In probability, a Venn diagram is a figure with one or more circles inside a rectangle that describes logical relations between events. The rectangle in a Venn diagram represents the sample space or the universal set, that is, the set of all possible outcomes. A circle inside the rectangle represents an event, that is, a subset of the sample space. Probability with Venn diagrams Google Classroom About Transcript Want to learn some probability? This video explains the probability of drawing a Jack or a Heart from a deck of 52 cards. It uses a Venn diagram to illustrate the concept of overlapping events and how to calculate the combined probability.
Calculating Probability Using Venn Diagrams YouTube
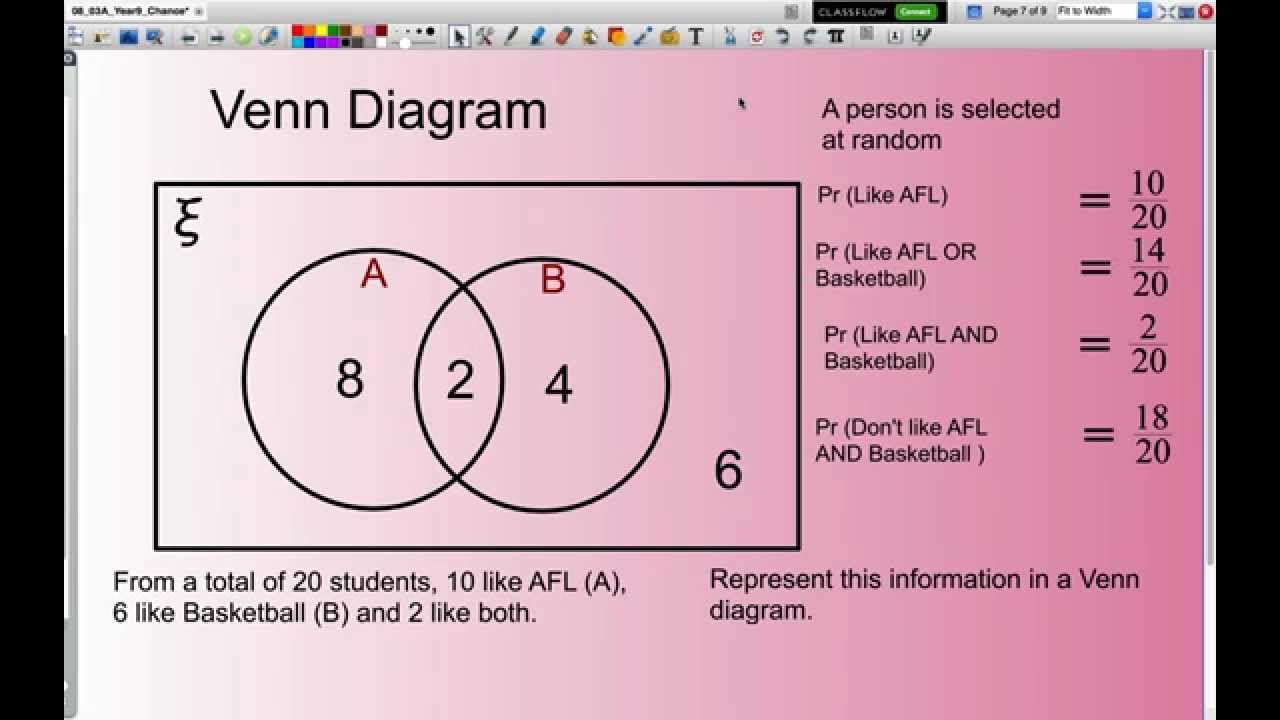
Venn diagram probability is used to state the probability of or predict the possible outcomes of one or more event (s) occurring. To do this we need to have a completed Venn diagram to be able to calculate probabilities from. E.g. The development of the Rules of Probability with the use of Venn diagrams can be shown to help as we wish to calculate probabilities from data arranged in a contingency table. Example 3.33. Table 3.11 is from a sample of 200 people who were asked how much education they completed. The columns represent the highest education they completed, and. Venn diagrams are often used to find the probability of events. They are used to sort data into sets, which may be presented showing all the individual elements or showing the number of. Example \(\PageIndex{6}\): Probability and Venn Diagrams. Forty percent of the students at a local college belong to a club and 50% work part time. Five percent of the students work part time and belong to a club. Draw a Venn diagram showing the relationships. Let \(\text{C} =\) student belongs to a club and \(\text{PT} =\) student works part time.
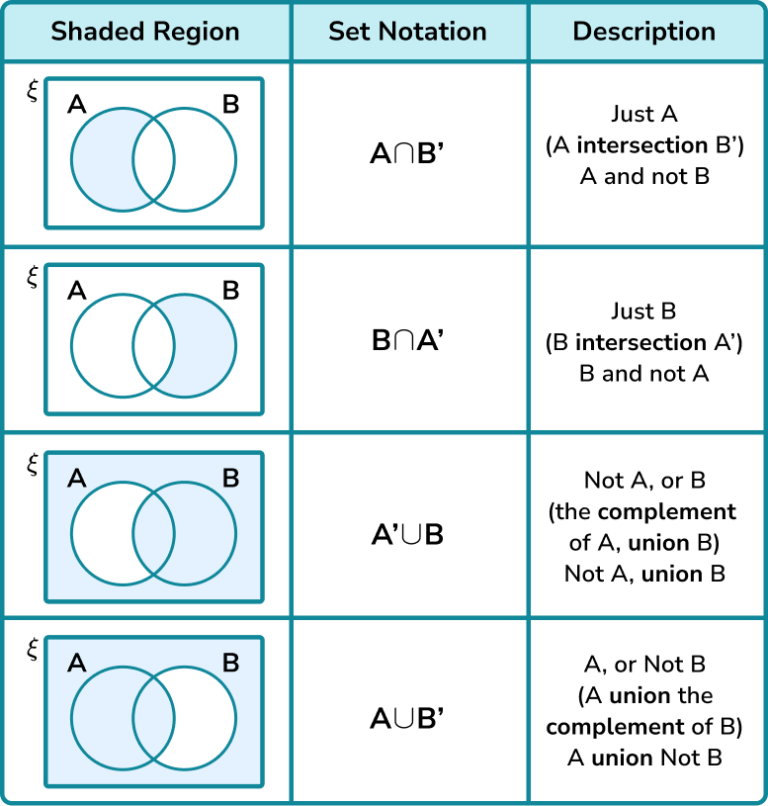
Venn Diagram Symbols Steps, Examples & Worksheet
Lesson 1: Venn diagrams and the addition rule Probability with Venn diagrams Addition rule for probability Addition rule for probability (basic) Two-way tables, Venn diagrams, and probability Math > Precalculus > Probability and combinatorics > Venn diagrams and the addition rule Two-way tables, Venn diagrams, and probability Google Classroom Venn Diagrams . In probability, a Venn diagram is a graphic organizer that shows a visual representation for all possible outcomes of an experiment and the events of the experiment in ovals. Normally, in probability, the Venn diagram will be a box with overlapping ovals inside. Look at the diagram below: Tree Diagrams A tree diagram is a special type of graph used to determine the outcomes of an experiment. It consists of branches that are labeled with either frequencies or probabilities. Tree diagrams can make some probability problems easier to visualize and solve. The following example illustrates how to use a tree diagram: Example 3.24 Statisticians use Venn diagrams to depict relationships between events in a sample space. In a Venn diagram, the sample space is represented by a rectangle. Events within the sample space are often represented by circles within the rectangle. Here is a simple Venn diagram: In this diagram, the blue circle represents Event A; and the area in.
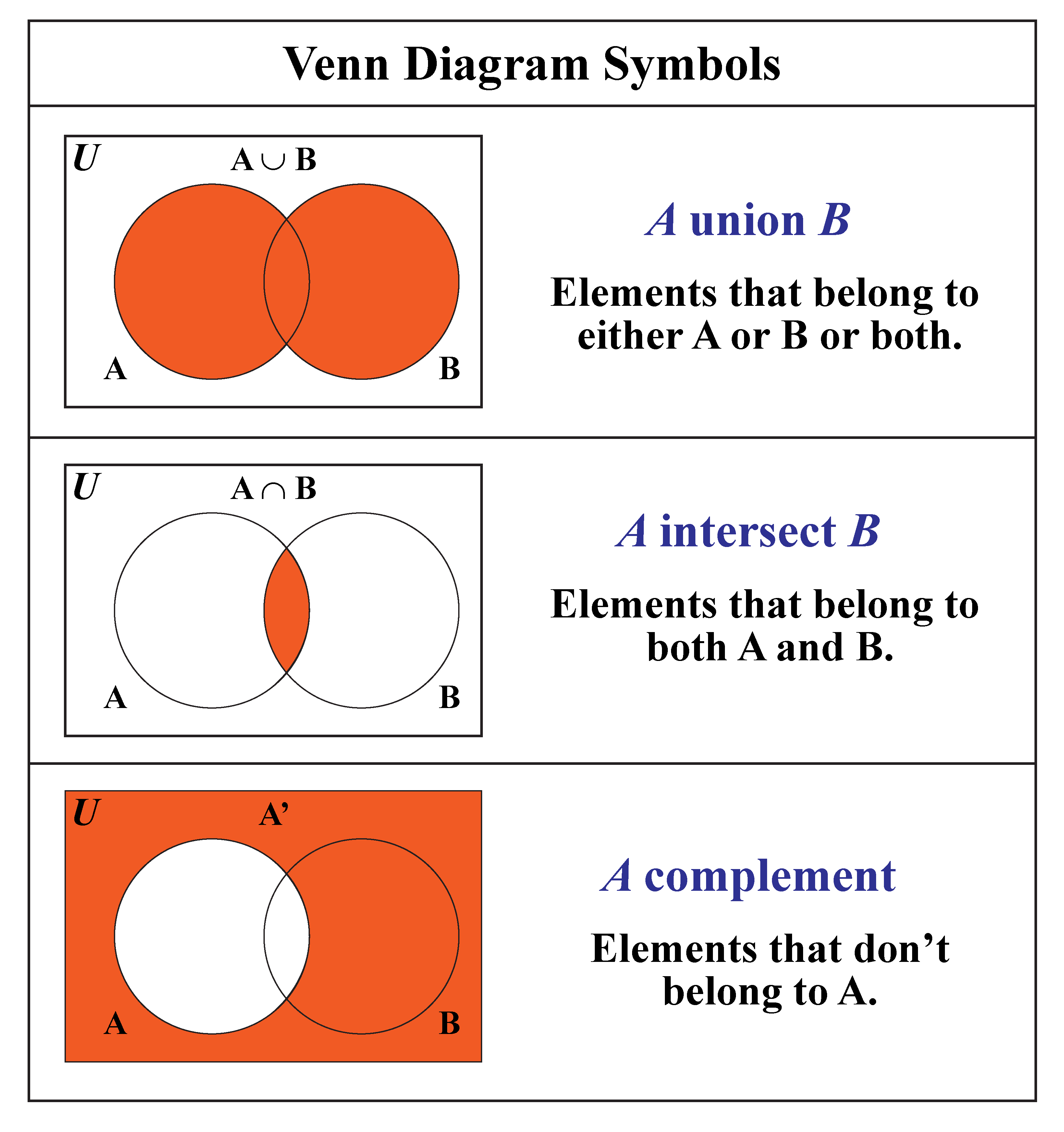
Venn Diagram Cuemath
To find the probability for only the front tire going flat or only the rear tire on the Venn diagram, look at the values in the circles, 0.135 and 0.085, respectively. In probability theory terminology, these are the joint probabilities of one tire going flat and the other tire not going flat. Venn Diagrams EE 178/278A: Basic Probability Page 1-5 Elements of Probability • Probability theory provides the mathematical rules for assigning probabilities to outcomes of random experiments, e.g., coin flips, packet arrivals, noise voltage • Basic elements of probability:
Unit 1 Exploring categorical data Unit 2 Exploring one-variable quantitative data: Displaying and describing Unit 3 Exploring one-variable quantitative data: Summary statistics Unit 4 Exploring one-variable quantitative data: Percentiles, z-scores, and the normal distribution Unit 5 Exploring two-variable quantitative data Unit 6 Collecting data This lesson covers how to use Venn diagrams to solve probability problems. Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. We have a new and improved read on this topic.

Probability from Venn diagrams Variation Theory
In order to use Venn diagrams when talking about events, we must first understand the term 'mutually exclusive'. Imagine there are two events: event A and event B. If they both cannot happen at. This video demonstrates how to solve probability questions using a Venn Diagram. Joint, union, complement, and conditional probabilities examples included.




