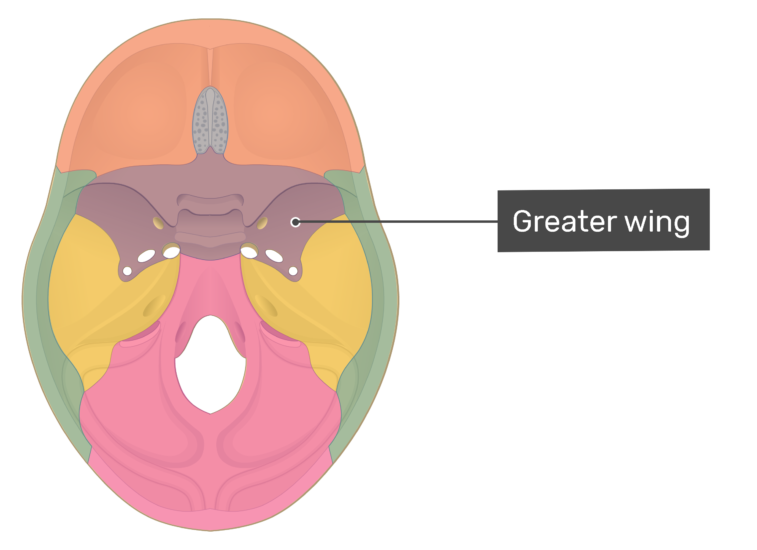
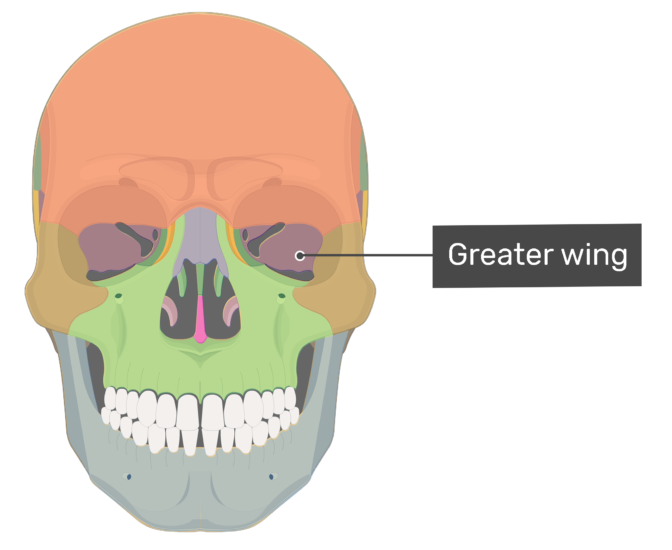
The greater wing of the sphenoid bone, or alisphenoid, is a bony process of the sphenoid bone, positioned in the skull behind each eye. There is one on each side, extending from the side of the body of the sphenoid and curving upward, laterally, and backward. Structure Anatomical Structure The sphenoid bone is said to be ' butterfly-shaped '. It consists of a body, paired greater wings and lesser wings, and two pterygoid processes. Body The body lies at the centre of the sphenoid bone and is almost completely cubiodal in shape.
Sphenoid Bone
The greater wings of the sphenoid bone (GWS) are the components of the sphenoid bone that project laterally from the central body and form the anterior and medial portions of the floor of the middle cranial fossa. Many skull base foramina in the GWS transit important neurovascular structures. The greater wing or ali-sphenoid of the sphenoid bone is a process which projects from either side of the lower part of the sphenoid body, at a common junction with the pterygoid process 1 . Synonyms: none The sphenoid bone is one of the most complex bones of the human body. Due to its shape, it is also referred to as the 'wasp bone'. It makes up most of the middle part of the base of the skull and contributes to the floor of the middle cranial fossa of the skull. greater wing lesser wing pterygoid process and plates Articulations The sphenoid bone articulates with twelve bones: unpaired bones include: frontal, ethmoid, vomer, and occipital paired bones include: zygomatic, parietal, temporal, and palatine. Fissures, foramina, grooves and canals The sphenoid bone includes: optic canal superior orbital fissure

Sphenoid bone anatomy, function, parts & sphenoid bone fracture
Greater Wings Emerging behind the lesser wings and also running to the sides are the two greater wings, which are also triangular and run lateral to the body. Their sides make up the infratemporal surfaces, which are convex in shape, and move backward and to the sides. two greater wings on the lateral side of the body and two lesser wings from the anterior side. Pterygoid processes of the sphenoides, directed downwards from the junction of the body and the greater wings. [4] Two sphenoidal conchae are situated at the anterior and inferior part of the body. Intrinsic ligaments of the sphenoid The sphenoid is just one of the twenty-two bones that form the skull and essentially helps to connect the neurocranium to the facial skeleton. It is a single bone in the midline of the cranial cavity situated posterior to the frontal bone but anterior to the occipital. Its name derives from the Greek 'sphenoeides,' which means wedge-shaped. Normal Anatomy The sphenoid bone forms the central skull base and viewed anteriorly resembles a bird with its wings unfurled. It is a compound bone with a median body and paired lateral greater and lesser wings ( Fig. 3.1 ).
Sphenoid bone anatomy, parts and labeled diagram GetBodySmart
The greater wings of the sphenoid bone (GWS) comprise the com-ponents of the sphenoid bone that make up most of the posterior orbital wall and form the anterior and medial parts of the floor of the middle cranial fossa. Many important skull base foramina, which transmit vital neurovascular structures, are present in these paired wings on either. The greater wing of the sphenoid bone also forms the anterior margin of the foramen lacerum, which is filled with cartilage during life. Anterior to the greater wing of the sphenoid is the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone. This shelf of bone forms the posterior part of the anterior cranial fossa and extends laterally, and articulates.
Greater wing Ala major. Latin synonym: Ala temporalis; Ala magna Related terms: Greater wing (Sphenoid bone) Definition The great wings, or ali-sphenoids, are two strong processes of bone, which arise from the sides of the body, and are curved upward, lateralward, and. The greater wing of the sphenoid bone can be seen in the below image as the oval shape in the center of the red rectangle. Site of the pterion. The sphenoid bone body sits behind the nasal cavity with various protrusions that play important roles in the construction of other bony structures.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/greater-wing-of-sphenoid-bone-2/pWSQtUKxgEdbdGFCnSYDCQ_Ala_major_ossis_sphenoidalis_02.png)
😊 Sphenoid bone location. Sphenoid Sinus Anatomy, Diagram & Location
The greater wing of the sphenoid is a bony projection arising from both sides of the sphenoid body forming a part of the floor of the middle cranial fossa. Jakob Benignus Winslow coined the term foramen spinosum because of the foramen's location in the spinous process of the greater wing of the sphenoid. [1] Go to: Structure and Function Functions It forms the base and lateral sides of the skull in combination with the orbital floor. Anatomy: Parts and Structure of the Sphenoid Bone The sphenoid bone consists of a central body, with two lateral paired wings on either side - the lesser and greater wings - and two pterygoid processes.



:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/greater-wing-of-sphenoid-bone-2/pWSQtUKxgEdbdGFCnSYDCQ_Ala_major_ossis_sphenoidalis_02.png)
