The Michaelis-Menten equation (see below) is commonly used to study the kinetics of reaction catalysis by enzymes as well as the kinetics of transport by transporters. Typically, the rate of reaction (or reaction velocity) is experimentally measured at several substrate concentration values. The range of substrate concentrations is chosen such that very low reaction rates as well as saturating. The Michaelis-Menten equation, named after biochemist Leonor Michaelis and physician Maud Menten, "describes the relationship between the rate of substrate conversion by an enzyme (V) and the concentration of the substrate ([S])," according to the Davidson College Chemistry website. Based on this equation, the Michaelis-Menten curve can be.

grafico MichaelisMenten Bald Mountain Science
Page ID. Two 20 th century scientists, Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten, proposed the model known as Michaelis-Menten Kinetics to account for enzymatic dynamics. The model serves to explain how an enzyme can cause kinetic rate enhancement of a reaction and explains how reaction rates depends on the concentration of enzyme and substrate. Michaelis-Menten kinetics. In biochemistry, Michaelis-Menten kinetics, named after Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten, is the simplest case of enzyme kinetics, applied to enzyme-catalysed reactions of one substrate and one product. It takes the form of an equation describing the reaction rate (rate of formation of product P, with. In biochemistry, the direct linear plot is a graphical method for enzyme kinetics data following the Michaelis-Menten equation. [1] In this plot, observations are not plotted as points, but as lines in parameter space with axes and , such that each observation of a rate at substrate concentration is represented by a straight line with. The Michaelis-Menten mechanism (Michaelis & Menten, 1913) is one which many enzyme mitigated reactions follow. The basic mechanism involves an enzyme ( E, a biological catalyst) and a substrate ( S) which must connect to form an enzyme-substrate complex ( ES) in order for the substrate to be degraded (or augmented) to form a product ( P ).

MichaelisMenten MichaelisMenten plot of MpIspS initial... Download Scientific Diagram
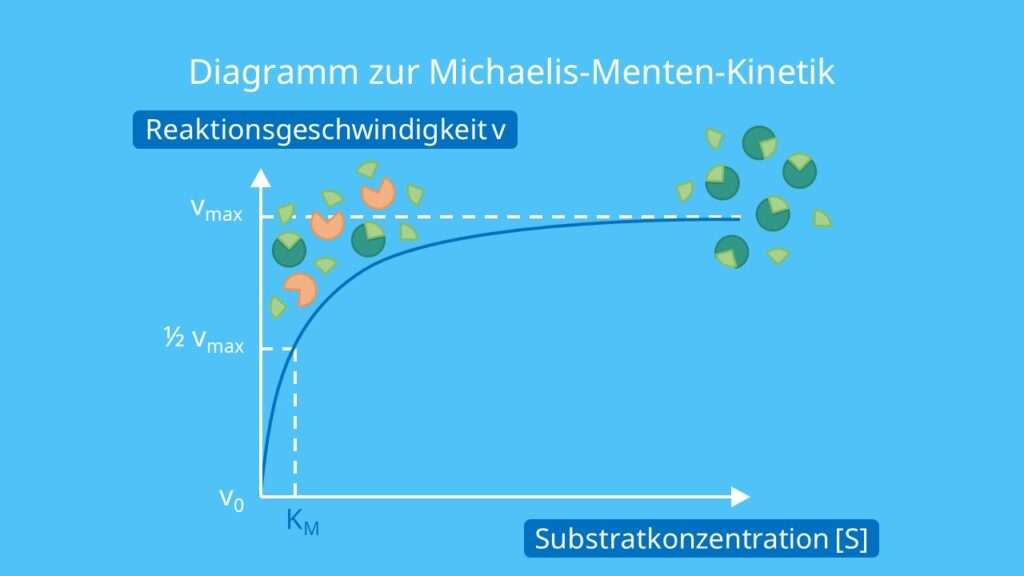
Michaelis-Menten derivation for simple steady-state kinetics. The Michaelis-Menten equation is a mathematical model that is used to analyze simple kinetic data.The model has certain assumptions, and as long as these assumptions are correct, it will accurately model your experimental data.The derivation of the model will highlight these assumptions. The Michaelis-Menten mechanism (Michaelis & Menten, 1913) is one which many enzyme mitigated reactions follow. The basic mechanism involves an enzyme ( E E, a biological catalyst) and a substrate ( S S) which must connect to form an enzyme-substrate complex ( ES E S) in order for the substrate to be degraded (or augmented) to form a product ( P. Michaelis and Menten equation (MM equation) has dominated biochemistry for more than a century after its seminal introduction in a paper published in 1913 in the journal Biochemische Zeitschrift, a predecessor of FEBS Journal [[]].Hence, publishing this guide in FEBS Journal would represent an apt dedication to the unmatched service rendered by this journal to the scientific community for more. The reaction is zero-order kinetics. Figure 5.3.2: Diagram of reaction velocity and Michaelis-Menten kinetics. v = Vmax 2 = Vmax[S] Km + [S] (5.3.17) (5.3.17) v = V m a x 2 = V m a x [ S] K m + [ S] Therefore, Km K m is equal to the concentration of the substrate when the rate is half of the maximum velocity.
MichaelisMentenGleichung · einfach erklärt Formel [mit Video] · [mit Video]
STEP 3: Plot Michaelis Menten Graph with Calculated Velocity. To plot the graph, you need to select the values of Concentration and corresponding Velocity. Here, we have selected the range B4:C14. After that, go to the Insert tab and click on the Insert Scatter icon. A drop-down menu will appear. Km is the Michaelis-Menten constant, in the same units as X. It is the substrate concentration needed to achieve a half-maximum enzyme velocity. Create a Lineweaver-Burk plot. Before nonlinear regression was available, investigators had to transform curved data into straight lines, so they could analyze with linear regression. One way to do.
This short video shows you how to set up the Michaelis-Menten model in Excel to model the creation of product as a function of substrate concentration. The NLFit dialog is an interactive tool which allows you to monitor the fitting procedure during the non-linear fitting process. This tutorial fits the Michaelis-Menten function, which is a basic model in Enzyme Kinetics, and shows you some basic features of the NLFit dialog. During the fitting, we will illustrate how to perform a Global Fit.
Physikalische Chemie
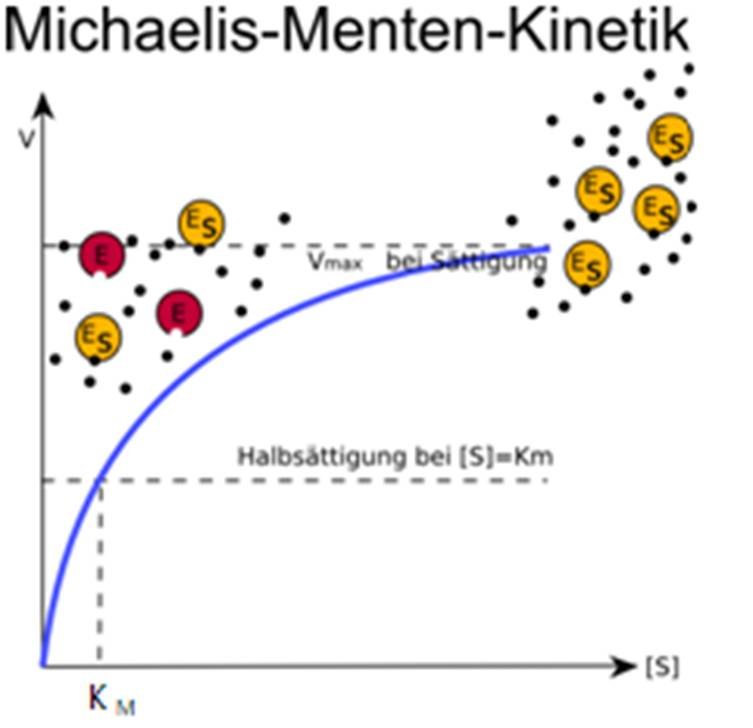
Step 4: Format the Scatter Plot. Next, format the scatter plot to turn it into a Michaelis-Menten plot. First, remove the vertical axis and format the horizontal axis to become a logarithmic scale. This can be done by right-clicking the horizontal axis and selecting "Format Axis.". Then, select "Logarithmic Scale" under the "Scale. In this article we will discuss about the Michaelis-Menten Constant and Significance of Michaelis-Menten Constant.. Michaelis-Menten Constant: In an enzyme catalysed reaction when there is large excess of substrate and the enzyme concentration is held constant, if substrate concentration (S) is plotted against velocity (V) or reaction rate, a hyperbolic curve is obtained (fig. 10.13).




