Grammar & Usage Commonly Confused When To Use 'Then' and 'Than' Here's how to keep them straight. What to Know Than is used in comparisons as in "she is younger than I am" and "he is taller than me". Quick summary Then and than are homophones that sound alike but have different meanings. Then can function as an adjective, adverb, or noun, and indicates time or consequence. Than is a conjunction or preposition used to indicate comparison. Then and than are among the 100 most frequently used words in the English language.

Then vs. Than How to Use Than vs. Then Correctly? Confused Words
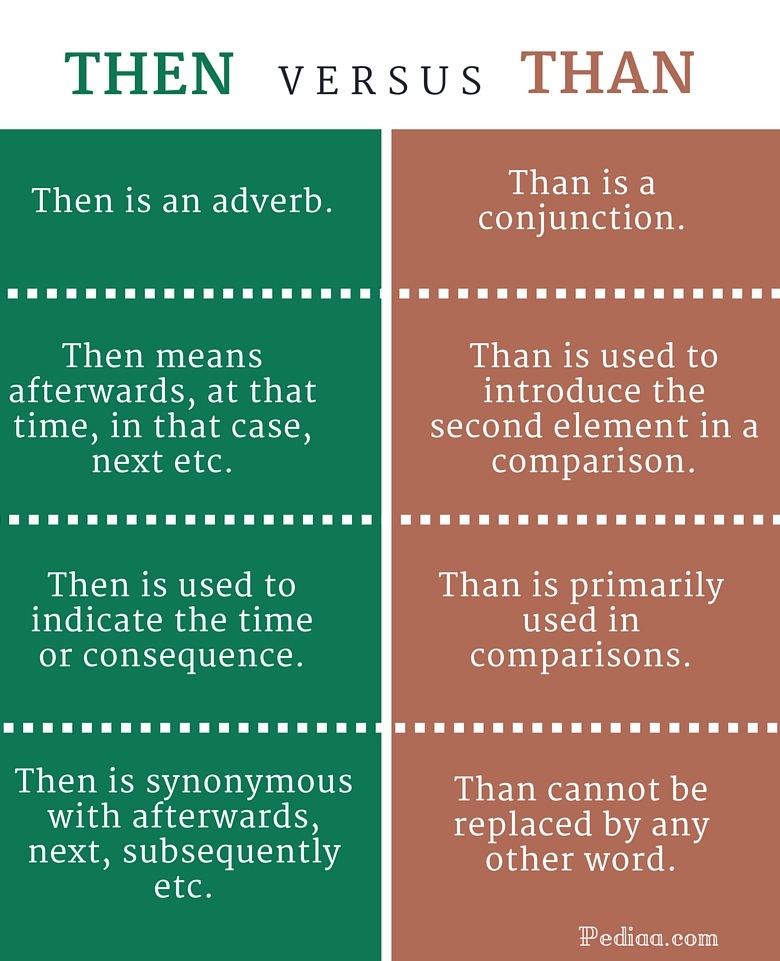
Knowledge Base Commonly confused words Then vs. Than | Meaning, Examples & Sentences Then vs. Than | Meaning, Examples & Sentences Published on August 8, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on March 11, 2023. Then and than are two commonly confused words with different meanings and grammatical roles. Than is a conjunction that is used for making comparisons between elements, objects, people, etc. He is taller than I am. She can run faster than I can. Your meal looks better than mine does. Coca-Cola is better than Pepsi. The word "then" means "at that time" and is used to talk about when things will happen. The word "than" is used to compare things. Below are some examples of each: I ate breakfast and then I went to work. The party is at 7--I'll see you then! Turn left at the light and then turn right on the next street. Then and than are two commonly confused words with different meanings and grammatical roles. Then (pronounced with a short 'e' sound) refers to time. It's typically an adverb, but it's also used as a noun meaning 'that time' and as an adjective referring to a previous status. Than (pronounced with a short 'a' sound) is used to express comparison.
Difference Between Then and Than
The word than is used for comparisons to show who or what something is compared against. For example,"cats are smarter than dogs." The word then is used to show time, as in "at that time" or "after that happened." For example,"I exercised then took a shower." When to use than Then is an adverb, noun, or adjective that indicates a previous time. Meanwhile, than is a conjunction used when comparing two items or people. Use then in writing or events when there is an element of time. In the English language, then means at that time, at that point, or next. Then and than are two commonly confused words with different meanings and grammatical roles. Then (pronounced with a short 'e' sound) refers to time. It's often an adverb, but it can also be used as a noun meaning 'that time' and as an adjective referring to a previous status. Than (pronounced with a short 'a' sound) is used for comparisons. Grammar Tips Then vs. than? Then is used to describe an event or subject in relation to time, such as the order of events in a story. In contrast, than is commonly used as a preposition to compare and contrast two subjects in the same sentence. What is the difference between than and then?

Then vs. Than How to Use Than vs. Then Correctly? Confused Words
The function word "than" is used to indicate a point of difference or comparison, as in: She's taller "than" you are. "Than" usually follows a comparative form, but it can also follow words such as "other" and "rather." More about "Than" and "Then" "Then" and "than" are common words, and your readers will expect you to use the right one. Than "Than" introduces a comparison. It is most often seen with comparatives and words like "more," "less," and "fewer." Craig is smarter than Paul. ("Smarter" is a comparative.) Money is better than poverty, if only for.
This, combined with the fact that then and than only differ by a single letter, helps explain why people have so much trouble choosing when to use the correct one. When to Use Then. Then as an adverb. Then is most commonly used as an adverb to place things or events in order. As seen before, then can be used to refer to past or future events. Here are some examples: I think studying for a bit and then grabbing some ice cream would be more rewarding.; The chocolate cake needs to rest for a while and then be eaten.; He went to Peru, then to Germany, and finally returned.

Than vs. Then What’s the Difference? QuillBot Blog
Wrapping Up. In short, "then" is for time or sequence, like "next," and "than" is for comparisons, indicating a difference. Remember, if you see words like "more" or "less," use "than.". Practice and grammar-check tools can help avoid mix-ups between these words. They were (then, than) required to eat live cockroaches. If you're going to leave, (then, than) you better go now, before the weather gets bad. Carl had driven 50,000 miles. By (then, than), he was in bad need of an oil change. Rather (then, than) take the highway, Misha avoided rush hour traffic by taking back roads.




