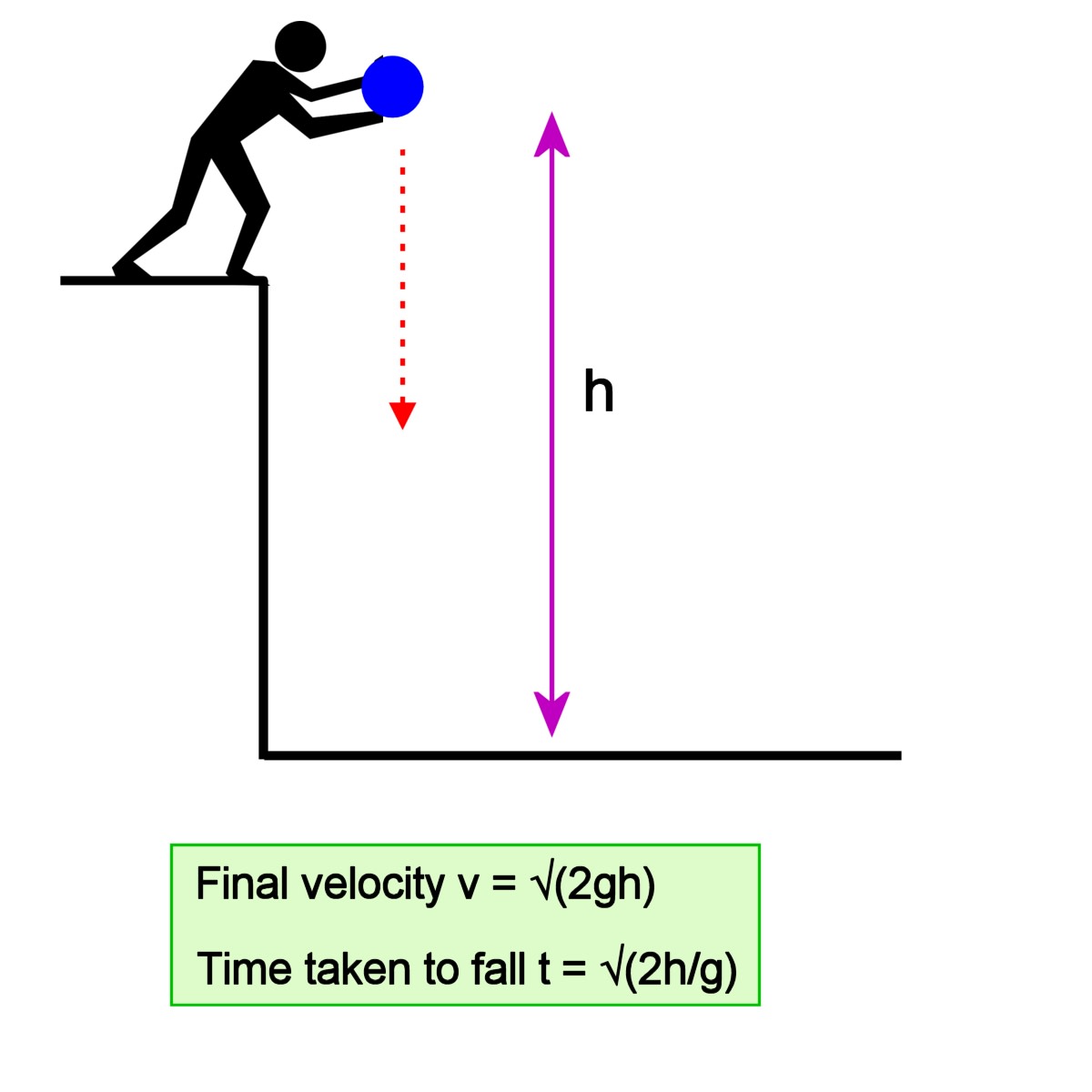
Als Freien Fall bezeichnen wir die Bewegung eines Körpers, der aus einer Anfangshöhe h "einfach losgelassen" wird. Der Körper führt dann eine gleichmäßig beschleunigte Bewegung ohne Anfangsgeschwindigkeit aus. Für die Fallzeit des Körpers gilt t F = 2 ⋅ h g. Wenn du die Animation in Abb. 1 startest, so wird ein Körper aus einer. Freier Fall einfach erklärt. Unter dem freien Fall verstehst du in der Physik, wenn ein Körper in Richtung des Erdmittelpunkts fällt. Seine Fallbewegung ist dabei geradlinig und gleichmäßig beschleunigt. Auf einen Körper im freien Fall wirken keine Kräfte, bis auf die Gewichtskraft. Die Gewichtskraft bewirkt eine Beschleunigung, die.

Der freie Fall Beispielaufgabe, Höhe Geschwindigkeit & Fallzeit berechnen (Physik) YouTube
Freier Fall. Die Fallbewegung eines Körpers, die nicht durch den Luftwiderstand behindert wird, nennt man freien Fall. Der freie Fall ist eine gleichmäßig beschleunigte geradlinige Bewegung, wobei die Beschleunigung gleich der Fallbeschleunigung g am jeweiligen Ort ist. Physik. In diesem Video erklären wir dir, was der freie Fall ist und wie man ihn berechnet. ⭐️⭐️Weitere Lernvideos und tolle Übungen⭐️⭐️ zu dem Thema, findest du hie. Freier Fall in stroboskopischer Mehrfachbelichtung: Der Ball fällt ab der zweiten Zeitspanne um jeweils zwei Längen mehr als in der vorherigen Zeitspanne (konstante Beschleunigung). Die Gesamtstrecke wächst wie + + +.. Der freie Fall ist in der klassischen Mechanik die Bewegung eines Körpers, bei der außer der Schwerkraft keine weiteren Kräfte wirken. Free fall. In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where gravity is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it. An object in the technical sense of the term "free fall" may not necessarily be falling.
Solving Projectile Motion Problems — Applying Newton's Equations of Motion to Ballistics Owlcation
On the Web: freefall, in mechanics, state of a body that moves freely in any manner in the presence of gravity. The planets, for example, are in free fall in the gravitational field of the Sun. An astronaut orbiting Earth in a spacecraft experiences a condition of weightlessness because both the spacecraft and the astronaut are in free fall. Free Fall. Decide on the sign of the acceleration of gravity. In Equation 3.15 through Equation 3.17, acceleration g is negative, which says the positive direction is upward and the negative direction is downward. In some problems, it may be useful to have acceleration g as positive, indicating the positive direction is downward.; Draw a sketch of the problem. There are two important motion characteristics that are true of free-falling objects: Free-falling objects do not encounter air resistance. All free-falling objects (on Earth) accelerate downwards at a rate of 9.8 m/s/s (often approximated as 10 m/s/s for back-of-the-envelope calculations) Because free-falling objects are accelerating downwards. An interesting application of Equation 3.3.2 through Equation 3.5.22 is called free fall, which describes the motion of an object falling in a gravitational field, such as near the surface of Earth or other celestial objects of planetary size.Let's assume the body is falling in a straight line perpendicular to the surface, so its motion is one-dimensional.
Freier Fall einfach erklärt 1a [Mit 2 Videos + Beispiele]
The two quantities are independent of one another. Light objects accelerate more slowly than heavy objects only when forces other than gravity are also at work. When this happens, an object may be falling, but it is not in free fall. Free fall occurs whenever an object is acted upon by gravity alone. Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page describes how this can be done for situations involving free fall motion.
This physics video tutorial focuses on free fall problems and contains the solutions to each of them. It explains the concept of acceleration due to gravity. Der freie Fall ist ein auch historisch bedeutsamer Spezialfall der eindimensionalen, gleichmäßig beschleunigten Bewegung.Dabei bewegt sich ein Massenpunkt oder Körper nur unter dem Einfluss der von der Schwerenanziehung der Erde, also, wie der Name schon andeutet, nach unten. Der Luftwiderstand wird beim freien Fall vernachlässigt. Unter dieser Voraussetzung gilt die wichtige physikalische.

FreierFall erklärung und alle Formeln + Online Rechner Simplexy
The acceleration of free-falling objects is referred to as the acceleration due to gravity gg. As we said earlier, gravity varies depending on location and altitude on Earth (or any other planet), but the average acceleration due to gravity on Earth is 9.8 m s2 m s 2. This value is also often expressed as a negative acceleration in mathematical. Freier Fall Physik - Das Wichtigste. Freier Fall in der Physik ist eine unter der Schwerkraft gleichmäßig beschleunigte Bewegung. Erdbeschleunigung bestimmt die Geschwindigkeit und Höhe im freien Fall. Die Geschwindigkeit im freien Fall berechnet sich durch die Formel: v = g ⋅ t. Die Höhe im freien Fall berechnet sich durch die Formel: h.




