In Python, operators are special symbols, combinations of symbols, or keywords that designate some type of computation. You can combine objects and operators to build expressions that perform the actual computation. So, operators are the building blocks of expressions, which you can use to manipulate your data. I think you're confusing two strange things: 1) b=a [:] copies the references to all the integers, so b [0] points to the same int as a [0] and a [0] is b [0] returns True. 2) refs to the numbers -5 through 256 are kept at all times. - Shep Nov 24, 2012 at 7:39 Add a comment 4 Answers Sorted by: 12 The -5 to 256 range has to do with the following:

python Select rows from dataframe based on substring A or B in a column Stack Overflow
In Python programming language Division Operators allow you to divide two numbers and return a quotient, i.e., the first number or number at the left is divided by the second number or number at the right and returns the quotient. There are two types of division operators: Float division Floor division Float division Bitwise operators are used to compare (binary) numbers: Operator Precedence Operator precedence describes the order in which operations are performed. Example Parentheses has the highest precedence, meaning that expressions inside parentheses must be evaluated first: print( (6 + 3) - (6 + 3)) Run example » Example W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more. The operator module exports a set of efficient functions corresponding to the intrinsic operators of Python. For example, operator.add (x, y) is equivalent to the expression x+y. Many function names are those used for special methods, without the double underscores.
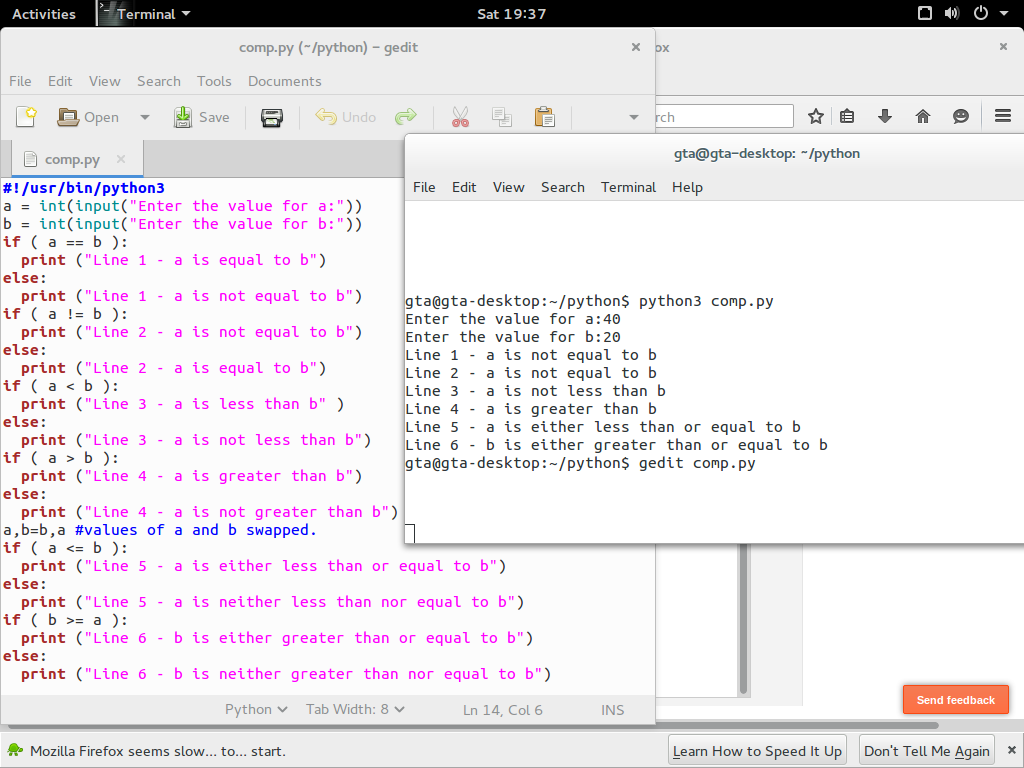
python Python Comparison Operators
Assume if a = 60; and b = 13; Now in the binary format their values will be 0011 1100 and 0000 1101 respectively. Following table lists out the bitwise operators supported by Python language with an example each in those, we use the above two variables (a and b) as operands −. a = 0011 1100. b = 0000 1101-----a&b = 0000 1100. a|b = 0011 1101. Basically, the Python modulo operation is used to get the remainder of a division. The modulo operator ( %) is considered an arithmetic operation, along with +, -, /, *, **, //. In most languages, both operands of this modulo operator have to be an integer. But Python Modulo is versatile in this case. The operands can be either integers or floats. These operators compare the values on either sides of them and decide the relation among them. They are also called Relational operators. Assume variable a holds 10 and variable b holds 20, then. [ Python Comparison Operators ] Operator. Name. Example. ==. Equal. But to simplify code, and reduce redundancy, Python also includes arithmetic assignment operators. This includes the += operator in Python used for addition assignment, //= floor division assignment operator, and others. Here's a list of all the arithmetic assignment operators in Python. Operator. Description. +=. a+=b is equivalent to a=a+b.

Ball Python Care Guide PetHelpful
Assignment Statement. First of all, you've got to understand that this operation a, b = b, a is a statement in Python, as opposed to an expression. Expressions are code that evaluates to a value. By contrast, statements execute an action without evaluating to a value. More specifically, the statement is an assignment statement because it uses. For example, [abc] will match any of the characters a, b, or c; this is the same as [a-c], which uses a range to express the same set of characters. If you wanted to match only lowercase letters, your RE would be [a-z]. Metacharacters (except \) are not active inside classes.
# Python program to demonstrate ternary operator a, b = 10, 20 # Use tuple for selecting an item print( (b, a) [a < b] ) # Use Dictionary for selecting an item print({True: a, False: b} [a < b]) # lambda is more efficient than above two methods # because in lambda we are assure that # only one expression will be evaluated unlike in # tuple and Dictionary print((lambda: b, lambda: a)[a < b. We'll also set a confidence level of 95%: α = 0.05. The α value is a threshold we set, by which we say "if the probability of observing a result as extreme or more ( p-value) is lower than α, then we reject the Null hypothesis". Since our α=0.05 (indicating 5% probability), our confidence (1 — α) is 95%. Don't worry if you are.
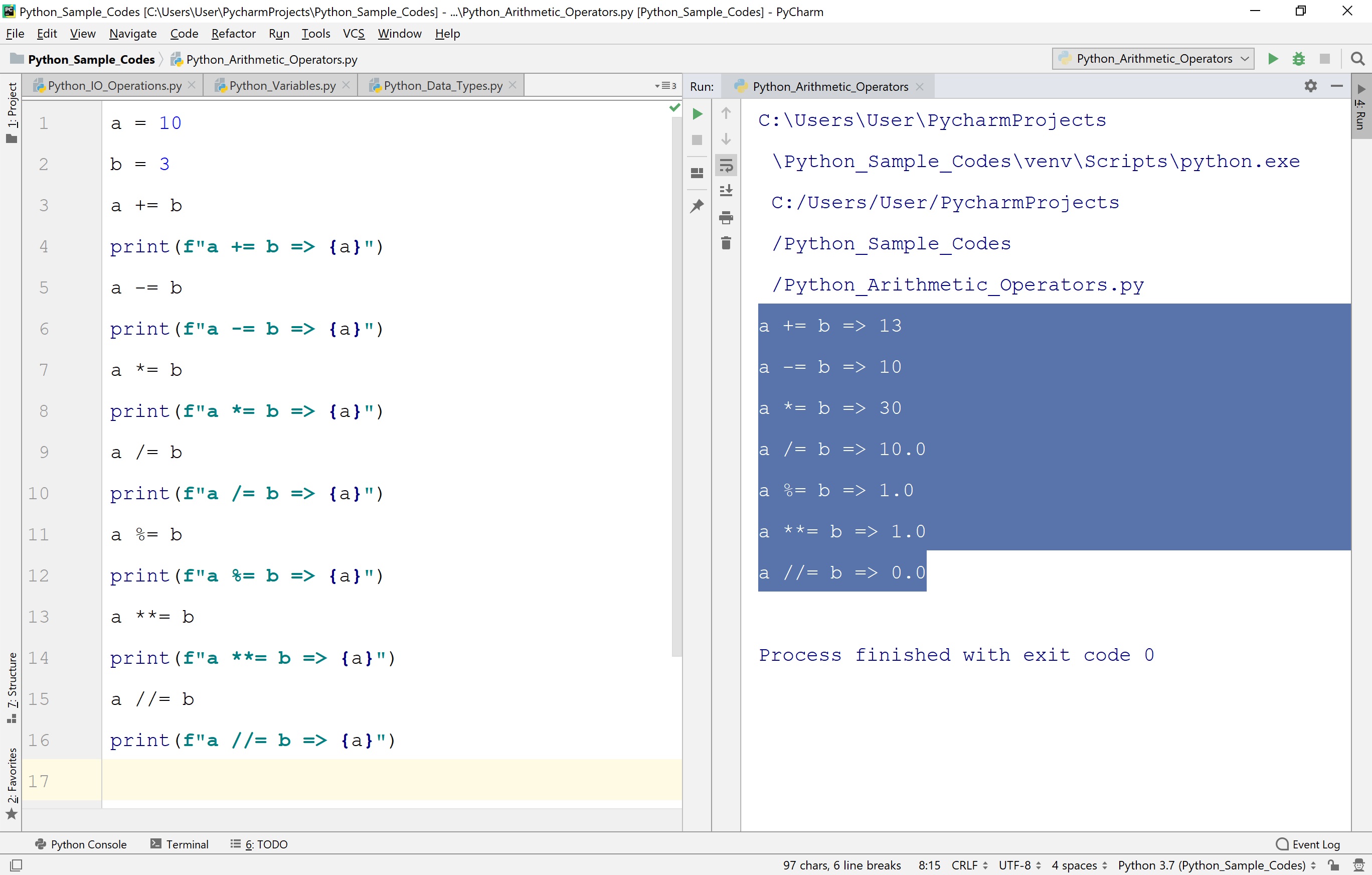
Python Tutorials Operators and its types
In Python, the 'b' character before a string is used to specify the string as a "byte string".By adding the 'b' character before a string literal, it becomes a bytes literal. This means that the string content should be interpreted as a sequence of bytes rather than characters. Get instructor-led training from experts. Microsoft Learn has partnered with our global network of official Microsoft Training Services Partners (TSPs) to deliver AI Bootcamp for Educators. TSPs offer this new instructor-led training in a language, location, and format suited to you—whether in person, online, or as a hybrid event.




