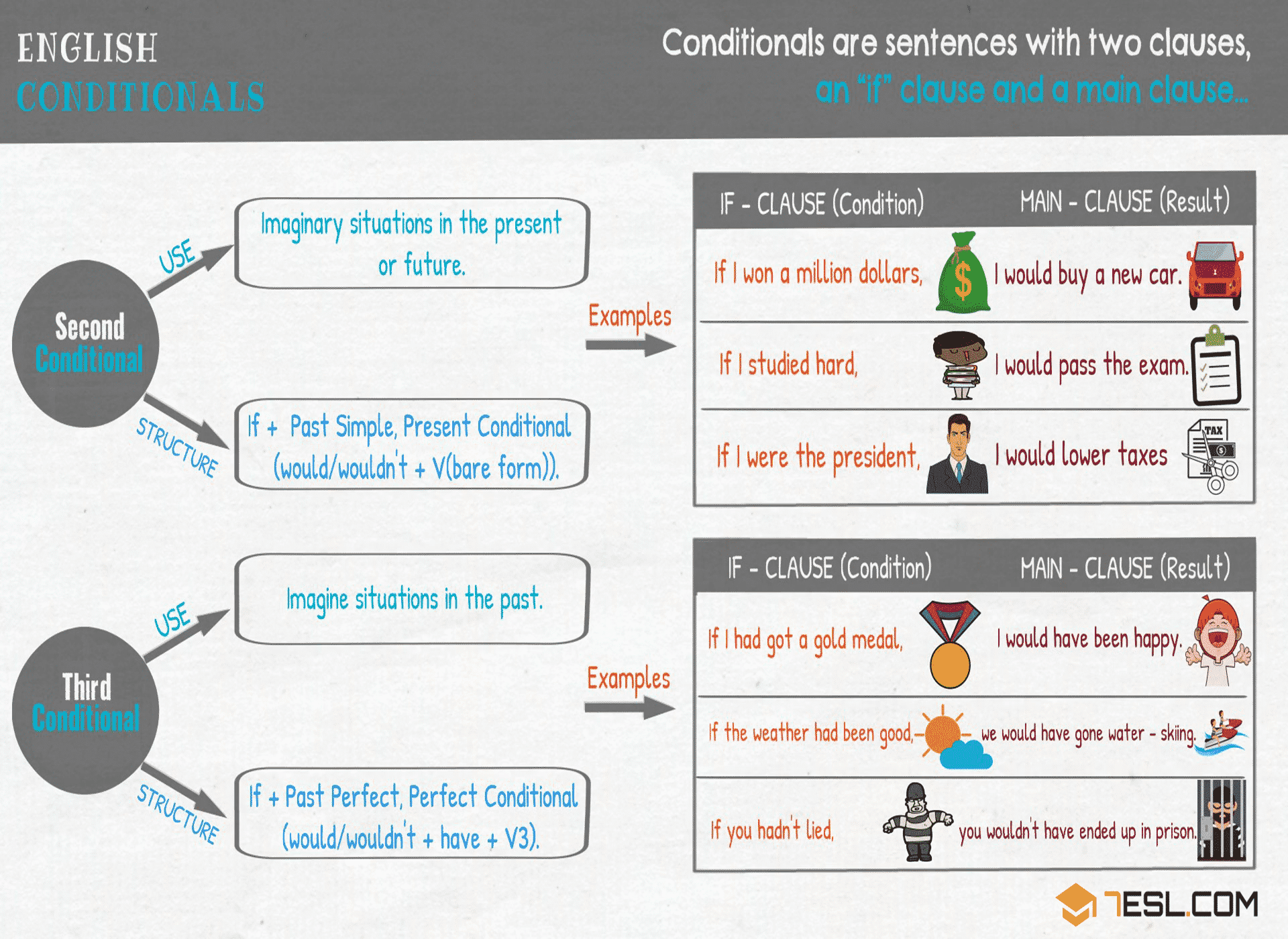
The conditional type 2 refers to an unlikely or hypothetical condition and its probable result. These sentences are not based on the actual situation. In conditional type 2 sentences, the time is now or any time and the situation is hypothetical. EXAMPLES If the weather wasn't so bad, we would go to the park. Form In a Type 2 conditional sentence, the tense in the 'if' clause is the simple past, and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional or the present continuous conditional.

Second conditional sentence (ifsentence type 2) English in General
1. Identify the form of Type 2 conditional sentence; 2. Use the Type 2 conditional sentence to talk about imaginary situations; 3. Distinguish Type 1 conditional from Type 2 conditional; 4. Show a deeper understanding of parents' love. To cite this resource: Zhang, Y., Mei, F., & Lee, J. F. K. (2019). Conditional type 2: If I could. If Clause Type 2 Form if + Simple Past, main clause with Conditional I (= would + Infinitive) Example: If I found her address, I would send her an invitation. The main clause can also be at the beginning of the sentence. In this case, don't use a comma. Example: I would send her an invitation if I found her address. A type 2 conditional sentence, also known as the second conditional sentence, refers to a condition (situation) that is impossible or unlikely to be true (in the present), and its result in the present or near future (very close to the present). We employ second conditional sentences when we want to talk about something that is opposite to reality. Conditional sentences - type II 1. Use It is theoretically possible to fulfil a condition which is given in the if-clause. 2. Form 3. Examples The if-clause can be at the beginning or at the end of a sentence. Mind the comma. if I were you or if I was you if - Omitting if - if vs. when - in case vs. if will and would in if-clauses You are here:
Second Conditional Conditional Sentences Type II English Grammar 7 E S L
Conditional sentences can also be created without if, using inversion. Inversion means reversing (inverting) the normal subject-verb word order in a sentence. This makes the sentence more formal. Three types of conditionals can be formed using inversion: first, second and third conditionals. Conditionals Type 2 statements refer to things that don't happen, or even that is unlikely to happen. In other words, the condition you have stated in these sentences does not express the real situations, it refers to the situations you imagine at that moment. Conditional Sentence Type 2 → It is possible but very unlikely, that the condition will be fulfilled. Form: if + Simple Past, Conditional I (= would + Infinitive) Example: If I found her address, I would send her an invitation. more on Conditional Sentences Type II Conditional Sentence Type 3 1. Form In a Type 2 conditional sentence, the tense in the 'if' clause is the simple past, and the tense in the main clause is the present conditional: Present conditional, form The present conditional of any verb is composed of two parts - the modal auxiliary would + the infinitive of the main verb (without 'to'.) Would: Contractions of would

First Conditional cglearn.it
Exercise on Conditional Sentences Type 2. Complete the Conditional Sentences (Type II) by putting the verbs into the correct form. Use conditional I with would in the main clause. If we (have) a yacht, we (sail) the seven seas. If he (have) more time, he (learn) karate. If they (tell) their father, he (be) very angry. If Clauses - Type 2 is used to express dreams, unreal situations and things that are unlikely to happen. In other words, The condition specified in the clause is not actual but is a condition that is currently being imagined. Although the verb is used in the past, we use type 2 when talking about present time or now. Examples:
The conditional sentences type 2 is used to talk about things which are unreal (not true or not possible) in the present or the future - things which don't or won't happen. For example: If I had a car, I would drive it every day. Conditional Sentences Type 2 | Image Conditional Sentences - Wish - Unless Examples: Type 2 mixed conditional sentences If you paid attention in school, you would have learned more. I would have invited you if I knew you were free. Common mistake: Adding "would" to the "if" clause. When using conditional sentences, people sometimes add the modal verb "would" to the subordinate clause. While "would" is.

Conditionals 04 Types Of Conditional Sentences In Grammar 7 E S L English grammar tenses
Conditional sentences - type II. If I (to come) home earlier, I (to prepare) dinner. If we (to live) in Rome, Francesco (to visit) us. If Tim and Tom (to be) older, they (to play) in our hockey team. If he (to be) my friend, I (to invite) him to my birthday party. If Susan (to study) harder, she (to be) better at school. The third conditional is used to imagine a different past. We imagine a change in a past situation and the different result of that change. If I had understood the instructions properly, I would have passed the exam. We wouldn't have got lost if my phone hadn't run out of battery. In third conditional sentences, the structure is usually: If.




