The crown of your head is located at the very top of your skull. You may also sometimes see it referred to as the vertex. Like other parts of your skull, the crown works to provide protection. Male pattern baldness (androgenic alopecia) is a type of hair loss that affects people assigned male at birth (AMAB). It causes you to lose hair on the skin covering your head (scalp), and your hair doesn't grow back. Other signs of male-pattern baldness include thinning hair and a hairline that moves farther back on your head (receding hairline).
Crown of head Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary
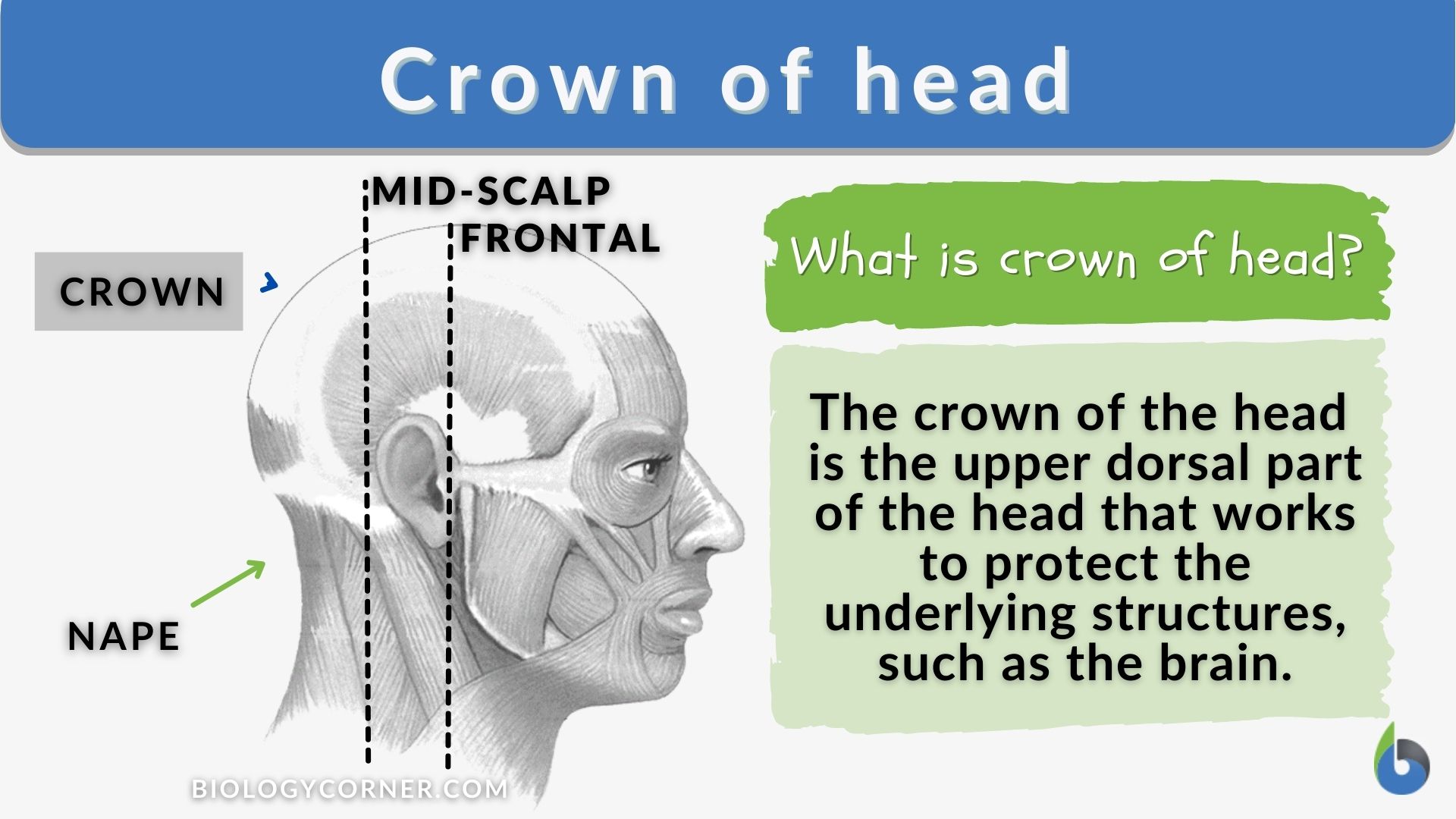
Definition: the area located at the upper dorsal (back) part of the head Table of Contents Crown of Head Definition The crown of the head is the upper dorsal part (or area) of the head. Several creatures have diverse crown anatomy. It consists of the scalp that lies atop the skull, which in humans, consists of five layers. In bird anatomy, the crown is the top of the head, or more specifically the zone from the frons, or forehead, extending posteriorly to the occiput and laterally on both sides to the temples. The upper part of the head, including frons, crown, and occiput, is called the pileum. [7] The crown of the head (vertex) is the topmost part of the scalp, located toward the back of the head.² Its boundaries are the mid-scalp on the front and the occipital and parietal on the sides and the back.³ You can locate the crown of your head by touching your skull's midline and moving your fingers toward the back of your head. Symptoms. Seborrheic dermatitis signs and symptoms may include: Flaking skin (dandruff) on your scalp, hair, eyebrows, beard or mustache. Patches of greasy skin covered with flaky white or yellow scales or crust on the scalp, face, sides of the nose, eyebrows, ears, eyelids, chest, armpits, groin area or under the breasts.

24+ Tips How To Make Crown Of Head MonroMoheeqa
Crown We're guessing you're already familiar with this term, but we'll go ahead and define it for you anyway just to make sure that we're all on the same page. The crown is the highest point on your scalp, toward the back of your head. It's also called the vertex. The more you learn about hair loss, the more you'll see this specific term used. What is occipital neuralgia? Most feeling in the back and top of the head is transmitted to the brain by the two greater occipital nerves. There is one nerve on each side of the head. Overview Hair loss (alopecia) can affect just your scalp or your entire body, and it can be temporary or permanent. It can be the result of heredity, hormonal changes, medical conditions or a normal part of aging. Anyone can lose hair on their head, but it's more common in men. Baldness typically refers to excessive hair loss from your scalp. Occipital neuralgia can cause sudden, sharp and intense pain. Usually, this pain runs along your scalp or feels like a throbbing sensation behind your eye. Occipital neuralgia shares many of the same symptoms as other headache disorders. Treatment options like hot and cold therapy, stretching and massage relieve the pain for many people.

Hair Loss NEU Hair 4 Men
A balding crown is one of the most common and recognisable signs of male pattern baldness (MPB) - or androgenetic alopecia, as it is medically known. This is a condition that many men experience - at any age. Despite the association with older gents, this most common type of hair loss can strike early too. Human head (anterior view) The human head is more than just a nuisance responsible for your headaches. It is a complex anatomical structure weighing up to five kilograms that rests on the bony skull and in turn, the neck.In addition to the evident ears, eyes, nose, and mouth, the head supports a variety of other important structures:. Muscles of mastication
In women, hair thinning at the crown could be a sign of alopecia. Most commonly, there are two types of alopecia: androgenic (or hormonally-triggered hair loss) and alopecia areata (an autoimmune disease), says Deanne Mraz Robinson, MD, FAAD, the chief medical officer of Ideal Image. Front of the Head Back of the Head When to See a Doctor Most people will experience a headache at some point in their life. Determining the type of headache a person has is key to knowing how to manage it best. It's also important for deciding if and when they should seek medical attention.

Man on a White Background Wears a Crown on His Head, in a Photo Studio Stock Photo Image of
Probably not. Head trauma from play or sports is a common concern for parents, but rarely does a bump on the head result in serious injury. The forehead and scalp have an abundant blood supply, and injury to these areas often results in bleeding under the skin. When the bleeding is in just one area, it causes bruising and swelling (hematoma). An uncomplicated closed head injury is a diagnosis of exclusion. If someone has been seen by a physician and more serious types of injury are deemed unlikely, this is a common variation of closed head injury. Rarity: Uncommon. Top Symptoms: head or face injury, face pain, headache resulting from a head injury, scalp pain, new headache




