saturated Solutions In everyday life, you find saturated alternatives, not just in a chemistry classroom. Also, water does not have to be the solvent. Here are some popular instances: Saturated carbon dioxide solution in water is a soda. That's why bubbles form when we remove pressure from carbon dioxide gas. These terms are also qualitative terms because each solute has its own solubility. A solution of 0.00019 g of AgCl per 100 g of H 2 O may be saturated, but with so little solute dissolved, it is also rather dilute. A solution of 36.1 g of NaCl in 100 g of H 2 O is also saturated, but rather concentrated. In some circumstances, it is possible to.
What is a supersaturated solution? A supersaturated solution contains more solute at a given temperature than is needed to form a saturated solution. Increased temperature usually increases the solubility of solids in liquids. For example, the solubility of glucose at 25 °C is 91 g/100 mL of water. The solubility at 50 °C is 244 g/100 mL of. Examples of Saturated Solution: 1. Drinking Beverages. One of the most widely seen and possibly widely enjoyed saturated solutions is a carbonated beverage, like soda. The solution, in this case the water that forms the base of the soda, is bombarded with carbon until no more can be introduced, meaning it gives off the excess carbon as gas.

PPT Chp 13. SOLUTIONS PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1098965
In the first example, the solution is saturated when the rate at which the pure substance dissolves in the solvent to enter the solution is exactly equal to the rate at which the dissolved substance leaves the solution (e.g., by crystallizing). In the second example, the rate at which the pure condensed (liquid or solid) material vaporizes is. A typical saturated solution example is air saturated with water vapor. When air, a solution of mostly nitrogen and oxygen, is saturated with water vapor (i.e., the concentration of water.




