Ulnar impaction syndrome, also called ulnocarpal abutment syndrome, is a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain. [1] [2] It is a degenerative condition in which the ulnar head abuts the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) and ulnar-sided carpals. Ulnar impaction syndrome, also known as ulnar abutment or ulnocarpal impaction or loading, is a painful degenerative wrist condition caused by the ulnar head impacting upon the ulnar-sided carpus with the injury to the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC).

What is Ulnar Impaction Syndrome or Ulnar Abutment Syndrome?
What is Ulnar Impaction Syndrome? Ulnar impaction syndrome occurs when the ulna is relatively larger than it should be when compared to the radius. This forces the ulna to bear more of the weight and force to the wrist on that side of the arm. Inflammation (swelling) and stiffness in the wrist joint. This may include osteoarthritis (wear and tear of the cartilage of bones in the wrist joint), inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, or arthritis due to crystal deposits in the joint from gout or pseudo-gout. Fractures. Ulnar Styloid Impaction Syndrome is a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain secondary to impaction between the ulnar styloid tip and the triquetrum. Diagnosis is made by PA wrist radiographs which reveal positive ulnar variance with subchondral sclerosis of the ulnar styloid and/or triquetrum. Treatment is a course of rest, NSAIDs and splinting. Ulnar impaction syndrome (when the ulna is longer than the radius, which can cause it to "bump into" the smaller wrist bones (Figure 2) Inflammation or irritation of the tendons that bend and extend the wrist
UlnaImpaktionsSyndrom Ursachen, Symptome, Behandlung KSW
Ulnar impaction syndrome, also referred to as ulnocarpal abutment, is a degenerative condition of the ulnar side of the wrist resulting from excessive load bearing across the ulnar carpus, triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC), and the ulnar head. Ulnar impaction syndrome is typically a degenerative condition that causes insidious ulnar-sided wrist pain secondary to abutment of the distal end of the ulna or triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) against the ulnar carpus. The pain is usually made worse with pronation of the forearm and ulnar deviation at the wrist. There are several distinct ulnar-sided wrist impaction and impingement syndromes. Underlying anatomical causes exist for each syndrome, however, repetitive or excessive use of the forearm and wrist can also contribute. ulnar impaction syndrome : positive ulnar variance ulnar impingement syndrome : acquired short ulnar Ulnar impaction syndrome is a common cause of ulnar-sided wrist pain that is thought to be a result of abutment between the ulna and the ulnar carpus. A systematic review of the literature was conducted to determine the effectiveness of different treatment options in managing ulnar impaction syndrome.

Pediatric Distal Forearm and Wrist Injury An Imaging Review RadioGraphics
The ulnar impaction syndrome can be defined as the impaction of the ulnar head against the triangular fibrocartilage complex and ulnar carpus resulting in progressive degeneration of those structures. Ulnar impaction syndrome is a degenerative wrist condition caused by the ulnar head impacting upon the ulnar-sided carpal bones.
Ulnar impaction syndrome results in a spectrum of triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) injuries and associated lunate, triquetrum, and ligamentous damage. Patients commonly present with insidious ulnar sided wrist pain and clicking, and a history of trauma or repetitive axial loading and rotation. The ulnar impaction syndrome can be defined as the impaction of the ulnar head against the triangular fibrocartilage complex and ulnar carpus resulting in progressive degeneration of those structures. The differential diagnosis in patients who present with ulnar wrist pain and limitation of motion can also include ulnar impingement syndrome and.

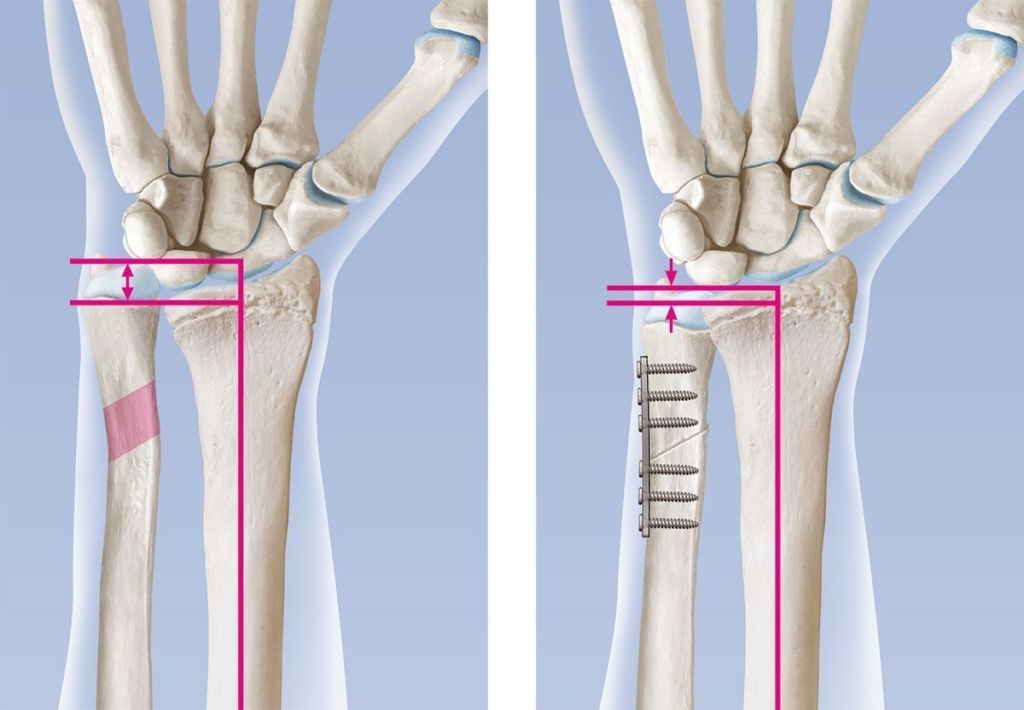
[PDF] Ulnar shortening osteotomy in idiopathic ulnar impaction syndrome. Surgical technique
Ulnar impaction syndrome (UIS - sometimes called ulnocarpal abutment) is a condition in which the ulna of the forearm is too long relative to the radius, resulting in excessive loading on the ulnar side of the wrist. In most cases, this condition is congenital and present from birth, but sometimes ulnar impaction syndrome can be secondary to. Ulnar impaction syndrome is a group of syndrome, including ulnar wrist pain and functional limitation. The ulnar wrist pain and activity limitation can occur in the TFCC damage and necrosis of lunate bone and triangular bone, which influence mutually. In this study, X-ray examination shows that, UIS is associated with osteosclerosis or/and.




