Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, also known as Binswanger disease or small vessel dementia, refers to slowly progressive, nonhereditary, exclusively white-matter vascular dementia. Clinical presentation Patients usually present with subcortical dementia symptoms including forgetfulness, personality and emotional changes. Die subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie (SAE, Synonyme: Morbus Binswanger, Binswanger-Krankheit, vaskuläre Enzephalopathie) ist eine durch Gefäßveränderungen ( Arteriosklerose) hervorgerufene Erkrankung des Gehirns ( Enzephalon ), die unterhalb der Großhirnrinde ( Cortex ), also subkortikal zu Schädigungen ( Pathologien) führt.

OHB EN EL SINDROME FRONTAL SUBCORTICAL POR ENFERMEDAD DE PEQUEÑAS ARTERIAS CON LEUCOARAIOSIS
Binswanger's disease, also known as subcortical leukoencephalopathy and subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy, is a form of small-vessel vascular dementia caused by damage to the white brain matter. White matter atrophy can be caused by many circumstances including chronic hypertension as well as old age. This disease is characterized by loss of memory and intellectual function and by. Definition Der Morbus Binswanger ist die häufigste Form einer vaskulären Demenz. Es handelt sich um eine subkortikale, arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie bei bestehender arterieller Hypertonie und nachfolgender Mikroangiopathie . Ätiopathogenese Bei der subkortikalen arteriosklerotischen Enzephalopathie (SAE) handelt es sich um eine Erkrankung des Gehirns, die durch Gefäßveränderungen wie Arterienverkalkung ( Arteriosklerose) entsteht. Dabei kommt es im subkortikalen Bereich unter der Großhirnrinde zu Schädigungen. Postmortem examination disclosed the vascular alterations and diffuse white matter degeneration which characterize subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE) or Binswanger's disease. The case underscores the need to consider vascular disease as an etiology of dementia -- even in the absence of focal neurological deficit. eLetters
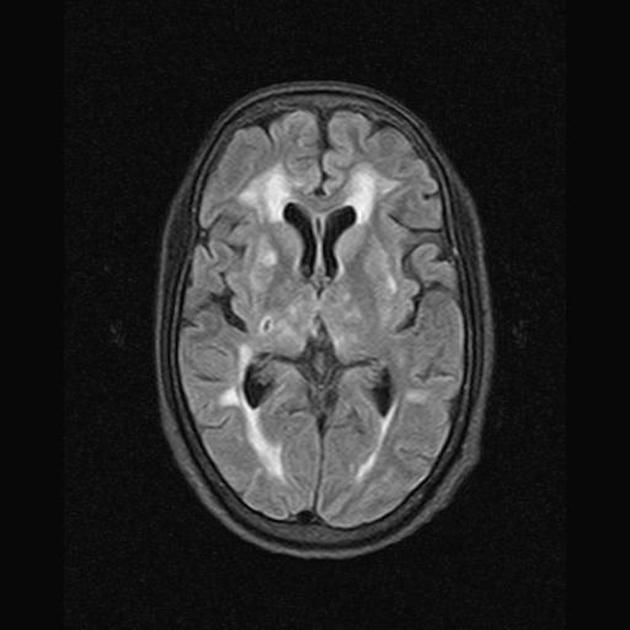
Subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie pacs
Because of recent papers suggesting that subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE) (Binswanger's disease) is more common than historically assumed, this investigation was initiated to assess the frequency of SAE, to gauge the reliability of CT in making this diagnosis, and to assess the strength of the correlation between SAE and arterial hypertension. Of 202 autopsied patients in a 17. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy is a chronic vascular dementia with hydrocephalus characterized clinically by: (i) subacute focal neurological deficit; (ii) acute strokes; (iii) dementia; (iv) motor signs and pseudobulbar palsy; (v) hydrocephalus; (vi) persistent hypertension and systemic vascular disease; and (vii) a lengthy course. Because of recent papers suggesting that subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE) (Binswanger's disease) is more common than historically assumed, this investigation was initiated to assess the frequency of SAE, to gauge the reliability of CT in making this diagnosis, and to assess the strength of the correlation between SAE and arteria. Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE) is a chronic progressive form of brain blood supply deficiency. Risk factors for SAE development were studied in 65 patients (42 men and 23 women, mean age 60.5 +/- 7.5 years). A control group included 31 patients (17 men and 14 women, mean age 59.3.

SAE (Subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie) Psychische Störungebilder YouTube
Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy disease is a sometimes dementing illness for which chronic arterial hypertension has been implicated as a major pathogenetic factor. It had been considered to be rare, but recent reports suggest that it is fairly common. Symptome: Gedächtnis-, Sprach-, Denk- und Bewegungsstörungen, Orientierungsschwierigkeiten, Stimmungsauffälligkeiten Der Verlauf der Krankheit hängt von der Anzahl, Schwere und Lokalisation der Schädigungen ab. Symptome der vaskulären Demenz
Die subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie (SAE, Synonym: Morbus Binswanger) ist eine durch Gefäßveränderungen (Arteriosklerose) hervorgerufene Erkrankung des Gehirns (Enzephalopathie), die Gehirnbereiche unterhalb der Großhirnrinde (Cortex) betrifft (subkortikal).Zuerst wurde sie von dem Schweizer Nervenarzt Otto Ludwig Binswanger (1852-1929) in Jena beschrieben. Since pathologico-anatomically identified severe arteriosclerotic changes of the long medullary arteries are most probably the cause of the hypoxically conditioned diffuse vacuolous demyelinisation of the medullaries, computerised tomography yields an important indirect pointer to the condition of the cerebral vascular periphery. : The article reports on 38 patients with subcortical.
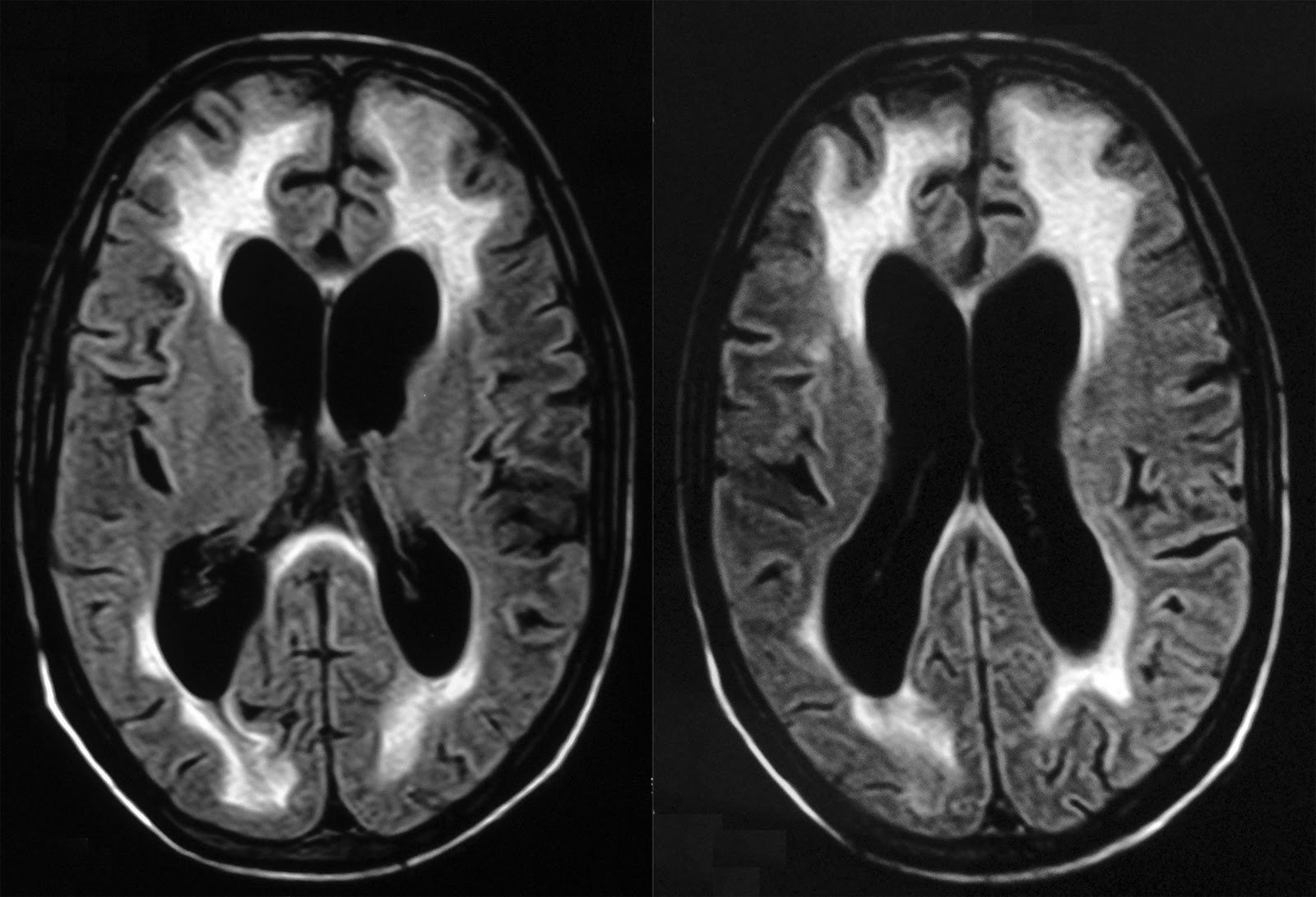
Radiodiagnosis Imaging is AmazingInteresting cases HIV Encephalopathy MRI
Aus pathoanatomischer Sicht ist die subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie wahrscheinlich mit einer zerebralen Mikroangiopathie verbunden, die zu einem Status lacunaris und demyelinisierenden Läsionen des Marklagers führt. Hirnstammlakunen sind nur selten im CT nachweisbar. Die subkortikale arteriosklerotische Enzephalopathie (SAE, Synonym: Morbus Binswanger oder auch Multiinfarkt-Demenz) ist eine durch Gefäßveränderungen ( Arteriosklerose) hervorgerufene Erkrankung des Gehirns ( Enzephalopathie ), die Gehirnbereiche unterhalb der Großhirnrinde ( Cortex) betrifft ( subkortikal ). Zuerst wurde sie von dem.




