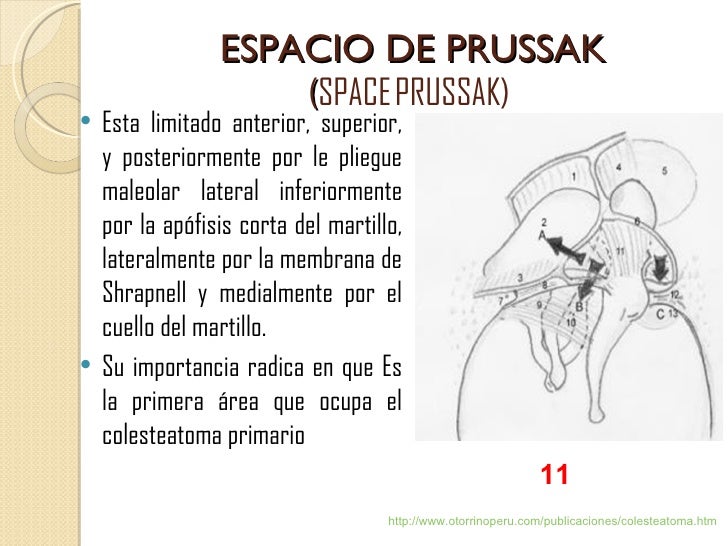
In human anatomy, Prussak's space is the small middle ear recess, bordered laterally by the flaccid part of Shrapnell's membrane, superiorly by the scutum (a sharp bony spur that is formed by the superior wall of the external auditory canal) and lateral malleal ligament, inferiorly by the lateral process of the malleus, and medially by the neck. Prussak space is a subcomponent of the lateral epitympanic space and extends from the level of the scutum to the umbo. This space is best demonstrated on the oblique coronal image. Gross anatomy Boundaries lateral: pars flaccida of the tympanic membrane and the scutum medial: neck of the malleus superior: lateral malleal ligament fold
anatomofisiologia del oido externo y medio
Prussak space is located between the lateral process of the malleus interiorly, pars flaccida of the tympanic membrane laterally, neck of the malleus medially and the lateral mallear ligament superiorly. 1 article features images from this case 6 public playlists include this case Related Radiopaedia articles Prussak space (advertising) Prussak space is a small area located within the middle ear. This space is bordered by the pars flaccida of the tympanic membrane (also known as the Shrapnell's membrane), the lateral process of the malleus bone, and the body of the incus bone. It is considered an important anatomical landmark for otologists, as it plays a significant role in. Prussak space is a subcomponent of the lateral epitympanic space and extends from the level of the scutum to the umbo. This space is best demonstrated on the. Prussak's space was formed and sufficient aeration routes established by 4 years of age in normal temporal bones. In temporal bones with otitis media with effusion, however, the growth of Prussak's space was suppressed and few routes for aeration established until 10 years of age.
PPT Atlas anatómico del hueso temporal PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID492281
Cholesteatomas appear as regions of soft tissue attenuation, exerting mass-effect and resulting in bony erosion. Findings depend on the part of the tympanic membrane that the cholesteatoma arises from: pars flaccida (82%) superior extension: most common, it expands into Prussak's space, eventually eroding the scutum and displacing the ossicles. Prussak space - " Prussak space is a subcomponent of the lateral epitympanic space and extends from the level of the scutum to the umbo. This space is best demonstr." View full size version of Prussak space - diagram Y el espacio de Prussak, cuyos límites son: superiormente, el scutum; inferiormente, la apófisis corta del martillo; medialmente, el cuello del martillo y lateralmente la membrana timpánica. Los colesteatomas suelen producir alteraciones en la mofología del scutum (en condiciones normales es afilado, y cuando está erosionado se vuelve romo. El espacio de Prussak está ventilado a través del saco posterior del Von Troltsch. La retracción de la membrana timpánica se define como el desplazamiento hacia adentro parcial o total de la Pars Fláccida (PF) o Pars Tensa (PT) de la membrana hacia el promontorio y tiene importancia clínica debido a que puede convertirse en un bolsillo de.

Prussak's space chronological development and routes of aeration Auris Nasus Larynx
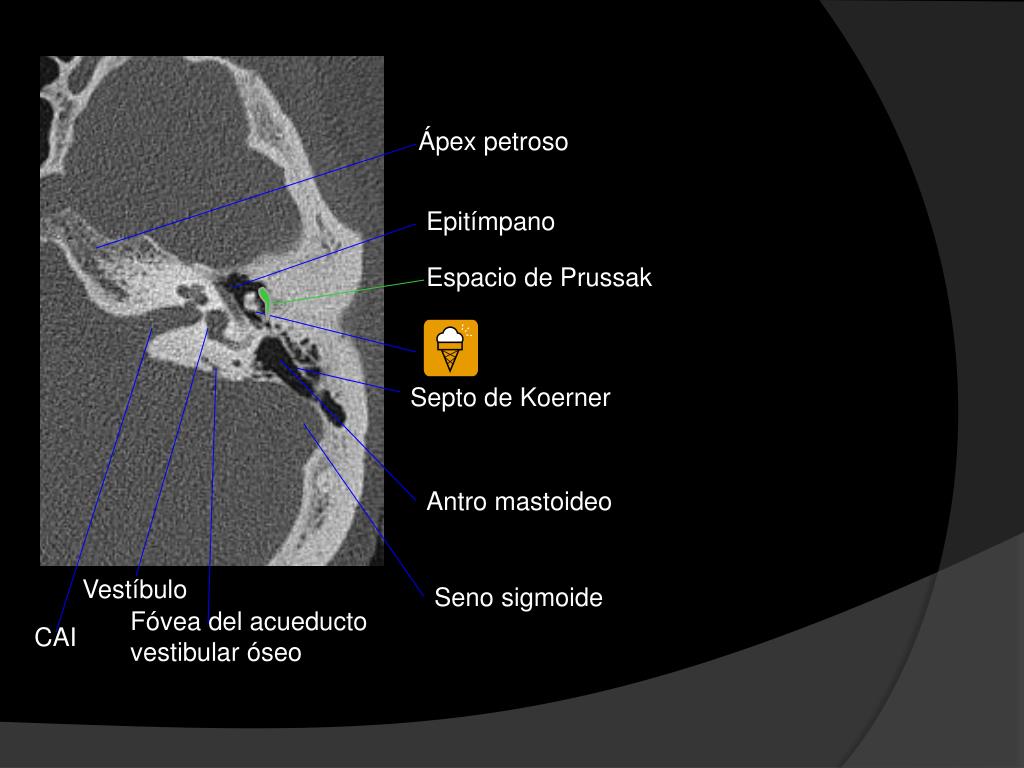
Se clasifica en congénito, adquirido y posquirúrgico ( tabla 1 ); aunque la mayoría son adquiridos (98%) y se localizan en el oído medio (siendo el sitio más frecuente el espacio de Prussak [ fig. 1 ]) y las celdillas mastoideas, donde normalmente no debe haber otro tejido diferente a la mucosa. Tabla 1. El espacio de Prussak se abre posteriormente al epitímpano y desde allí se extiende hacia el áticoposterolateral, aditus ad antrum, antro y celdillas mastoideas (FIGURA 16). El ensanchamiento del aditus es una imagen diagnóstica importante. - El colesteatoma de la pars tensa es mucho menos frecuente.
Espacio de Prussak: espacio en el ático entre el ligamento externo del martillo, la membrana de Shrapnell y el cuello del martillo. Es una depresión fisiológica, o receso, que produce en la cara interna la membrana timpánica en su porción flácida y situada en el ático externo.. En anatomía humana , el espacio de Prussak es el pequeño receso del oído medio , bordeado lateralmente por la parte flácida de la membrana de Shrapnell , superiormente por el scutum (un espolón óseo afilado que está formado por la pared superior del conducto auditivo externo) y el ligamento maleal lateral . inferiormente por el proceso lateral d.

ATLAS ANATMICO DEL HUESO TEMPORAL Leonor de Pablo
Típicamente ocupa el espacio de Prussak y el epitímpano Fig. 19, produce desplazamiento osicular y erosionael scutum y la cadena osicular. En la mayoría de los casos, hay una reducción de la neumatización mastoidea. Fig. 18: colesteatoma adquirido. Ocupación del espacio de Prussak y el epitímpano, con retracción de la membrana timánica. Published in 2012. Anatomía del hueso temporal. Guía para residentes. E. L. Echevarria Silvia Cisneros Carpio Maria Victoria Bárcena Robredo J. C. Urdampilleta Roberto de Miguel García Naroa Nates Uribe. Fig. 12: Reconstrucción coronal: membrana timpánica (MT), espacio de Prussak (círculo) - "Anatomía del hueso temporal. Guía para.




