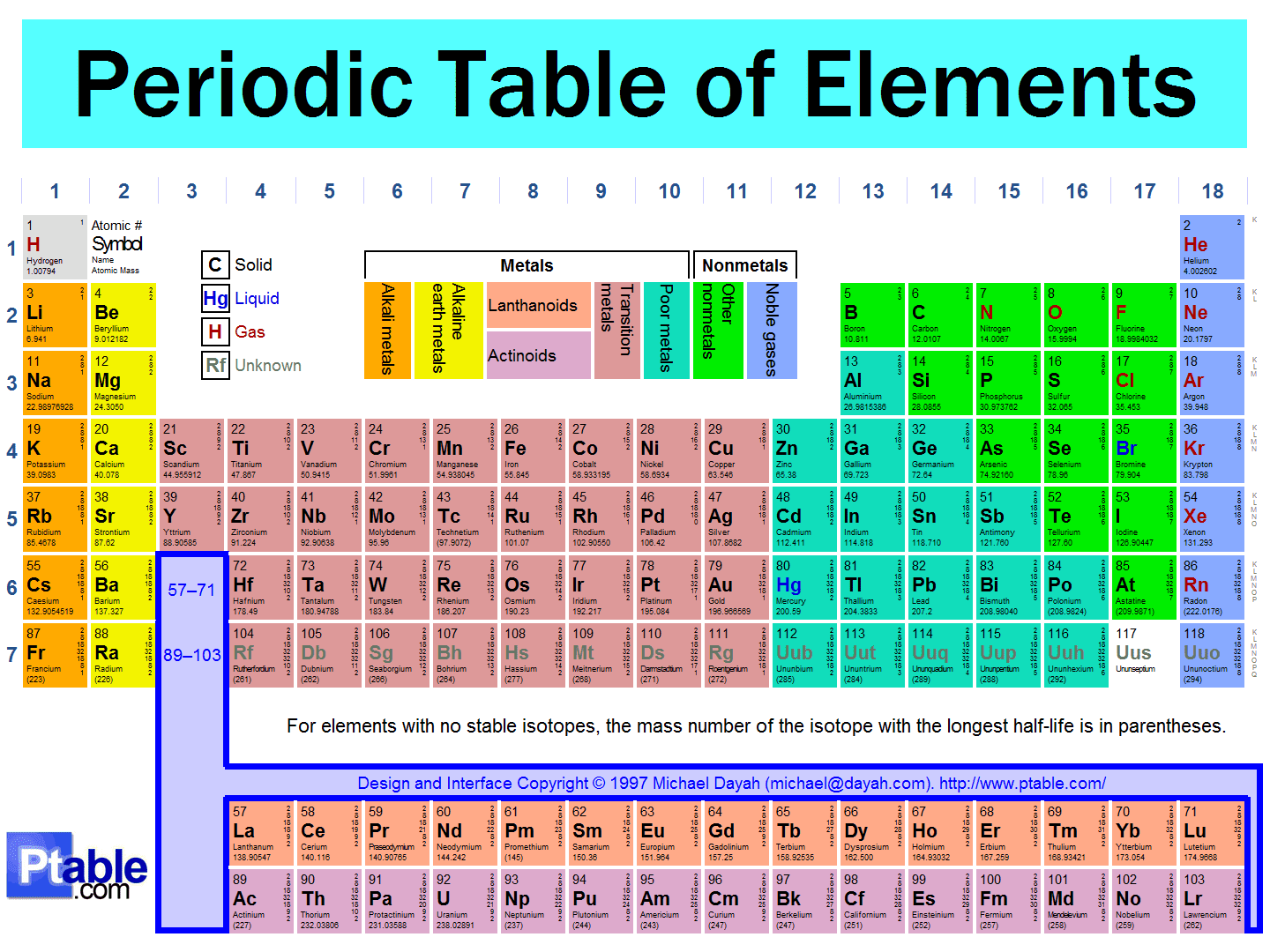
Figure 2.5.1 2.5. 1: The Periodic Table Showing the Elements in Order of Increasing Z. The metals are on the bottom left in the periodic table, and the nonmetals are at the top right. The semimetals lie along a diagonal line separating the metals and nonmetals. An interactive Periodic table can be found Periodic Table of the Elements, LibreTexts. Periodic table of the chemical elements showing the most or more commonly named sets of elements (in periodic tables), and a traditional dividing line between metals and nonmetals. The f-block actually fits between groups 2 and 3; it is usually shown at the foot of the table to save space. Part of a series on the Periodic table Periodic table forms
Ojasvi Garg New element in periodic table IIT Student
A chemical element, often simply called an element, is a type of atom which has a specific number of protons in its atomic nucleus (i.e., a specific atomic number, or Z ). [1] Periodic Table of Elements TABLE LIST W/PROPERTIES GAME Display Property/Trend 17 Cl Chlorine halogen Plot Atomic Mass 1 H Hydrogen nonmetal 2 He Helium noble gas 3 Li Lithium alkali metal 4 Be Beryllium alkaline earth metal 5 B Boron metalloid 6 C Carbon nonmetal 7 N Nitrogen nonmetal 8 Updated on February 01, 2021 The electron configuration of an atom of any element is the of electrons per sublevel of the energy levels of an atom in its ground state . This handy chart compiles the electron configurations of the elements up through number 104. Key Takeaways: Electron Configurations A chemical element is a chemical substance that cannot be broken down into other substances by chemical reactions. The basic particle that constitutes a chemical element is the atom.
/complete-periodic-table-of-elements-royalty-free-vector-166052665-5a565f0e47c2660037ab8aca.jpg)
List of Halogens (Element Groups)
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present). Each of the elements found in this column, which are boxed in lavender in Figure 2.2.1 2.2. 1, reacts readily with metals to form compounds that can be broadly classified as salts and, therefore, are known as the halogens, which is derived from a combination of Greek words that translate to "salt makers." A modern periodic table arranges the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers and groups atoms with similar properties in the same vertical column (Figure 2.5.2 2.5. 2 ). Each box represents an element and contains its atomic number, symbol, average atomic mass, and (sometimes) name. The elements are arranged in seven horizontal. Figure 2.25 (a) Dimitri Mendeleev is widely credited with creating (b) the first periodic table of the elements. (credit a: modification of work by Serge Lachinov; credit b: modification of work by "Den fjättrade ankan"/Wikimedia Commons) By the twentieth century, it became apparent that the periodic relationship involved atomic numbers.

The Periodic Table and its Design Pathways to Chemistry
Two-element wattmeters are generally used in delta connected systems. They require two line-line voltages and only two phase currents. Three-element wattmeters are used in wye connected systems. They require three line-neutral voltages and three phase currents. What are electron configurations? Electron Configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and orbitals groupings of the periodic table. The electron configuration for the first 10 elements H 1s1 He 1s2
This electron configuration calculator will instantly show you the distribution of electrons in the orbitals of any periodic element you choose. Typically, you need at least 8 steps to determine the electron configuration, starting with finding the atomic number by looking at the list of orbitals and understanding the notation.. But wait — you can avoid all this if you use our tool! Tennessine. [Rn]7s 2 5f 14 6d 10 7p 5 [note] Praseodymium. [Xe]6s 2 4f 3. Oganesson. [Rn]7s 2 5f 14 6d 10 7p 6 [note] Notes on the Electron Configuration of particular elements: Dubnium: Value is a guess based on periodic table trend. Seaborgium: Value is a guess based on periodic table trend.
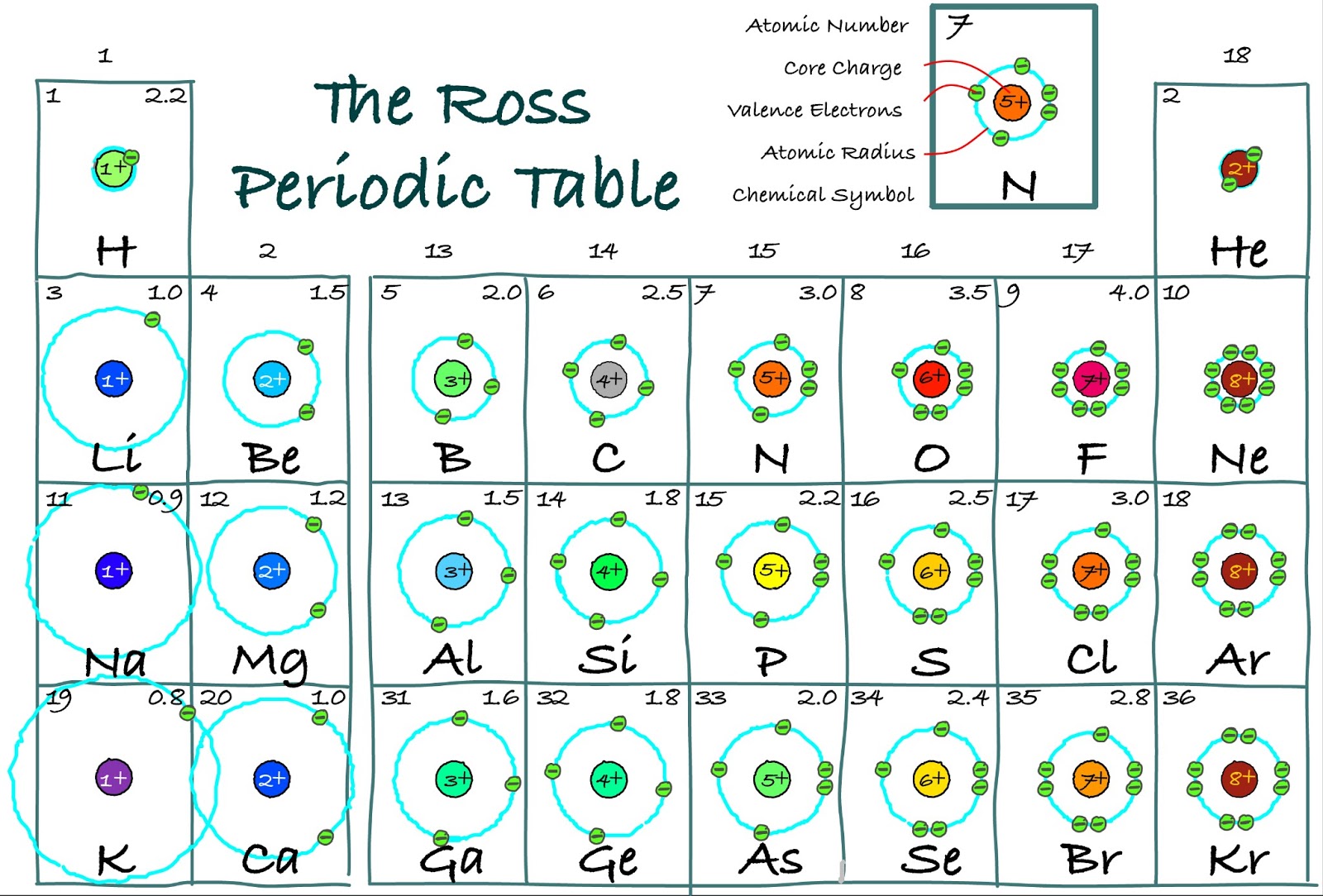
The Ross Periodic Table Core Charge Its Periodicity Across the Table
Chemistry 10 2.5 The Periodic Table Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you will be able to: State the periodic law and explain the organization of elements in the periodic table Predict the general properties of elements based on their location within the periodic table Use the element blocks of the periodic table to find the highest electron orbital. Alternatively, remember group 1 (alkali metals) and group 2 (alkaline earth metals) are s-block, groups 2 through 12 are the d-block, 13 to 18 are the p-block, and the two rows at the bottom of the table (the lanthanides and actinides) are f-block.

/complete-periodic-table-of-elements-royalty-free-vector-166052665-5a565f0e47c2660037ab8aca.jpg)


