Symptoms & causes Diagnosis & treatment Doctors & departments Care at Mayo Clinic Overview Bipolar disorder, formerly called manic depression, is a mental health condition that causes extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Here's how to recognize the signs and symptoms of manic depression, including mania, hypomania, bipolar depression, and cyclothymia. Copy Link Download PDF By Melinda Smith, M.A., Jeanne Segal, Ph.D. and What is bipolar disorder? Signs and symptoms of bipolar disorder Types of bipolar disorder Getting an accurate diagnosis

Bipolar disorder symptoms icon set in flat style. Mood disorder symbols
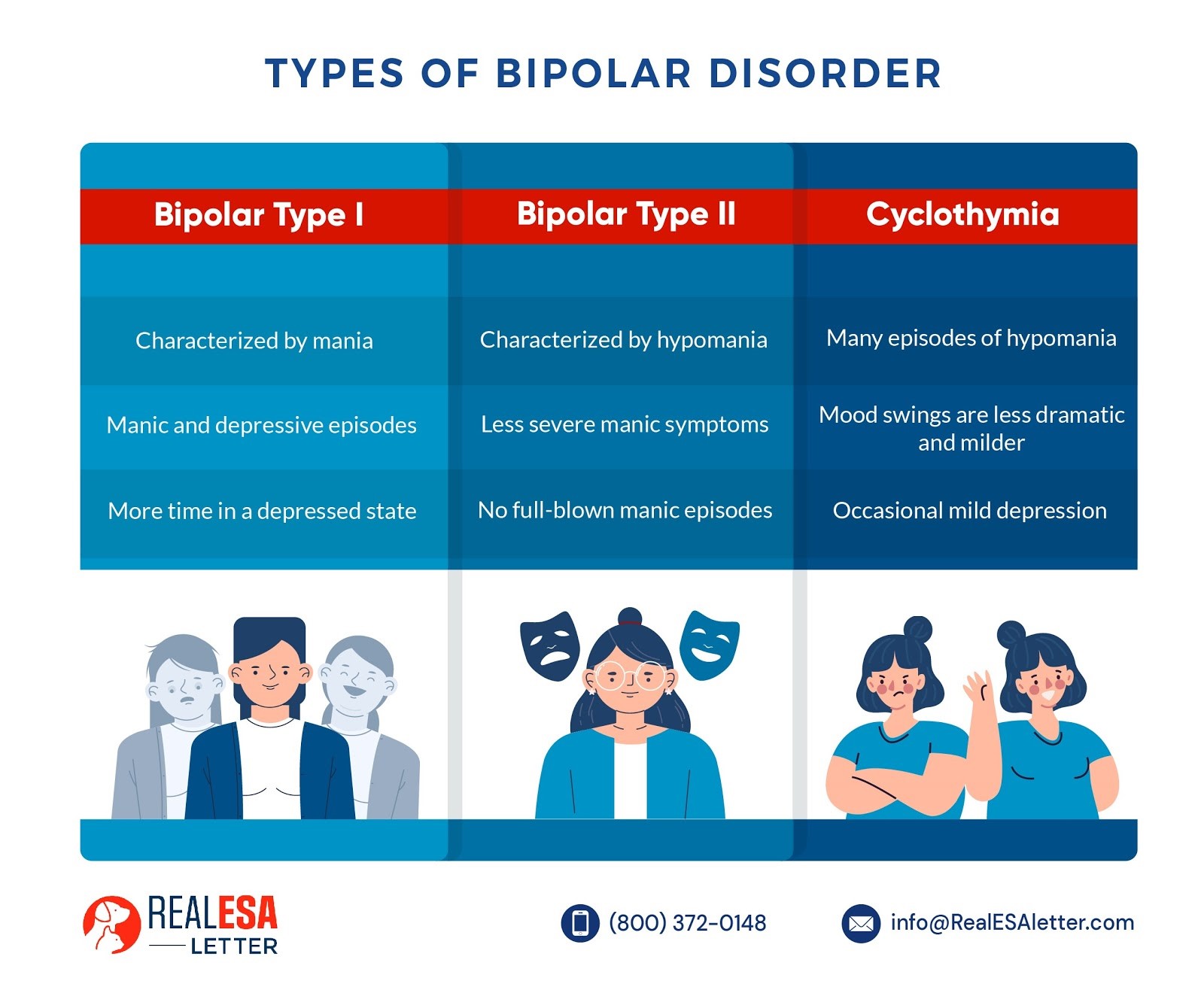
Types and symptoms There are four common types of bipolar disorder. Bipolar I and II are the most common types. Bipolar I To have bipolar I, a person must experience manic episodes. In. Overview Bipolar disorder (formerly called manic-depressive illness or manic depression) is a mental illness that causes unusual shifts in a person's mood, energy, activity levels, and concentration. These shifts can make it difficult to carry out day-to-day tasks. There are three types of bipolar disorder. a decreased need for sleep. racing thoughts. talking quickly and changing the subject often. feelings of elation or irritability. feeling jumpy, wired, or full of energy. excessive desire for. The bipolar spectrum is a term used to refer to conditions that include not only bipolar disorder as traditionally defined (that is, clear episodes of mania or hypomania as well as depressive.

Bipolar Disorder From A to Z Sina Health Centre
Bipolar disorder is a treatable serious mental illness. It can affect a person's thoughts, feelings, mood and overall functioning. Formerly known as manic-depression, bipolar disorder is marked by dramatic shifts in mood, energy, and activity levels. People with this disorder typically swing between intense episodes of mania and depression. Health Library / Diseases & Conditions / Bipolar Disorder Bipolar disorder is a chronic mood disorder that causes intense shifts in mood, energy levels and behavior. Manic and hypomanic episodes are the main sign of the condition, and most people with bipolar disorder also have depressive episodes. Bipolar disorder is a mental illness that can be chronic (persistent or constantly reoccurring) or episodic (occurring occasionally and at irregular intervals). People sometimes refer to bipolar disorder with the older terms "manic-depressive disorder" or "manic depression.". Everyone experiences normal ups and downs, but with bipolar. Bipolar disorder, also known as manic depression, is a mental illness that brings severe high and low moods and changes in sleep, energy, thinking, and behavior. People who have bipolar disorder.
What is Bipolar Disorder Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Symptoms of a manic or hypomanic episode include: Being easily distracted Decreased need for sleep Delusions or hallucinations Elevated or expansive mood Grandiosity or inappropriate behavior Impulsive risk behaviors (including gambling and lavish spending) Increased sexual desire The bipolar symbol is typically comprised of a circle divided into two halves of contrasting colors. One half is often depicted in vibrant shades representing the manic phase, while the other half represents the depressive phase with darker or cooler tones. The division symbolizes the stark dichotomy between the two poles of bipolar disorder.
The following are the most common symptoms: Depressive symptoms may include: Constant sad, anxious, or empty mood Loss of interest in things that you once enjoyed, including sex Feeling restless or irritable Inability to focus, think, or make decisions Low energy, fatigue, being slowed down Bipolar disorder is a mood disorder that can cause intense mood swings: Sometimes you may feel extremely "up," elated, irritable, or energized. This is called a manic episode. Other times you may feel "down," sad, indifferent, or hopeless. This is called a depressive episode. You may have both manic and depressive symptoms together.

Bipolar Disorder Icon Set in Colored Line Style Stock Illustration
Major depressive disorder -- often referred to as unipolar depression -- is different from bipolar disorder II -- also called bipolar depression -- in that unipolar depression has no. Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that each last from days to weeks. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or.


