It talks about completed, sequential or one-time actions that took place on a specific occasion. Use the passé composé to: answer the question que s'est-il passé? - what happened? Example: J'ai reçu un appel. express a past action that happened on a specific occasion (usually with a specific time marker) Example: Imparfait details what used to happen on a regular basis, or happened an indefinite number of times. Passé composé expresses what happened a specific number of times. Ongoing vs New Imparfait indicates an ongoing state of being or feeling. Passé composé reports a change in a state of being, a new feeling. All in the past vs Relevance to present

Do your students struggle with knowing when and how to use the passe composé versus the
Phrases Textes Passé composé ou imparfait ? - Chansons Passé composé / Imparfait Discrimination formelle et prononciation Passé composé Imparfait Présent Système verbal du passé L'alternance passé composé / Imparfait : Observation Le passé composé L'imparfait Comprendre l'actualité Parler des vacances passées The passé composé is a French tense used for the past. The passé composé corresponds mostly to the English simple past or the present perfect. The passé composé describes specific actions that were completed in the past : Dans ma jeunesse, une fois, je suis allée au Canada - In my youth, once, I went to Canada. Click to Post The imparfait, or imperfect past, is used to describe conditions and continual/repeated actions, which we'll explain in greater depth later on. First, let's look at how to form the imparfait. Conjugating (Most) Verbs in the Imparfait The imparfait isn't difficult to conjugate. Le passé composé est le plus souvent utilisé dans la langue parlée tandis que l'on emploie le passé simple surtout dans la langue écrite. Exemple : Mais un jour, pendant que je parlais avec un agriculteur, j' ai reçu un appel. (Passé composé) → Mais un jour, pendant que je parlais avec un agriculteur, je reçus un appel. (Passé simple)
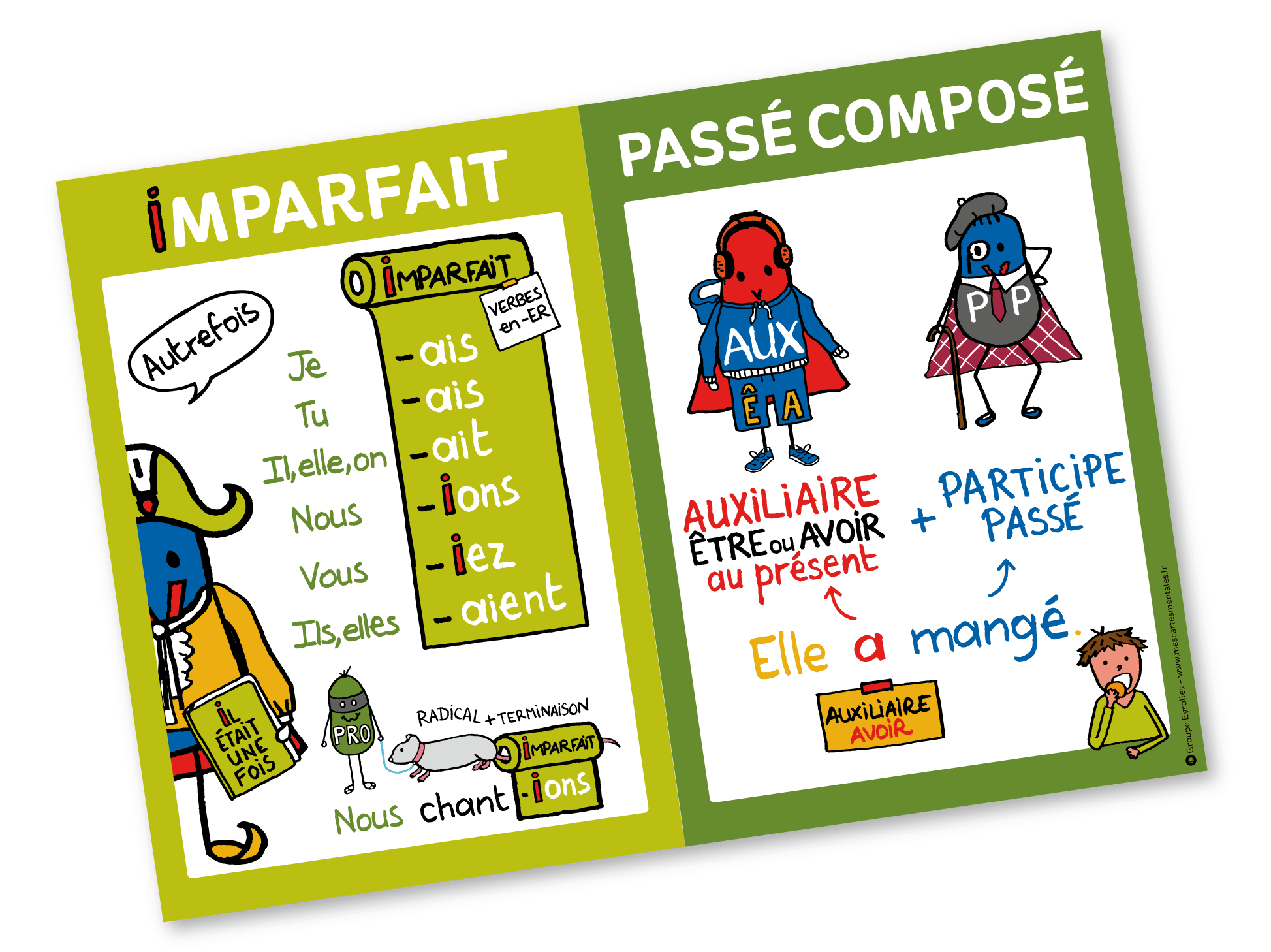
Imparfait / passé composé Affiche format A2
Meanwhile, l'imparfait is more like the progressive past / continuous past. En 2012, je vivais en France. = In 2012, I was living in France. That's the main technique you can use to quickly decide whether to use the passé composé or l'imparfait. Both tenses are very common in both written and especially spoken French. Knowing whether to use the passé composé or imparfait is particularly difficult when translating certain verbs into French. Before reading this lesson, be sure you understand the basics of passé composé vs imparfait. Very broadly speaking, the French imperfect is equivalent to the English past progressive (was/were + ___ing), but some. It's important to note that the passé composé is formed using the auxiliary verb "avoir" (to have) followed by the past participle of the main verb. The imparfait, on the other hand, is formed by taking the nous form of the present tense and adding the following endings: -ais, -ais, -ait, -ions, -iez, -aient. To summarize, use the. Here Le Passé Composé (Indicatif) is used to express a sudden action that interrupts or "cuts" an ongoing action, a habit or repeated action in L'Imparfait (Indicatif). Il faisait froid hier soir. It was cold last night. -> Here, I'm stating that it was cold during the night, insisting on the fact that this situation was ongoing then.

On parle français Le passé composé vs l’imparfait
Knowing whether to use passé composé or imparfait sometimes depends on the meaning of the verb itself. Before reading this lesson, be sure you understand the basics of passé composé vs imparfait. Seven French verbs have different meanings in the passé composé and imparfait. avoir - to have Imperfect = "had" Generally, the Passé Composé is used to relate events while the Imparfait is used to describe what was going on in the past, states of being in the past, or past. 5 Imparfait ou Passé Composé?-French - Learn French [ Test] Imparfait ou Passé Composé? Mettez le verbe soit à l'imparfait,soit au passé- composé. Bonne Chance.
Il/elle était. He/she was. Nous étions. We were. Vous étiez. You were. Ils/elles étaient. They were. Learn the rules of the passé composé vs. imparfait so you can form and correctly use the two most common past tenses in French. Résumé des différences entre imparfait et passé composé; Usages de l'imparfait Exemples contextuels Usages du passé composé Exemples contextuels; Habitual past actions: Je faisais du surf tous les jours. Single past actions: Il a dîné chez Carole la semaine dernière. Description of past state: Il y avait beacoup d'élèves dans mon.

WK 6 Le passé composé vs imparfait Diagram Quizlet
Generally, the passé composé is used to relate events while the imparfait is used to describe what was going on in the past, states of being in the past, or past habits. All this takes on special importance in narration of past actions, when both tenses often occur in the same story. The passé composé is the most important past tense in French. It corresponds to the English simple past. The passé composé talks about actions that were completed in the past and emphasises their results or consequences in the present. Learn about the passé composé with Lingolia's examples, then check your knowledge in the free exercises.




