Cosines Tangents Cotangents Pythagorean theorem Calculus Trigonometric substitution Integrals ( inverse functions) Derivatives v t e Basis of trigonometry: if two right triangles have equal acute angles, they are similar, so their corresponding side lengths are proportional. Sine, Cosine and Tangent (often shortened to sin, cos and tan) are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle: For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is To calculate them: Divide the length of one side by another side Example: What is the sine of 35°?
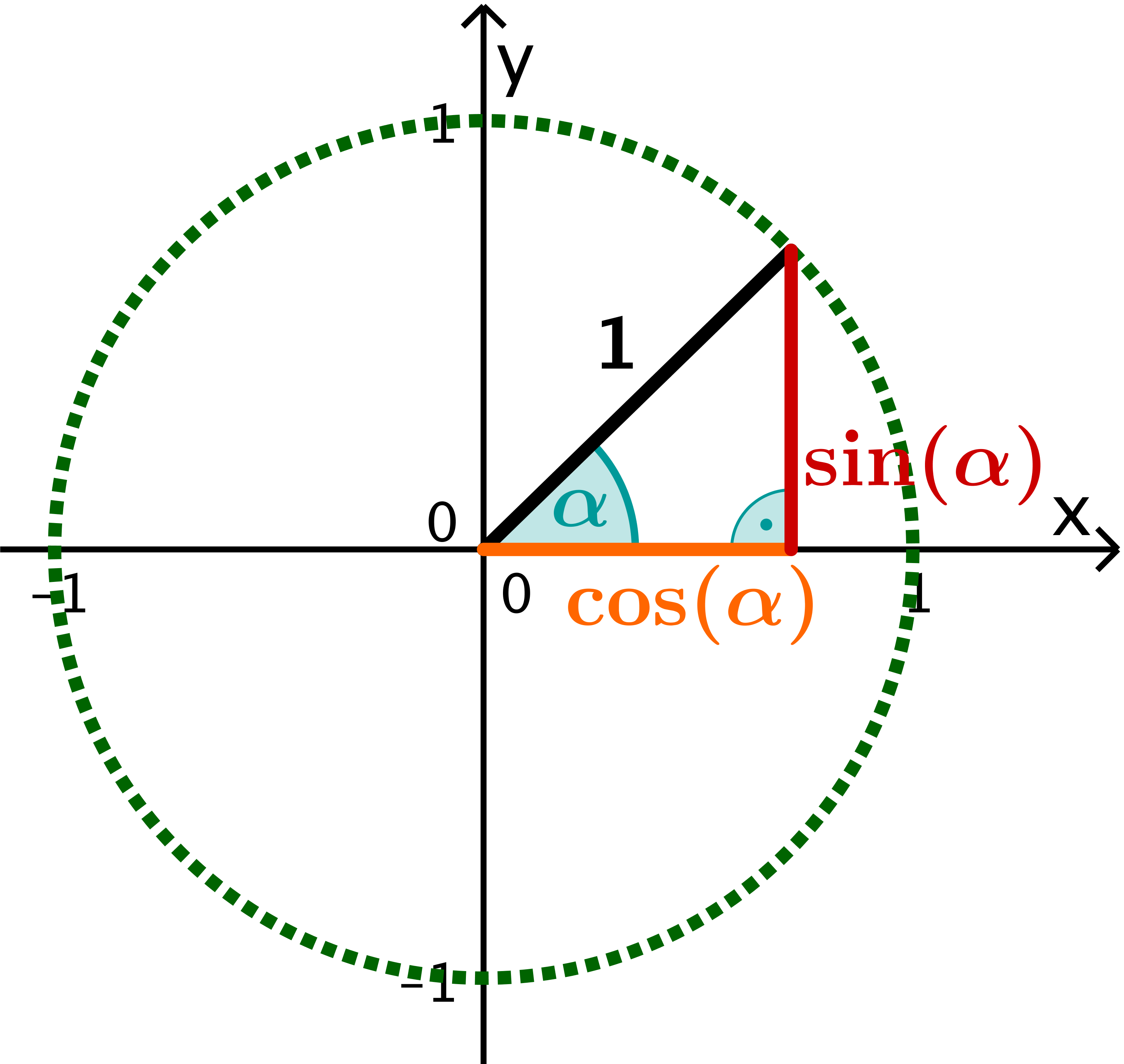
Trigonometrie am Einheitskreis lernen mit Serlo!
The Tangent function has a completely different shape. it goes between negative and positive Infinity, crossing through 0, and at every π radians (180°), as shown on this plot. At π /2 radians (90°), and at − π /2 (−90°), 3 π /2 (270°), etc, the function is officially undefined, because it could be positive Infinity or negative. Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics. The word itself comes from the Greek trigōnon (which means "triangle") and metron ("measure"). As the name suggests, trigonometry deals primarily with angles and triangles; in particular, it defines and uses the relationships and ratios between angles and sides in triangles.The primary application is thus solving triangles, precisely right triangles. The sine and cosine of an acute angle are defined in the context of a right triangle: for the specified angle, its sine is the ratio of the length of the side that is opposite that angle to the length of the longest side of the triangle (the hypotenuse ), and the cosine is the ratio of the length of the adjacent leg to that of the hypotenuse. The sine of an angle has a range of values from -1 to 1 inclusive. Below is a table of values illustrating some key sine values that span the entire range of values. The Cosine Ratio The cosine of an angle is always the ratio of the (adjacent side/ hypotenuse).
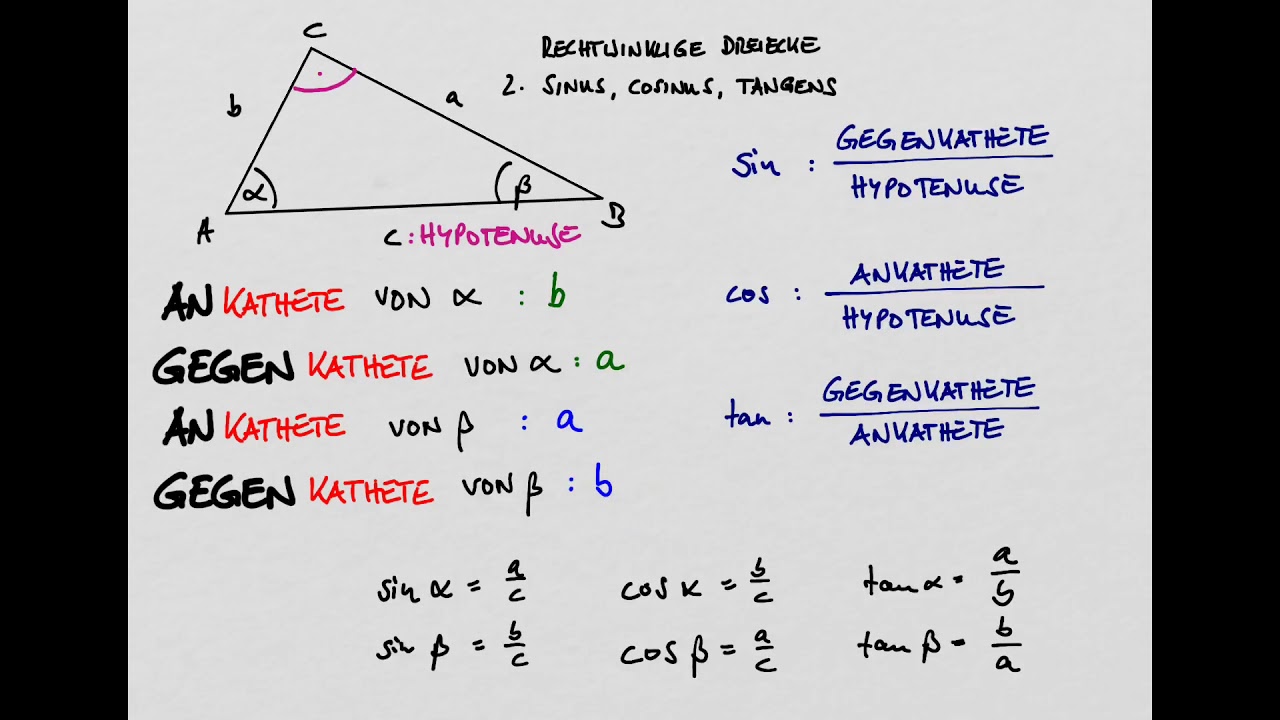
sinus cosinus tangens 2 formeln YouTube
This video is a quick introduction to sine, cosine, and tangent. It teaches you how to find the values of sine, cosine, and tangent if you are told the leng. Sin, cos, and tan are trigonometric ratios that relate the angles and sides of right triangles. Sin is the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse, cos is the ratio of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse, and tan is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. They are often written as sin (x), cos (x), and tan (x), where x is an. To calculate sine, cosine, and tangent in a 3-4-5 triangle, follow these easy steps: Place the triangle in a trigonometric circle with an acute angle in the center. Identify the adjacent and opposite catheti to the angle. Compute the results of the trigonometric functions for that angle using the following formulas: sin (α) = opposite. The differentiation of trigonometric functions is the mathematical process of finding the derivative of a trigonometric function, or its rate of change with respect to a variable.For example, the derivative of the sine function is written sin′(a) = cos(a), meaning that the rate of change of sin(x) at a particular angle x = a is given by the cosine of that angle.
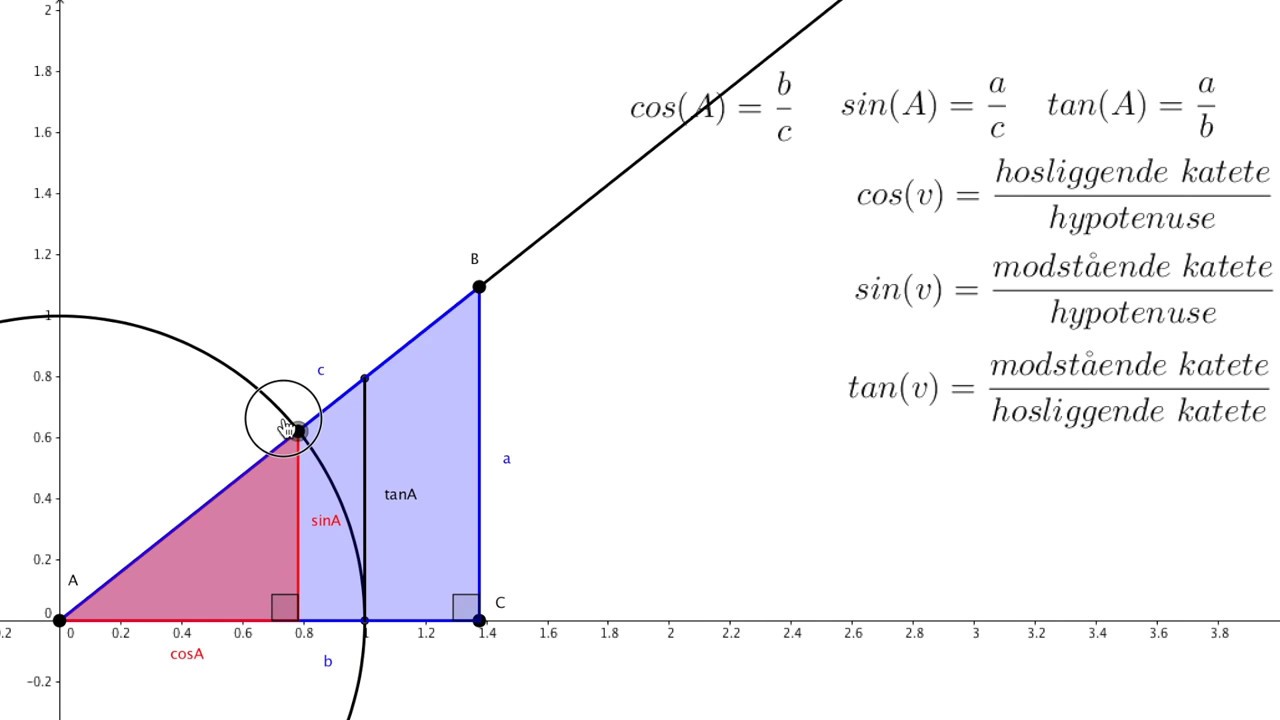
Cosinus Sinus Tangens YouTube
Trigonometriske funksjoner Funksjonene sinus, cosinus, tangens og cotangens. Defineres enklest for en spiss vinkel i en rettvinklet trekant som forholdet mellom to av sidene i trekanten. trigonometriske funksjonene er: Sinus En trigonometrisk funksjon. Lad os tage nogle eksempler. Vi ønsker at finde v i følgende trekant. Vi ser at vi kender den modstående katete (modstående i forhold til vinkel v) og hypotenusen. Derfor skal vi have fat i sinus. sin(v) = modstående katete hypotenuse sin ( v) = modstående katete hypotenuse sin(v) = 3 5 = 0, 6 sin ( v) = 3 5 = 0, 6
Diese Formeln erhält man, indem man die Definitionen von Sinus, Kosinus und Tangens je nach b b, a a und c c auflöst. Im ersten Fall, wenn die Hypotenuse c c gegeben ist, geht das wie folgt. \sin\alpha=\dfrac {a} {c}\Rightarrow a=\sin\alpha\cdot c sinα = ca ⇒ a = sinα ⋅c \cos\alpha=\dfrac b c \Rightarrow b=\cos \alpha\cdot c cosα = cb ⇒ b = cosα ⋅c Vérifier Triangle 2 : G H I cos ( G) = Vérifier sin ( G) = Vérifier tan ( G) = Vérifier Un dernier exercice Dans ce triangle, a c est égal à. Choisissez toutes les réponses possibles :
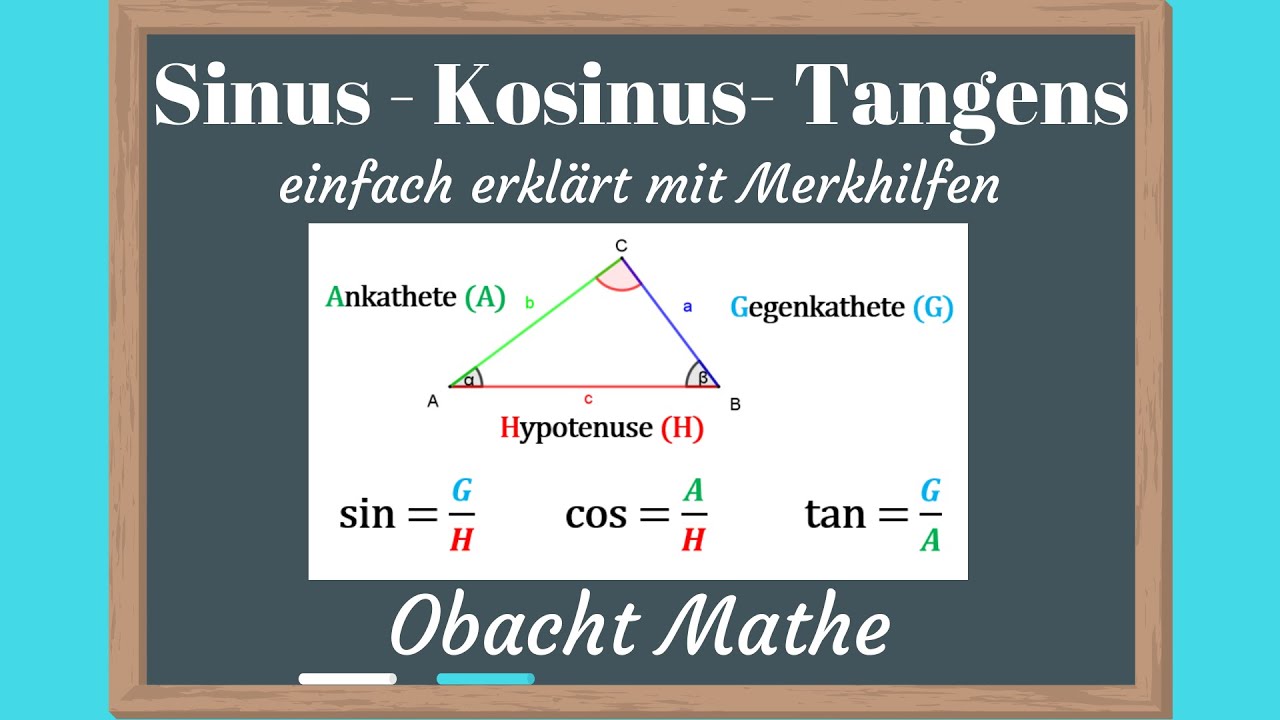
SINUS KOSINUS TANGENS mit Merkhilfen genial einfach&schnell erklärtTrigonometrie
Sinus , Cosinus und Tangens sind trigonometrische Funktionen , mit denen du die Winkel in einem Dreieck berechnen kannst. Beachte, dass du sie nur bei rechtwinkligen Dreiecken anwenden kannst! Sie sind folgendermaßen definiert: Rechtwinkliges Dreieck: sin cos tan In einem rechtwinkligen Dreieck gibt es immer eine lange und zwei kurze Seiten. Sinus, Kosinus und Tangens geben nun unterschiedliche Verhältnisse im Dreieck an: Welche Seiten damit genau gemeint sind, ist von der Lage des betrachteten Winkels abhängig. Mit der Gegenkathete ist immer die Kathete gemeint die sich gegenüber von dem jeweiligen Winkel befindet.




