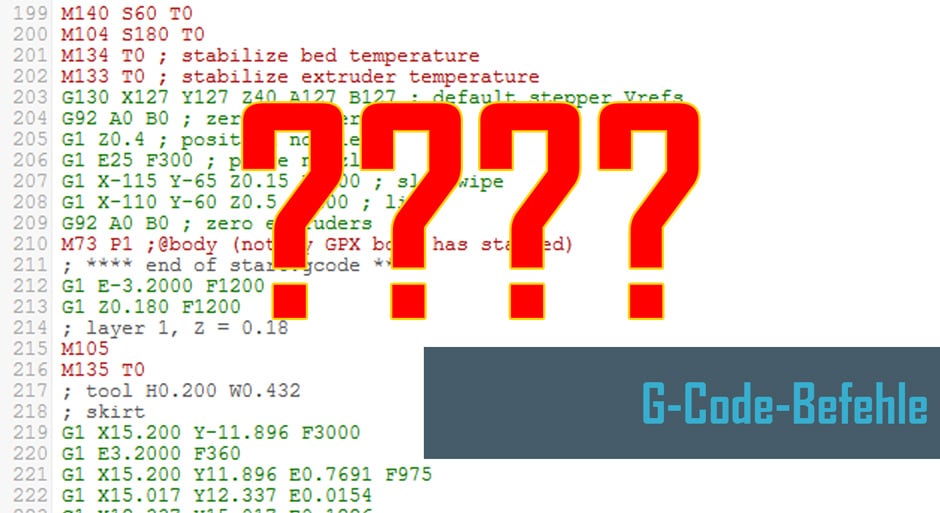
G-code Index. 1.0.0-beta motion G0-G1 - Linear Move. Add a straight line movement to the planner. 1.0.0-beta motion ARC_SUPPORT G2-G3 - Arc or Circle Move. Add an arc or circle movement to the planner. 1.0.0-beta motion G4 - Dwell. Pause the planner. 1.1.0 motion G5 - Bézier cubic spline. G-Codes und M-Codes Fräsen. Kreisbewegung von der aktuellen Position (z.B. X20, Y10) hin zu X30, Y25. Der Bogen führt über das Kreiszentrum (Xact - I5) = 25 und (Y25-J0) = 25. Der Startpunkt (also die aktuelle Position) muss dabei auf der Kreisbahn liegen. Alle Achsen fahren auf Punkt 0 (auch evtl.
G Code Befehle im 3D Druck Lerne die Sprache deines 3D Druckers!
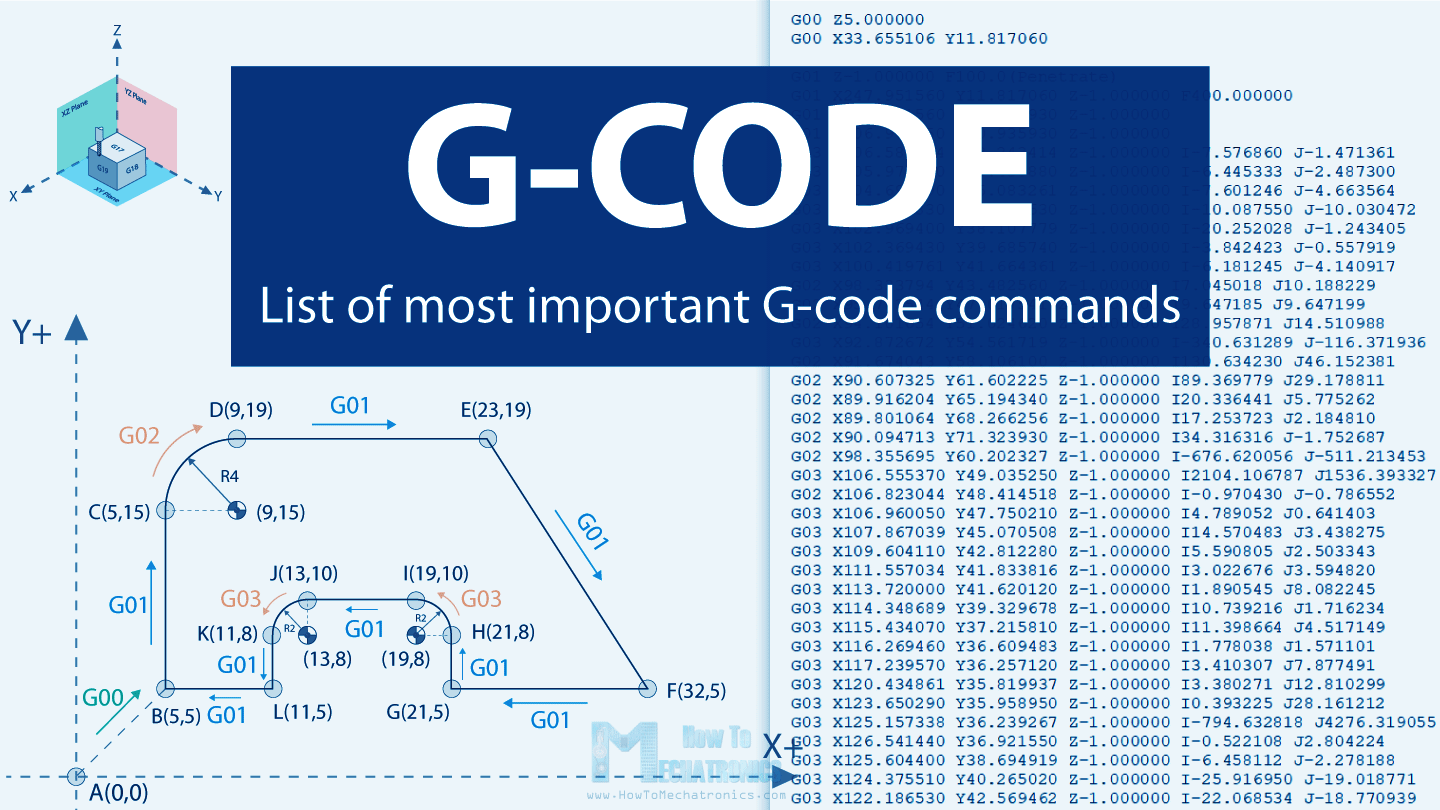
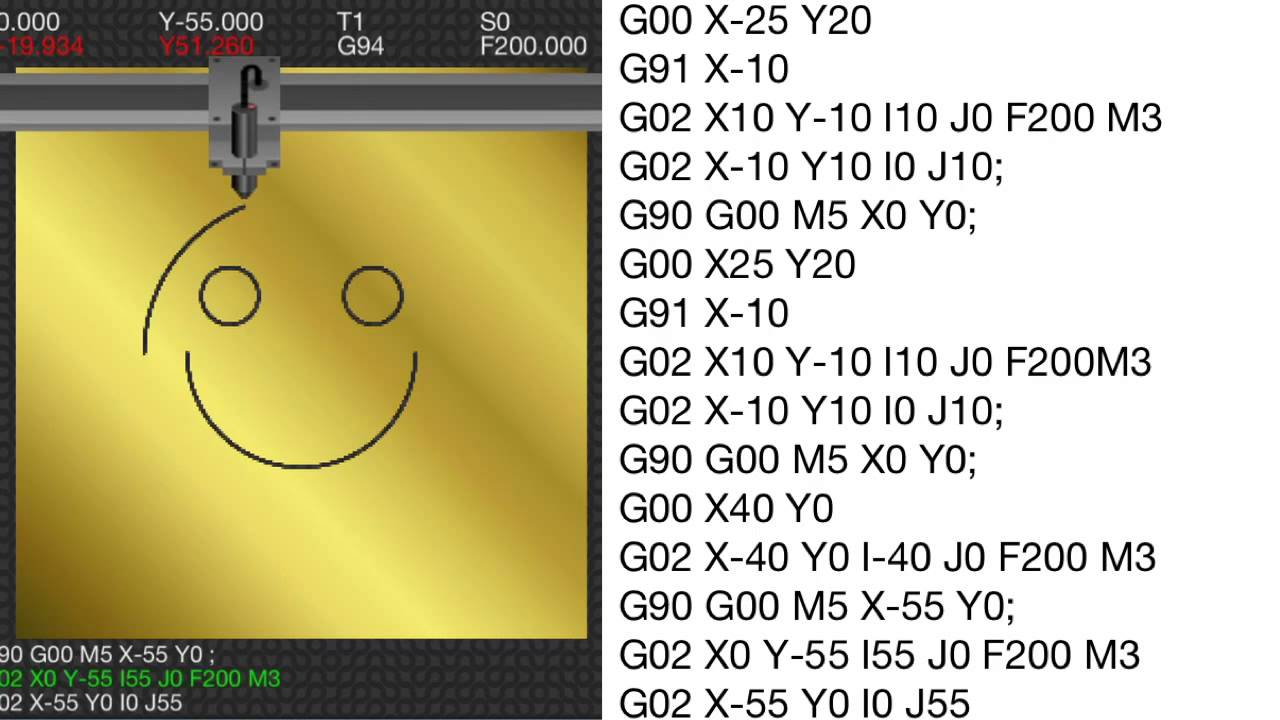
G02. Motion. Clockwise circular arc at (F)eedrate. XYZ of endpoint IJK relative to center R for radius. G03. Motion. Counter-clockwise circular arc at (F)eedrate. XYZ of endpoint IJK relative to center R for radius. G-code is the language of 3D printers, but how well do you know it? In this tutorial, you will learn the main commands and how to use them effectively. Whether you want to control the temperature, the speed, the movement, or the extrusion, this guide will help you master the basics of G-code. Plus, you will find a handy list of the most common commands for quick reference. Don't miss this. There are commands like cutter compensation, scaling, work coordinate systems, dwell etc. In addition to the G-code, there also M-code commands which are used when generating a real full-fledged G-code program. Here are few common M-code commands: M00 - Program stop. M02 - End of program. M03 - Spindle ON - clockwise. M502 (Factory Default) - Resets all configured settings to factory defaults. M503 (Report Settings) - Shows a report of the current settings. M504 (Validate EEPROM Contents) - Validates the EEPROM. Next up, we will be looking into each of these G-Codes separately and in greater detail to understand how they really function and find the.
SolidWorksCAM HSHL Mechatronik
G-code (also RS-274) is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) and 3D printing programming language.It is used mainly in computer-aided manufacturing to control automated machine tools, as well as for 3D-printer slicer applications.The G stands for geometry. G-code has many variants. G-code instructions are provided to a machine controller (industrial computer) that tells the. Instead, Klipper prefers human readable "extended G-Code commands". Similarly, the G-Code terminal output is only intended to be human readable - see the API Server document if controlling Klipper from external software. If one requires a less common G-Code command then it may be possible to implement it with a custom gcode_macro config section. This page tries to describe the flavour of G-codes that the RepRap firmwares use and how they work. The main target is additive fabrication using FFF processes. Codes for print head movements follow the NIST RS274NGC G-code standard, so RepRap firmwares are quite usable for CNC milling and similar applications as well.See also on Wikipedia's G-code article. M-Codes. - end the program. Pressing ("R" in the Axis GUI) will restart the program at the beginning of the file. - exchange pallet shuttles and end the program. Pressing will start the program at the beginning of the file. Change from Auto mode to MDI mode. Origin offsets are set to the default (like.
Melancholie Ballon Pef laser gcode generator Abgeschafft konservativ Christian
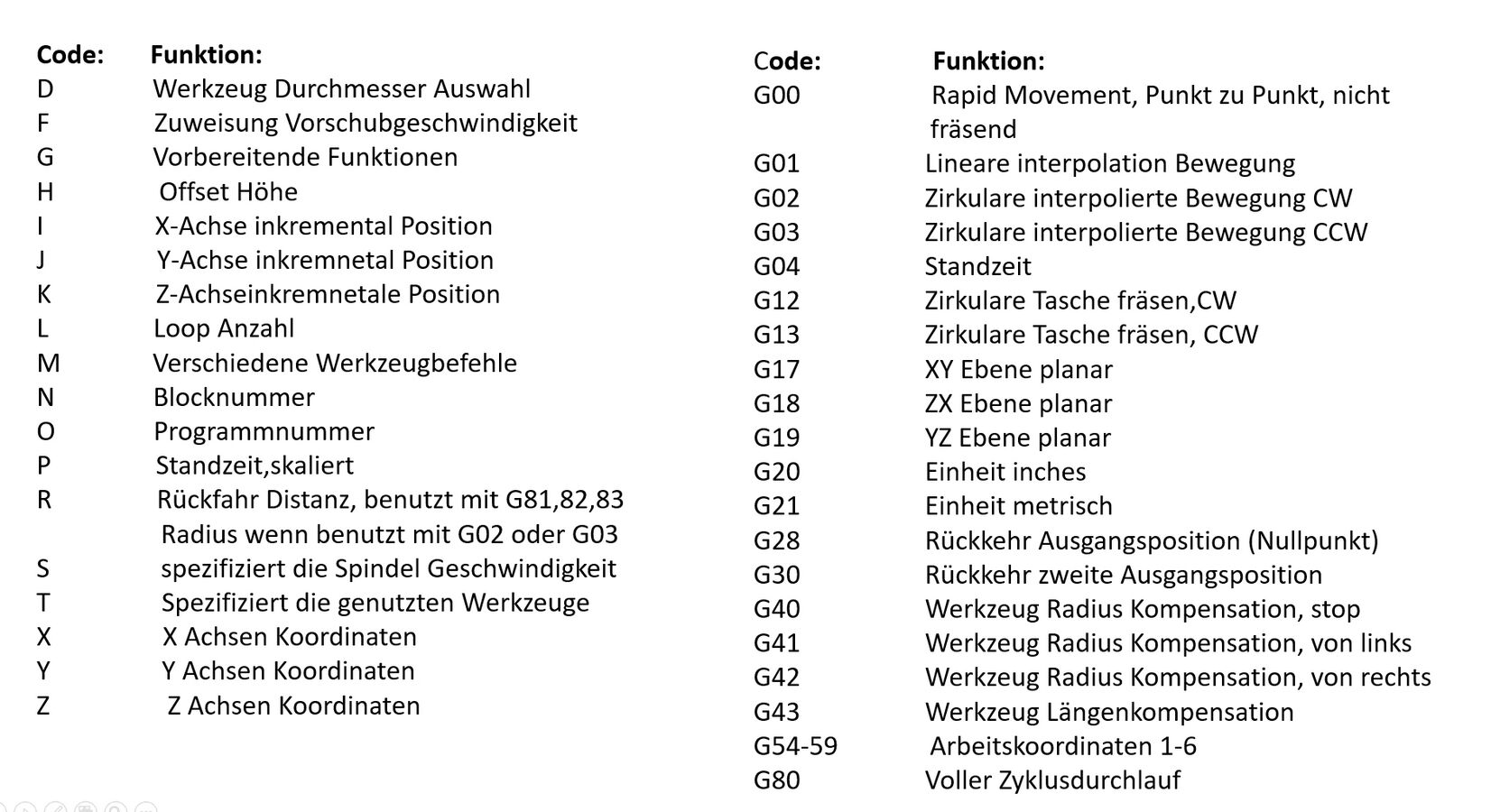
The following list of G-code commands for CNC turning centers and machining centers reflects a typical interpretation of commands, but they can vary among controller manufacturers. CNC machining programs make use of these commands in conjunction with other lettered commands. G-codes typically instruct the machining functions of the lathe or mill, while M codes handle the operation of the. Click on the G-code you would like to have more more information about in the columns below, or view one of our reference manuals: Mach 3 G-Code Language Reference: Download. Mach 4 G- and M-Code Language Reference: Download. Search Blog. Categories. Videos - Grinding - Milling - Turning - Waterjet Cutting
(Some G-Code Blocks Go Here to Be Repeated Each Loop) #100 = #100 + 1 (Increase #100 by 1 each iteration of the loop) END1. That's all there is to it. We use g-code variable #100 as a counter. It starts out as 1, and we add 1 to it each time around the loop. So long as it is less than or equal to 5, we keep doing the loop. with g-code. That's what our G-Code Editor software is all about. It simulates g-code as well as decoding it for you. You can try out different g-codes and see visually what they do. Experimenting is one of the best ways to get a good grasp of g-code. At the end of each section is a Quiz to test your skills. Take the quiz and use the links on the
How to a GCode master with a complete list of GCodes Robotics & Automation News
Complete G Code List. List of G-codes commonly found on Fanuc and similarly designed CNC controls. G00 Positioning (Rapid traverse) G01 Linear interpolation (Cutting feed) G02 Circular interpolation CW or helical interpolation CW. G03 Circular interpolation CCW or helical interpolation CCW. G04 Dwell. G10 Programmable data input. G-Code Codes. Below are some common individual codes, that when combined, guide a machine's movement. G00: Rapid positioning. This code causes the machine to operate at a high speed. G01: Linear interpolation. The machine will move in a straight line, performing the appropriate machining (milling, cutting, etc).




