The common iliac artery is a large artery of the abdomen paired on each side. It originates from the aortic bifurcation at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra. It ends in front of the sacroiliac joint, one on either side, and each bifurcates into the external and internal iliac arteries . Structure The common iliac artery (CIA) is a short artery transporting blood from the aorta towards the pelvic region and lower extremity. Sometimes this paired artery is also referred to as its plural form common iliac arteries. The left and right common iliac arteries are the terminal branches of the abdominal aorta.
Surgery Assistant
Iliac arterial aneurysms are focal dilatations of the iliac artery . Although the dimensions that define the aneurysm are dependent on the sex of the patient and the portion of the artery involved, a common iliac artery (CIA) with a diameter ≥1.7 cm in males or ≥1.5 cm in females is considered ectatic. A diameter >2.5 cm is considered aneurysmal 3. Common iliac vein In human anatomy, the common iliac veins are formed by the external iliac veins and internal iliac veins. The left and right common iliac veins come together in the abdomen at the level of the fifth lumbar vertebra, [1] forming the inferior vena cava. They drain blood from the pelvis and lower limbs. The common iliac arteries (CIAs) enter the pelvis on the medial aspect of the psoas muscle. The left CIA is shorter than the right. The right CIA passes anterior to the left common iliac vein and then anterior and parallel to the right common iliac vein. The left CIA course is simpler, running parallel and lateral to the left common iliac vein. The common iliac vein (CIV) (TA: vena iliaca communis), corresponding with the common iliac artery, drains venous blood from the pelvis, lower limbs and their associated structures. Summary location: pelvis, anterior to the sacroiliac joint or.

Endovaskulær behandling af mykotisk arteria iliacaaneurisme Ugeskriftet.dk
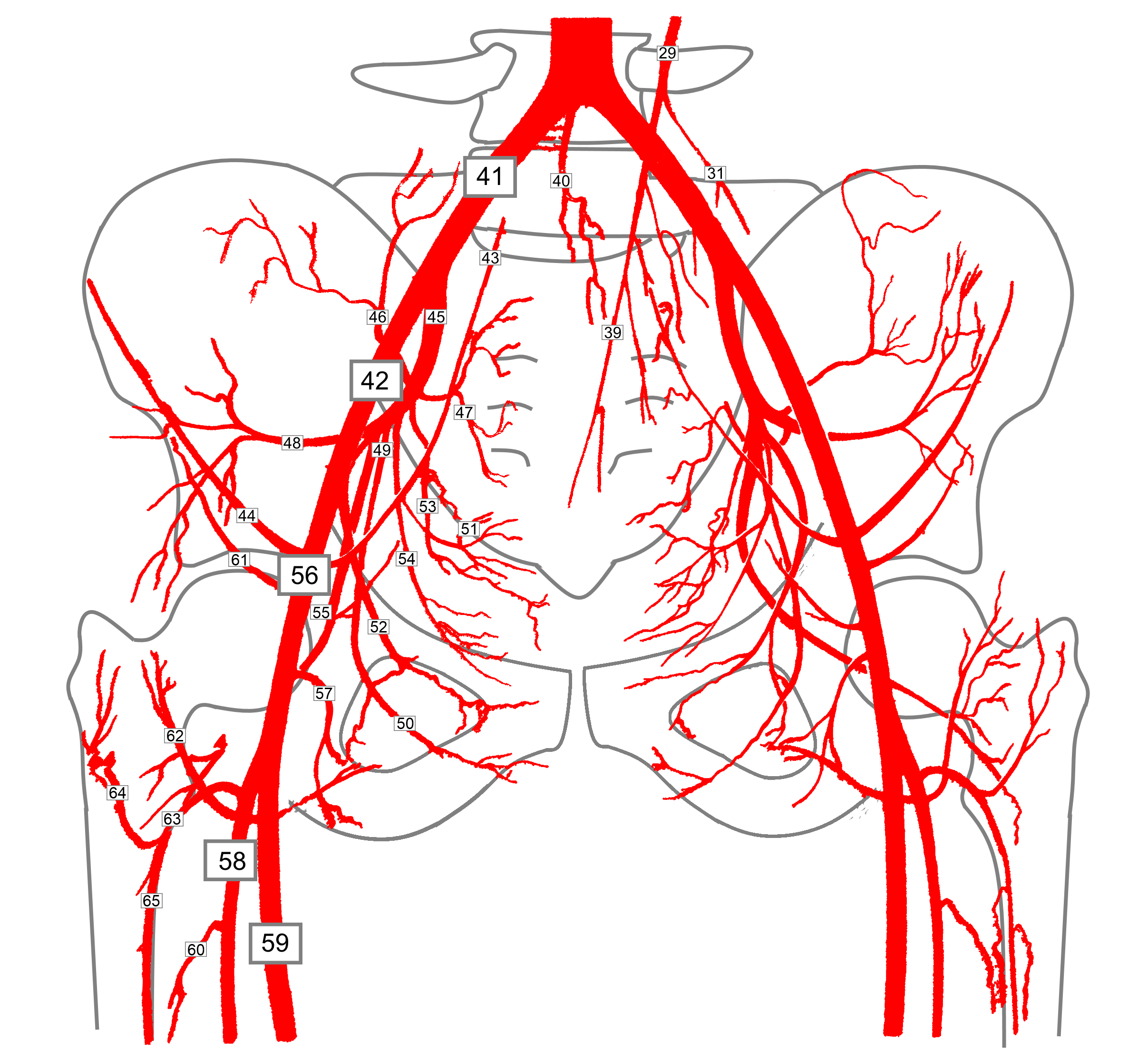
The aa. iliacae communes divide further into the aa. iliacae internae and externae. The aorta abdominalis (see C) and its major branches give origin to various "subbranches" that supply the abdomen and pelvis (see D ). B Projection of the aorta abdominalis and its major branches onto the columna vertebralis and pelvis A ureteric branch arises from the common iliac artery where the ureter crosses anterior to the artery near its terminal bifurcation. The internal iliac artery crosses the pelvic brim and enters the pelvic cavity. The external iliac artery continues inferiorly along psoas major as it travels towards the lower limb. Arteria iliaca communis Autor: Sophie Eckert • Geprüft von: Claudia Bednarek, Ärztin Zuletzt geprüft: 30. Oktober 2023 Lesezeit: 5 Minuten Die paarige Arteria iliaca communis (gemeinsame Beckenarterie) liegt retroperitoneal in der Bauchhöhle und entsteht aus der Bauchaorta (Aorta abdominalis).. Sie versorgt mit ihren Ästen die untere Extremität, das kleine Becken sowie Teile der Rumpfwand. Common iliac artery (Arteria iliaca communis) The common iliac artery has a diameter 7-12mm it is covered by the parietal peritoneum and runs laterally and distally along the medial edge of the psoas major muscle without giving off any significant branches ( Fig.3). The right common iliac artery crosses over the start of the
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1064/mAILbcS3t2vnVZMAu3OZQ_arteries-of-the-sacrum_latin.jpg)
Arteria Iliaca communis Anatomie, Verlauf, Äste & pAVK Kenhub
Verschlussprozesse an der A. iliaca interna sind häufig symptomfrei, da ein ausgedehntes Kollateralsystem zur Gegenseite sowie zu femoralen, lumbalen und mesenterialen Gefäßen besteht. Klinisch wird die Erkrankung meist durch eine Gefäßclaudicatio und/oder vaskuläre Impotenz symptomatisch. A. iliaca communis dx. et sin. vznikají rozvětvením břišní aorty Oblast zásobení A. iliaca communis vysílá jen drobné větve do m. psoas major, k mízním uzlinám a k ureteru . Průběh a větvení A. iliaca communis dextra přechází kolmo přes levou v. iliaca communis a hned poté pokračuje před pravostrannou v. iliaca communis.
2 Altmetric Explore all metrics Zusammenfassung Klinisches Problem Isolierte Aneurysmen der iliakalen Arterien sind wesentlich seltener als infrarenale Aortenaneurysmen und treten ebenfalls vorwiegend bei älteren männlichen Patienten auf. Sie sind meist asymptomatisch und werden zufällig radiologisch diagnostiziert. Verlauf. Die Arteria iliaca communis ist beim Erwachsenen nur etwa 3-4 cm lang, hat aber einen Durchmesser von mehr als 10 mm. Nach kurzem Verlauf teilt sie sich in der Nähe des Iliosakralgelenks in zwei Äste auf: Die Arteria iliaca communis wird von der gleichnamigen Vena iliaca communis begleitet.

AMIGOS PARA SIEMPRE Anatomía humana Arterias
Isolierte Iliakaaneurysmen sind eine seltene Form aortoabdominaler Aneurysmen und weisen eine hohe Komplikations- und Rupturrate auf, die mit einer hohen Mortalität einhergeht. Unspezifische Symptome verzögern die Diagnosestellung. 1 Allgemeines 1.1 Inzidenz und Lokalisation 48 % der Patienten < 45 Jahre mit Claudicatio-Symptomatik haben eine Erkrankung der Iliakalarterien. 20 % unabhängig vom Alter multisegmentale Erkrankung < 10 % singuläre Verschlüsse im Bereich der Aortenbifurkation Einteilung der aorto-iliakalen Verschlussprozesse nach Vollmar Wichtig


:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/1064/mAILbcS3t2vnVZMAu3OZQ_arteries-of-the-sacrum_latin.jpg)

