. Nitrogen exists in the atmosphere as N 2 gas. In nitrogen fixation, bacteria convert N 2 into ammonia, a form of nitrogen usable by plants. When animals eat the plants, they acquire usable nitrogen compounds. Nitrogen is a common limiting nutrient in nature, and agriculture. Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.

How the Nitrogen Cycle Works Britannica
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. The nitrogen cycle — Science Learning Hub Article The nitrogen cycle Resource Related topics & concepts Add to collection Nitrogen is the most abundant element in our planet's atmosphere. Approximately 78% of the atmosphere is made up of nitrogen gas (N 2). Topics Concepts Citizen science Teacher PLD Glossary Sign in Email Us The nitrogen cycle is the cyclic movement of nitrogen in different chemical forms between living organisms and the environment. The steps of the nitrogen cycle are described below. Nitrogen fixation: During this step, atmospheric nitrogen gas is fixed, or converted into a form that can be used by plants and animals. Definition The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. Nitrogen Cycle Explained
What is the Nitrogen Cycle? Science for Kids
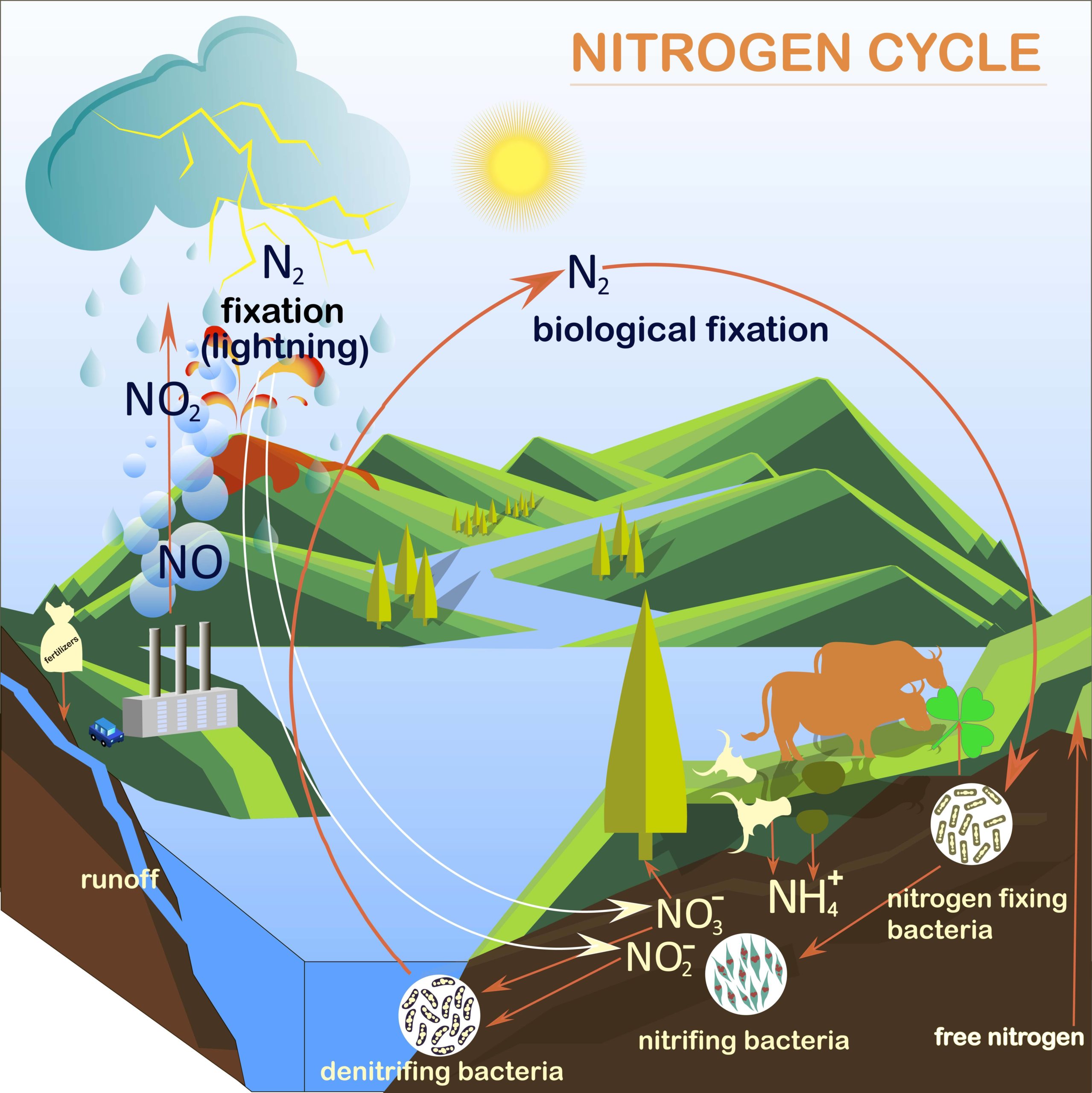
The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical cycle that converts nitrogen into various forms throughout the ecosystem. Nitrogen is an essential element for life that organisms use in the synthesis of amino acids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Yet, while the atmosphere is rich in nitrogen (about 78%), this nitrogen (N 2) is largely inaccessible to. Animals secure their nitrogen (and all other) compounds from plants (or animals that have fed on plants). Figure 17.2.2.1 Nitrogen cycle. Four processes participate in the cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere: (1) nitrogen fixation, (2) decay, (3) nitrification, and (4) denitrification. Microorganisms play major roles in all four of these. Nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on Earth. Although 78 percent of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this gas is unusable by most organisms until it is made available by a series of microbial transformations. The process of converting N 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. N 2 gas is a very stable compound due to the strength of the triple bond between the nitrogen atoms.

Nitrogen Cycle QCE Biology Revision
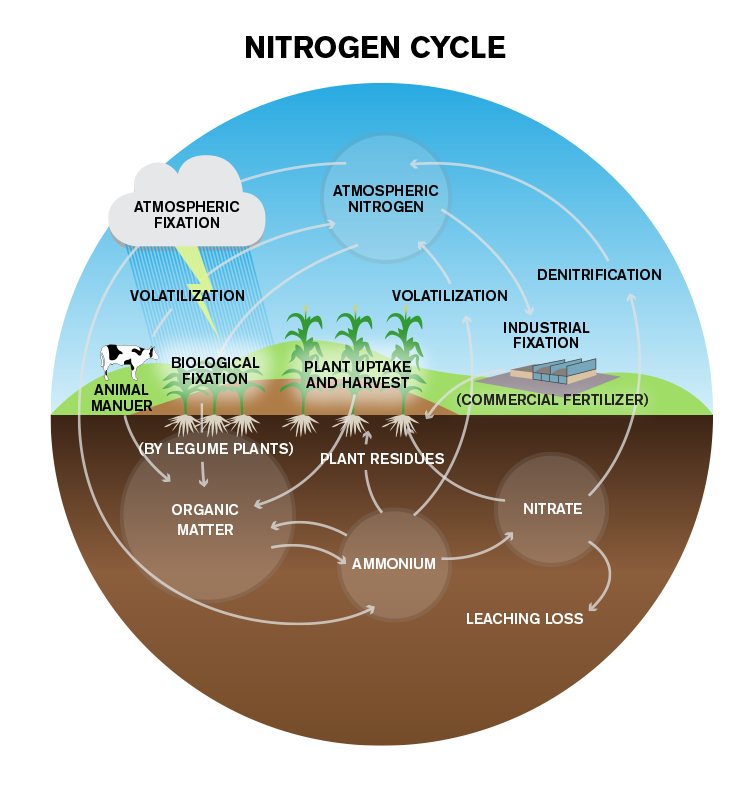
Nitrogen (N) is an essential component of , the building blocks of life. All require nitrogen to live and grow. Although the majority of the air we breathe is N, most of the nitrogen in the is unavailable for use by organisms. Detailed Description This diagram of the nitrogen cycle shows were in the cycle antibiotics could impact the ability of denitrifying bacteria to process nitrates and nitrites in groundwater. The diagram is a modified version of figure 9 from USGS SIR 2004-5144, page 16. This study was funded by the USGS's Toxic Substances Hydrology Program.
cycle to aid in reaching that goal. plant available N. Denitrification, volatilization, immobilization, and leaching result in permanent or temporary N losses from the root zone. Read on for specifics about each of the N cycle processes. Fixation refers to the conversion of atmospheric N to a plant available form. Nitrogen Cycle Diagram The entire process of the Nitrogen Cycle, one of the important biogeochemical cycle takes place in five stages: 1) Nitrogen Fixation by Bacteria - Converting inert atmospheric nitrogen (N 2 )into biologically available forms such as ammonia (NH 3 ), nitrates, or nitrites
Nitrogen Cycle Steps Process Explanation Diagram
Understanding Nitrogen Cycle with a Diagram Similar to other biogeochemical cycles, the nitrogen cycle is essential for regulating the concentration of nitrogen in the atmosphere. Read on to know more about this cycle through the diagram given below, which will help you in understanding the sequence of steps involved in this cycle. Diagram of the nitrogen cycle Processes in the Nitrogen Cycle Fixation - Fixation is the first step in the process of making nitrogen usable by plants. Here bacteria change nitrogen into ammonium. Nitrification - This is the process by which ammonium gets changed into nitrates by bacteria. Nitrates are what the plants can then absorb.




