Lexikon Biologie 2 Äußerer und innerer Bau von Organismen 2.4 Grünalgen 2.4.0 Überblick Euglena Euglena Im Frühjahr sind viele Tümpel, Teiche und Pfützen durch kleine (0,05 mm), bewegliche, spindelförmige, begeißelte Einzeller grün gefärbt („Algenblüte"). Einzeller Euglena Wichtige Inhalte in diesem Video Euglena einfach erklärt (00:14) Euglena Aufbau (00:59) Euglena Lichtorientierung (02:47) Euglena Ernährung (03:32) Euglena Fortpflanzung (04:34) Was die Euglena ist und alles Wichtige über sie zeigen wir dir hier und in unserem Video dazu! Inhaltsübersicht Euglena einfach erklärt

Euglena, Tier oder Pflanze Diagram Quizlet
Zellbiologie Euglena Euglena Konntest du schon einmal beobachten, dass sich kleine Teiche im Garten oder anderswo komplett grün verfärbt haben? In diesen grünen Wassertümpeln fühlt sich ein bestimmter eukaryotischer Einzeller besonders wohl. Der Einzeller Euglena, auch Augentierchen genannt. Inhalt von Fachexperten überprüft Da Euglena sowohl pflanzliche als auch tierische Merkmale zeigt, war früher eine eindeutige Zuordnung zum Pflanzen- oder Tierreich nicht möglich. Lebensweise Die meisten Augentierchen enthalten Chloroplasten mit den grünen Farbstoffen Chlorophyll a und b. Mit ihrer Hilfe betreiben sie Photosynthese (phototrophe Ernährung). Euglenen sind einzellige Geisselträger mit 2 Geisseln, wovon eine meist nicht zu sehen ist. Sie sind je nach Art in sauberen bis stark nährstoffreichen, steh. Form and function When feeding as a heterotroph, Euglena takes in nutrients by osmotrophy, and can survive without light on a diet of organic matter, such as beef extract, peptone, acetate, ethanol or carbohydrates.
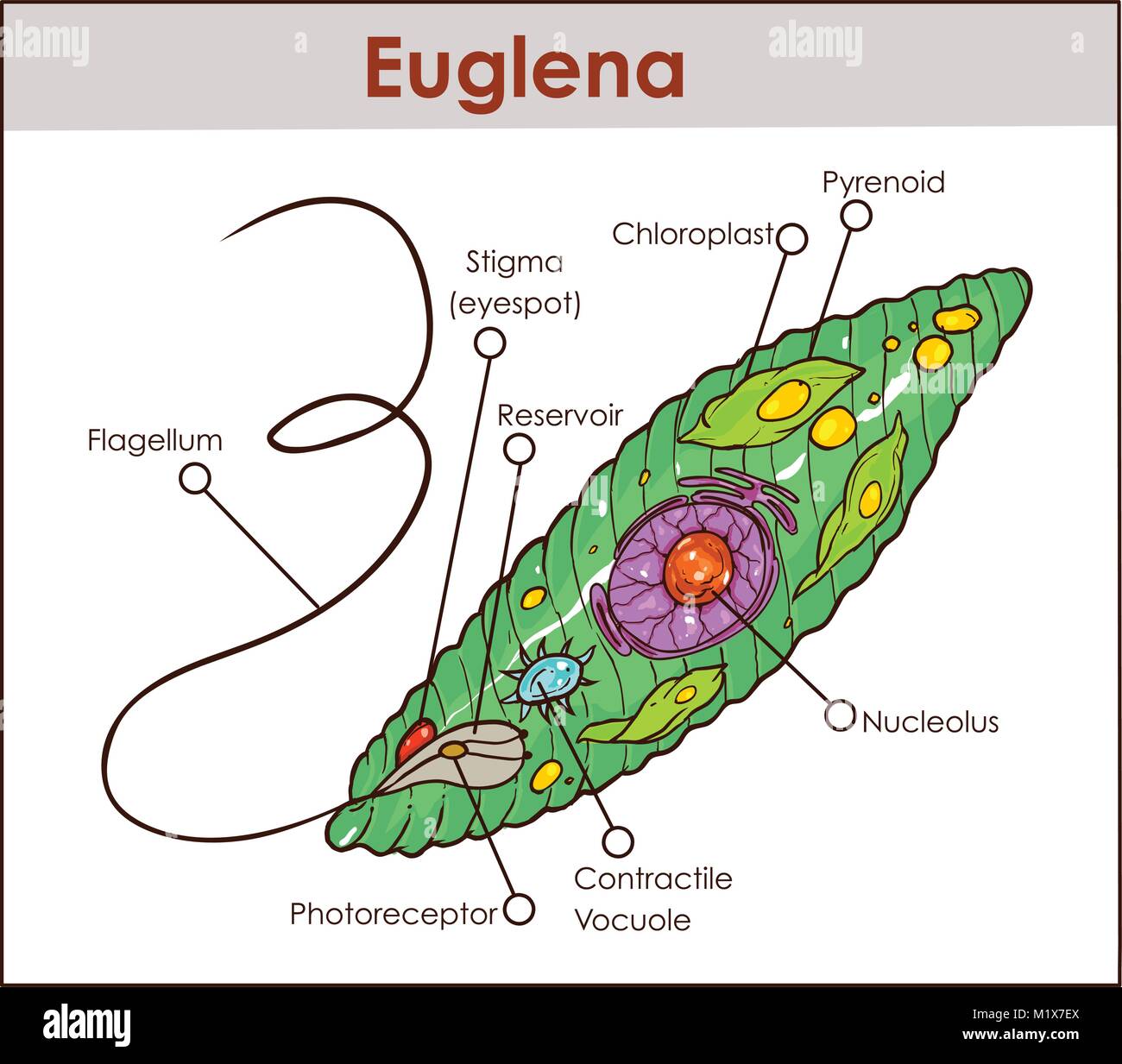
Vektor Euglena Querschnittsdiagramm Vertreter Protisten euglenoid Pflanze wie Tier wie
Wir stellen vor: Die Euglena -Verwandtschaft und ihre aktuelle systematische Einordnung. Das Augentierchen Euglena und seine Verwandten, zu denen rund 40 Gattungen und 800 Arten zählen, sind einzellige Geißelträger ( Flagellaten ), die meist im Süßwasser in so großen Massen vorkommen, dass sie eine Wasserlache grün anzufärben vermögen. Euglena are characterized by an elongated cell (15-500 micrometres [1 micrometre = 10 −6 metre], or 0.0006-0.02 inch) with one nucleus, numerous chloroplasts (cell organelles that contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis), a contractile vacuole (organelle that regulates the cytoplasm), an eyespot, and one or two flagella. 1 Beurteile die folgenden Befunde A, B und C im Hinblick auf die Frage, ob es sich bei Euglena um ein Tier oder eine Pflanze handelt. - Befund A spricht für: Pflanze, da die Orientierung zum Licht typisch für Pflanzen ist (Fotosyn-these). Befund B spricht für: Tier, da freie Ortsbewegung ein eher typisches Merkmal für Tiere ist. Structure. Euglena is a unicellular organism with a complex internal structure that includes a contractile vacuole that can expel water and a red 'eyespot' . Photosynthetic forms contain a chloroplast. They possess two flagellae, one long, one short, which can allow the organisms to move. Euglena are also able to move by means of changing its.

Ist Euglena eine Pflanze oder ein Tier? (Klausur Sek. II)
Euglena is a genus of unicellular, freshwater organisms that are very common in ponds and small bodies of water, especially if they are rich in nutrients and consequently high in algae (aka 'pond scum'). As noted below, Euglena itself is sometimes photosynthetic and is a component of the green sludge in such ponds. But at other times it is non-photosynthetic and is a component of the. Abstract. Human exploration of space and other celestial bodies bears a multitude of challenges. The Earth-bound supply of material and food is restricted, and in situ resource utilisation (ISRU) is a prerequisite. Excellent candidates for delivering several services are unicellular algae, such as the space-approved flagellate Euglena gracilis.
Euglena has a unique, elongated cell structure that measures between 15-500 micrometres. The organism is primarily green due to the presence of chlorophyll pigment. Some Euglena species contain carotenoid pigments, which give them a distinct color, such as red. Euglena is a unicellular organism with a single nucleus. Scientific Classification Structure Euglena is an elongated or spindle-shaped cell with a size around 15-500 x 10 -6 m. Parts Euglena The internal structures found in a typical photosynthetic Euglena are as follows: Pellicle: A thin, flexible membrane that supports the plasma membrane and helps them to change shape
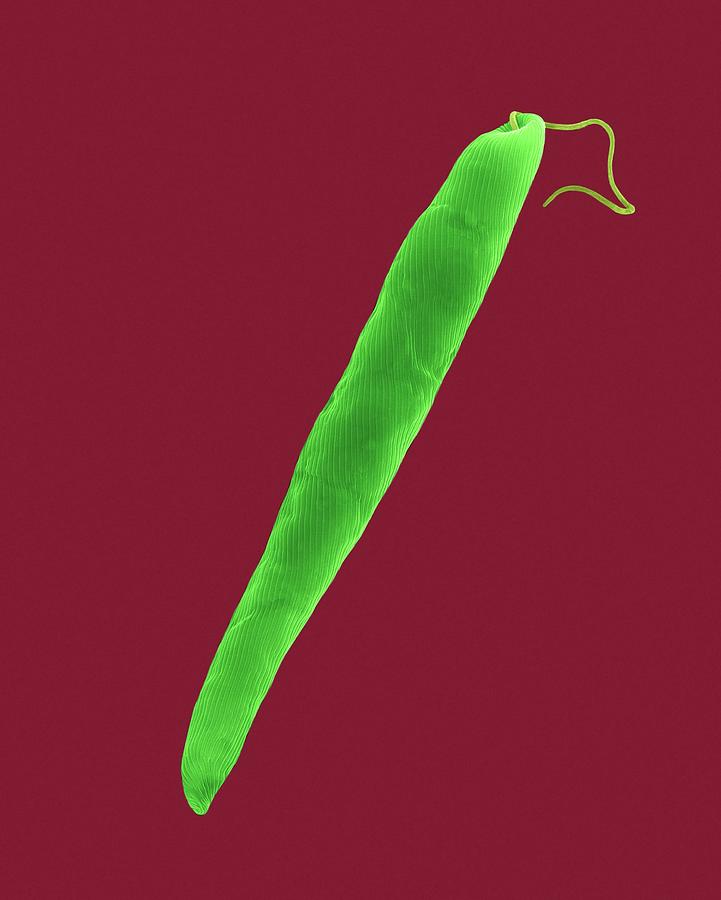
Euglena Gracilis Photograph by Dennis Kunkel Microscopy/science Photo Library Fine Art America
Euglena are tiny protist organisms that are classified in the Eukaryota Domain and the genus Euglena. These single-celled eukaryotes have characteristics of both plant and animal cells. Like plant cells, some species are photoautotrophs (photo-, -auto, -troph) and have the ability to use light to produce nutrients through photosynthesis. Euglena Reproduction. Euglena reproduces asexually by binary fission and there's no evidence of sexual reproduction. In binary fission the nucleus of the parent cell divides by mitosis (part of the cell cycle where DNA is replicated and chromosomes are separated into two nuclei), then the cell begins to divide at the anterior end of the cell, with the duplication of the flagella forming a V.




