The Mohs scale of mineral hardness ( / moʊz /) is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. By Alan Bernau Jr The Mohs Hardness Scale ranks metals and minerals by harness. This chart shows how steel, silver, aluminum, titanium, tin, brass, and other minerals compare.
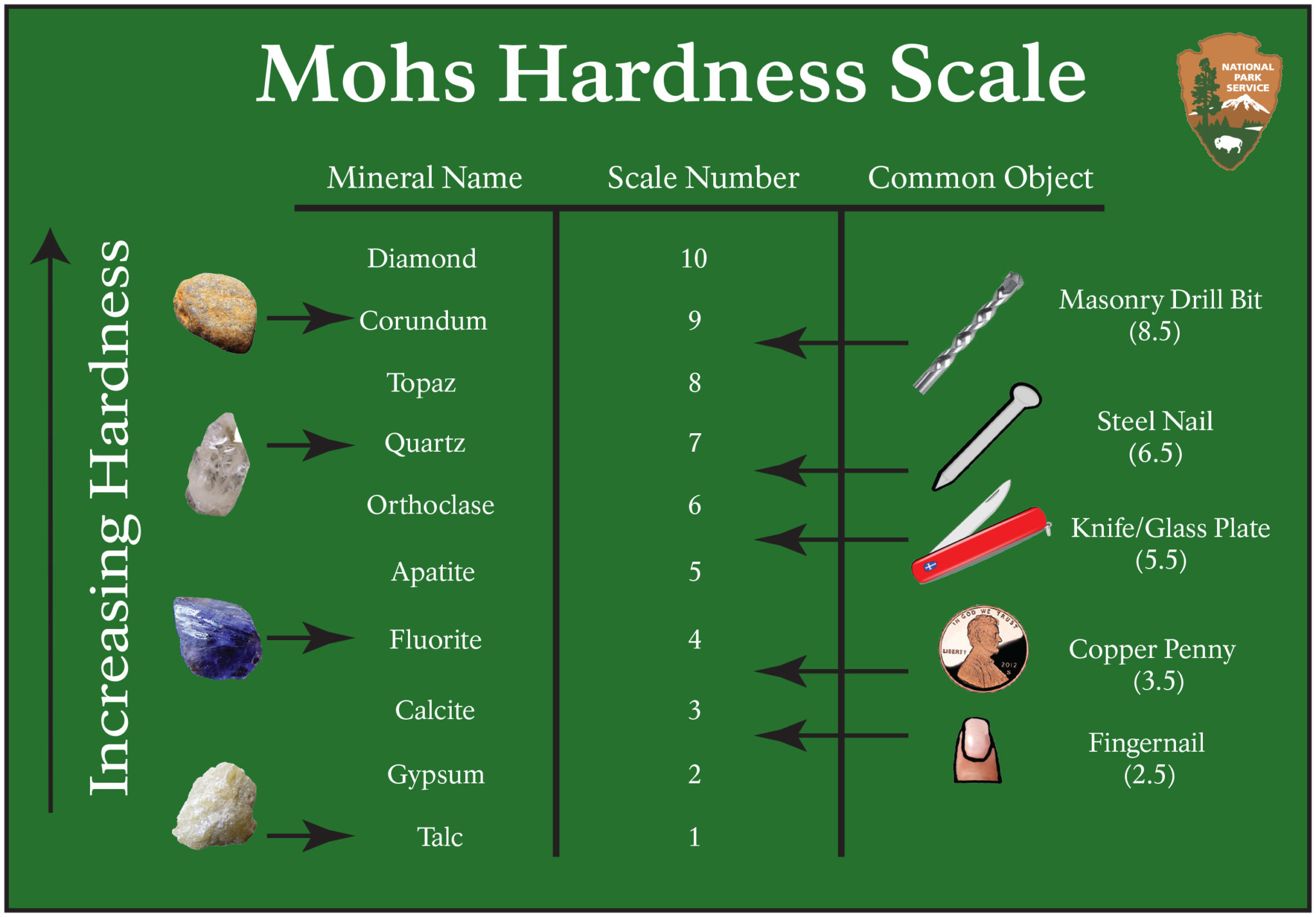
Moh's Hardness Scale International Granite And Stone
Mohs hardness, rough measure of the resistance of a smooth surface to scratching or abrasion, expressed in terms of a scale devised (1812) by the German mineralogist Friedrich Mohs. The Mohs hardness of a mineral is determined by observing whether its surface is scratched by a substance of known or defined hardness. Mohs scale of mineral hardness; Mohs hardness of materials (data page) Vickers hardness test; Brinell scale This page was last edited on 14 September 2023, at 23:16 (UTC). Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 4.0; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you. It consists of a steel ball dropped from a fixed height. This type of hardness is related to elasticity. Within each of these classes of measurement there are individual measurement scales. For practical reasons conversion tables are used to convert between one scale and another. Measuring Hardness ADVERTISEMENT What is Mohs Hardness Scale? The Mohs Hardness Scale is a set of ten reference minerals (numbered 1 through 10) that are used to determine the relative hardness of minerals and other objects. In this test the hardness of a mineral is defined as its "resistance to being scratched".
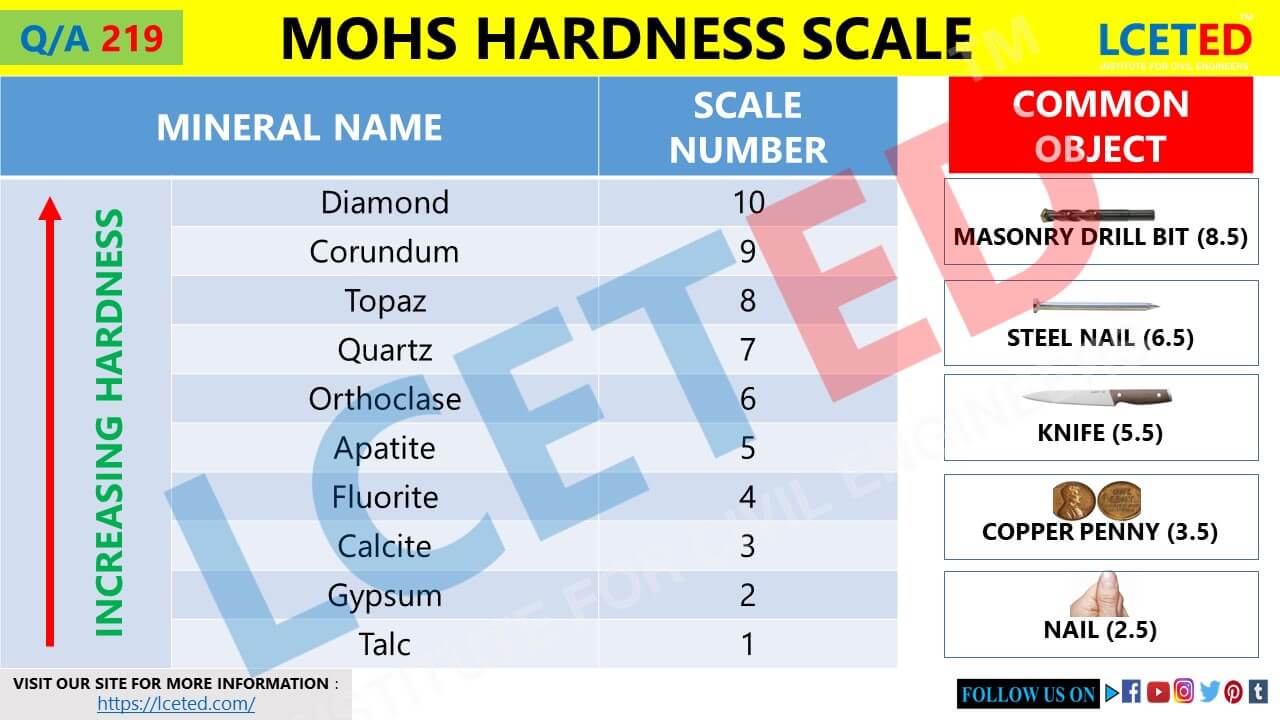
What Is Mohs Scale Of Hardness? And How To Use It lceted LCETED
The Mohs hardness test is one of the earliest attempts at defining and comparing the hardness of mineral materials. The Mohs scale consists of values from 1 to 10, which correlate with the ability of the test material to withstand scratching by progressively harder minerals.. (typically used for steel). The result of the testing process is a. The name's Mohs, not Moh or Moh's. - andselisk ♦ Jan 22, 2022 at 23:11 Add a comment 1 Answer Sorted by: 7 You can find Mohs hardness values for various pure metals, but it sounds like you want something more specialized: Mols hardness values for specific alloys. That's probably harder to find. The Mohs hardness scale is a qualitative test that measures the hardness of a mineral by its ability to visibly scratch softer minerals. The scale isn't perfect, but it's a great tool for quick identification of rocks in the field.. topaz, cubic zirconia, spinel, hardened steel: 8.5: chrysoberyl, silicon nitride, tantalum carbide. The Common Objects for hardness comparisons are listed a column to the left as: Masonry Drill Bit, 8.5; Steel Nail, 6.5; Knife/Glass Plate, 5.5; Copper Penny, 3.5; and Fingernail, 2.5.. The Mohs Hardness Scale is used as a convenient way to help identify minerals. A mineral's hardness is a measure of its relative resistance to scratching.
.jpg)
The Mohs Hardness Scale Geology In
The Mohs hardness scale. Image credit: Philip Brayne for IFLScience Since then, other substances have been added using decimals. This guide, for example, slots in such relevant items as nails,. The Brinell hardness test uses a ball made of hardened steel or a hard alloy with a diameter of D as the indenter. A specified test force F is applied to the surface of the material being tested, and after a designated hold time, the test force is removed, leaving an indentation with a diameter of d.
April 25, 2018. This metal hardness chart organizes different types of metal using the Mohs hardness scale, a metric used by scientists to determine the scratch resistance of different minerals. With diamond at the top of the scale at a score of 10, elements and alloys can fall along the metal hardness scale from 10 (the most scratch-resistant. The Mohs scale is a system used to rank materials on their hardness, which is graded using numbers from 1 to 10. It can be used to compare gemstones, metals and other materials, and evaluate their relative durability. Where a metal stands on the Mohs scale indicates which other metals can scratch it.

Mohs Scale Of Mineral Hardness Hardness Comparison Hardened Steel, PNG
For instance, metals like gold (Mohs hardness 2.5-3) and copper (Mohs hardness 3) are softer, while steel and iron (Mohs hardness 4-4.5) have intermediate hardness, and tungsten carbide (Mohs hardness ≥9) is one of the hardest materials. These metals can be used to scratch rocks to determine their hardness approximately and aid in identifying. The Mohs hardness scale is based on ten minerals of different hardness, divided into ten levels from low to high: 1. Talc; 2. Gypsum; 3. Calcite; 4. Fluorite; 5. Apatite; 6. Orthoclase; 7. Quartz; 8. Topaz; 9. Corundum; 10. Diamond. In use, standard minerals are scratched against minerals of unknown hardness.


.jpg)

