Sal mentions that the problem states that x AND y are differentiable funtions, so x is also a differentiable function, which means x is a function. the problem then says dx/dt is 12 so that is basically giving us the answer that x's independent variable is t. so you can think of y as y(x) or y of x and x as x(t) or x of t. and y ( t) , here's what the multivariable chain rule says: d d t f ( x ( t), y ( t)) ⏟ Derivative of composition function = ∂ f ∂ x d x d t + ∂ f ∂ y d y d t Written with vector notation, where v → ( t) = [ x ( t) y ( t)] , this rule has a very elegant form in terms of the gradient of f and the vector-derivative of v → ( t) .
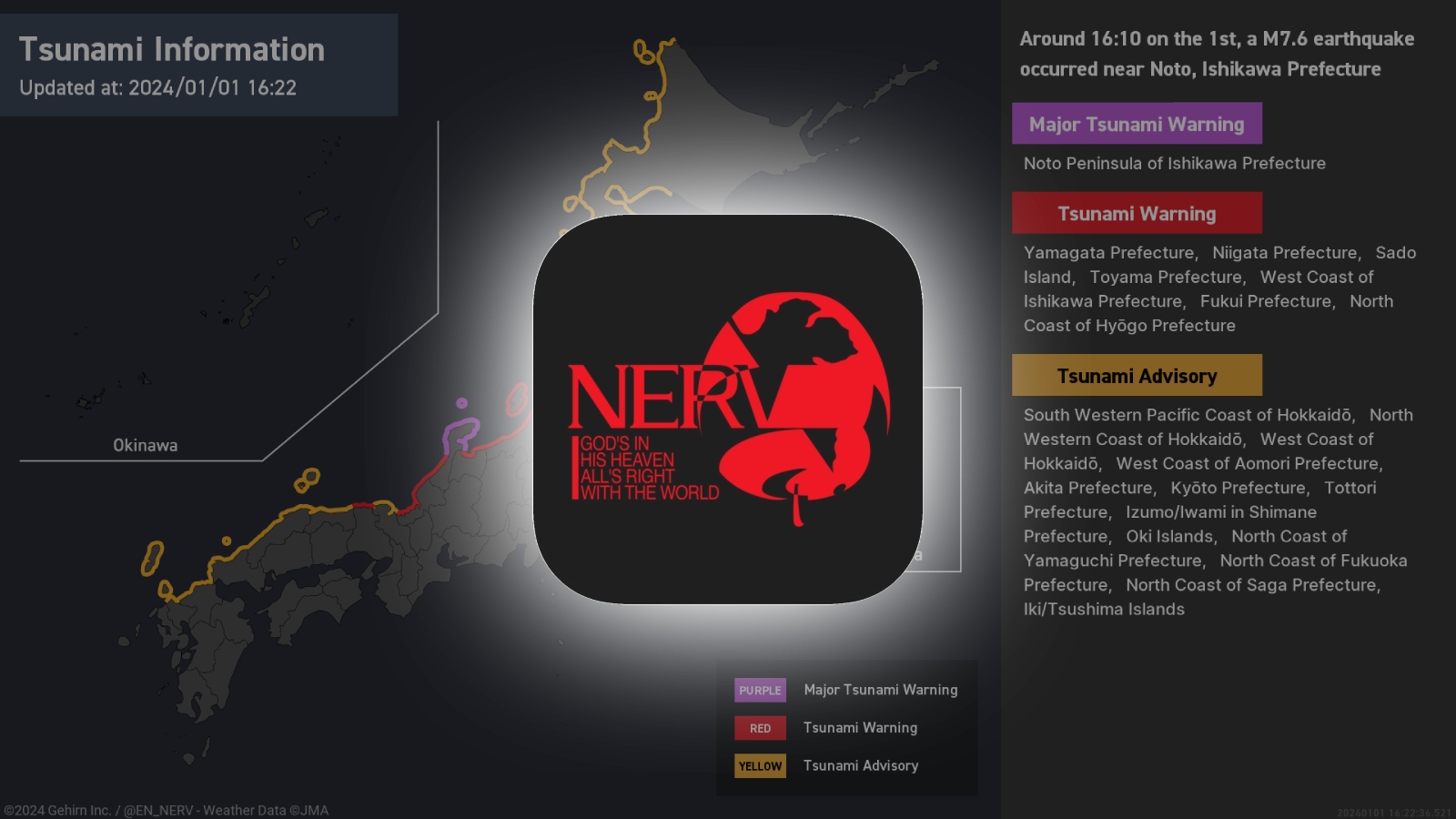
Japanese disaster prevention X account can’t post anymore after hitting
The y-axis (ordinate) reads the temperature value, and the x-axis (abscissa) corresponds to the mole fraction of benzene. We can use the x-axis to find the mole fraction of benzene in the liquid and vapour phase. Use an integrating factor to transform an equation into an exact equation: 2 t exp (2y)y' = 3 t^4 + exp (2y) Chini-Type Equations Solve a Riccati equation step by step: x^2 v' (x) + 2 x v (x) = x^4 v (x)^2 + 4 solve y' = y^2/x^2 - y/x + 1, y (1) = 0 Solve an Abel equation of the first kind with a constant invariant: The following theorem gives us the answer for the case of one independent variable. Theorem 4.8 Chain Rule for One Independent Variable Suppose that x = g(t) and y = h(t) are differentiable functions of t and z = f(x, y) is a differentiable function of xandy. Then z = f(x(t), y(t)) is a differentiable function of t and 7 Answers Sorted by: 16 Hint: Decomposing (1 x −yT I) as lower ⋅ upper and upper ⋅ lower gives (1 x 0 I) ⋅(1 0 −yT I + xyT) = (1 +xTy 0 −yT I) ⋅(1 x 0 I). Share Cite Follow edited Jun 14, 2013 at 12:07

Ray Dee Ft Y Celeb x Nacci LP Ipalo Mp3 Download Zambian Music
Some relationships cannot be represented by an explicit function. For example, x²+y²=1. Implicit differentiation helps us find dy/dx even for relationships like that. This is done using the chain rule, and viewing y as an implicit function of x. For example, according to the chain rule, the derivative of y² would be 2y⋅ (dy/dx). Definition 5.1.1 5.1. 1: Linear Transformation. Let T: Rn ↦ Rm T: R n ↦ R m be a function, where for each x ∈ Rn, T(x ) ∈ Rm. x → ∈ R n, T ( x →) ∈ R m. Then T T is a linear transformation if whenever k, p k, p are scalars and x 1 x → 1 and x 2 x → 2 are vectors in Rn R n (n × 1 ( n × 1 vectors),), Math Input More than just an online derivative solver Wolfram|Alpha is a great calculator for first, second and third derivatives; derivatives at a point; and partial derivatives. Learn what derivatives are and how Wolfram|Alpha calculates them. Learn more about: Derivatives Tips for entering queries Enter your queries using plain English. To shift the graph down by 2 units, we wish to decrease each y -value by 2, so we subtract 2 from the function defining y: y = t2 − t − 2. Thus our parametric equations for the shifted graph are x = t2 + t + 3, y = t2 − t − 2. This is graphed in Figure 9.22 (b). Notice how the vertex is now at (3, − 2).

Answered Given two functions x(t) and h(t) as… bartleby
Consider the trajectory of a golf ball which will be hit with a club, where the initial speed of the ball is #v_o# and the angle at which the golf ball leaves the golf club is #alpha#.Assume that the horizontal acceleration is #a_x=-kv_x^2# (where #v_x# is the horizontal speed) and vertical acceleration is only due to gravity #g#. Find expressions for x and y positions of a ball as a function. Proof. The proof of this theorem uses the definition of differentiability of a function of two variables. Suppose that \(f\) is differentiable at the point \(P(x_0,y_0),\) where \(x_0=g(t_0)\) and \(y_0=h(t_0)\) for a fixed value of \(t_0\).
Hover on the slider and click the "x/y" icon. Move each slider or input your preferred DPI levels. Razer Synapse 3. Open Razer Synapse and click on your mouse. Go to "PERFORMANCE" tab. Click and drag the sensitivity slider up to youu preferred DPI level. With patience you can verify that x, t) and x, y, t) do solve the 1D and 2D heat initial conditions away from the origin correct as 0, because goes to zero much faster than 1 blows up. since the total heat remains at u dx = 1 or u dx dy = 1, we have a valid solution.). The zero are

SOLVED 2 Find (d y)/(d x) if y=e^sin xtan x
The third round of documents from a lawsuit connected to Jeffrey Epstein, the convicted pedophile who died in jail before he could face trial on federal sex-trafficking charges, was publicly. Organized by textbook: https://learncheme.com/Uses an interactive simulation to explain how to read a T-x-y diagram for a binary mixture that obeys Raoult's.




