Nose Breathing vs Mouth Breathing Face Shape Twins who are genetically identical still show more contrast in the shape of their jaws than any other part of their skeleton showing that much of the variation is due to non-genetic environmental factors such as open mouth postures, unusual swallowing habits, and tooth extraction that can distort. Mouth breathing is closely related to the facial skeletal development and malocclusion. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the effect of mouth breathing on facial skeletal development and malocclusion in children. Methods

ASMR Twin Tongue Fluttering & Clicking Mouth Sounds / Breathing for
The mouth-breathing syndrome (MBS) is when a child has mixed breathing i.e., the nose is supplemented by the mouth. 1 Exclusively oral breathing patterns are rare or non-existent. Mouth breathing is when people can't breathe through their nose so they take in air through their mouths. Mouth breathing can cause sleep disorders that affect daily life. It also can change the structure of people's faces. Healthcare providers treat mouth breathing by surgery or medication to enable people to breathe through their nose. Mouth breathing is closely related to the facial skeletal development and malocclusion. The purpose of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to assess the effect of mouth breathing on facial skeletal development and malocclusion in children. An electronic search in PubMed, the Cochrane Library, Medline, Web of Science, EMBASE and Sigle through February 23rd, 2020, was conducted. PMID: 3267786 No abstract available Case Reports English Abstract Maxillofacial Development* Nasal Bone / injuries Twins* [Mouth breathing and facial growth: the evidence of twins]

Optimal Airway Development and Myofunctional Therapy Mouth Matters
Within the limitations of the study, the results indicated that mouth breathers tended to have a retrognathic maxilla and mandible, vertical growth pattern with high mandibular plane angle, downward and backward rotation of the mandible and an increase in total and lower anterior facial height and decrease in posterior facial height. The traditional mandibular advancement device, twin block (TB), can guide the forward development of the mandible. However, the side effect of increasing the vertical dimension of the lower facial third, worsens the facial profile of children with divergent growth trends. 20824738 Objectives/hypothesis: To determine the effect of mouth breathing during childhood on craniofacial and dentofacial development compared to nasal breathing in malocclusion patients treated in the orthodontic clinic. Retrospective study in a tertiary medical center. Introduction This is a story about a vast and serious epidemic afflicting the developed world increasingly over the last few centuries, one that has gone virtually unrecognized. Jaws is about its origins, how it was discovered, and what we can do about it.

Twin A (left) and twin B (right) at 12 years of age. Download
(January 2021) Mouth breathing, medically known as chronic oral ventilation, is long-term breathing through the mouth. It often is caused by an obstruction to breathing through the nose, the innate breathing organ in the human body. [3] [4] Chronic mouth breathing may be associated with illness. [5] MZbis exhibited a more severe dysfunctional situation (Table I), thus accounting perhaps for the phenotype differences: former thumb-sucking, lingual piercing and mouth-breathing associated with a low position of the tongue all pointed to greater hypodevelopment of the mid-third and a more pronounced mandibular discrepancy in MZbis, notably at symphysal level.
Introduction. Mouth breathing is an undesirable habit that affects the muscular balance amongst the tongue, cheeks, and perioral muscles. 1 Chronic and allergic rhinitis have been associated with mouth breathing. 2 Inflammation or environmental irritation in the nasal cavity may lead to nasal mucosal edema, which decreases nasal ventilation and oxygen delivery efficiency. 3 Let's see some of the problems caused by mouth breathing: Dry mouth and lips Bad breath Long face Baggy eyes with dark circles Prey eyes vs hunter eyes Narrow nostrils Trouble sealing lips Narrow upper jaw overbite or underbite Crowded teeth Constant fatigue and irritation Brain fog Snoring and drooling during sleep Sleep disorders (insomnia)
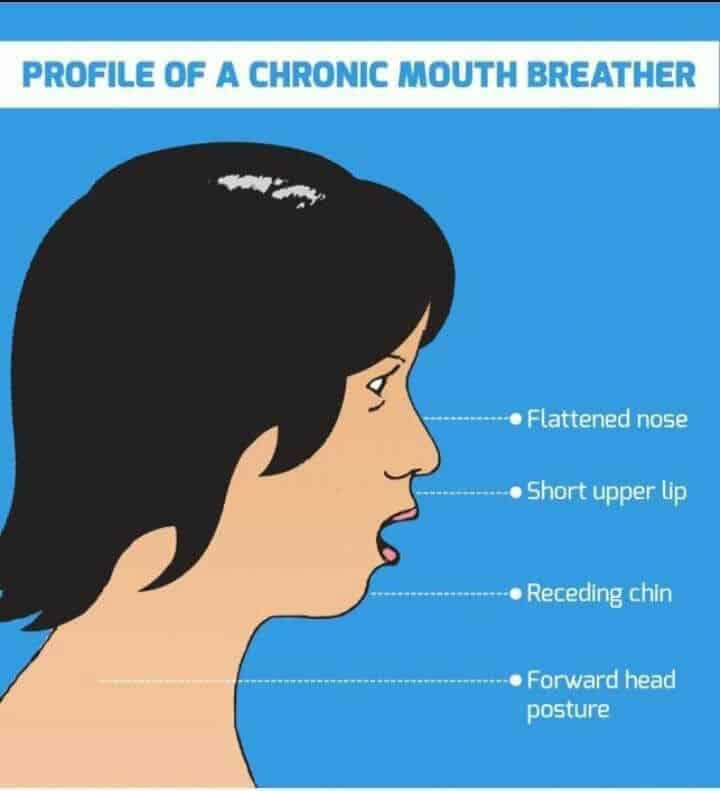
Mouth Breather vs Nose Breather Faces
But i think mouth breathing cause overbite not underbite. This article say that the position of feet can influence the teeth.. Yeah there was a video I watched once where one twin was a mouth breather (due to obstructed airway in his nose) and the other was fine, and the difference between their skeletal structure had changed dramatically. Historically, "mouth breather" has been used as a derogatory term to describe someone as stupid or unintelligent. This is an unfair characterization; how you breathe has nothing to do with intelligence. Nose Breathing




