DESCRIPTION If --list is given, or if there are no non-option arguments, existing branches are listed; the current branch will be highlighted in green and marked with an asterisk. Any branches checked out in linked worktrees will be highlighted in cyan and marked with a plus sign. In Git, a branch is a new/separate version of the main repository. Let's say you have a large project, and you need to update the design on it. How would that work without and with Git: Without Git: Make copies of all the relevant files to avoid impacting the live version

Git Branching Model — MAP Client latest documentation
As the documentation of git branch explains, git branch --all (or -a) lists all the branches from the local repository, both the local and the remote tracking branches. A Git branch is just a pointer to a commit. A new repository (just created with git init) does not contain any commits. The current branch on a new repo is master but the master. Git - Basic Branching and Merging Chapters 2nd Edition 3.2 Git Branching - Basic Branching and Merging Basic Branching and Merging Let's go through a simple example of branching and merging with a workflow that you might use in the real world. You'll follow these steps: Do some work on a website. The git branch command lets you create, list, rename, and delete branches. It doesn't let you switch between branches or put a forked history back together again. For this reason, git branch is tightly integrated with the git checkout and git merge commands. Common options git branch List all of the branches in your repository. A branch in Git is simply a lightweight movable pointer to one of these commits. The default branch name in Git is master . As you start making commits, you're given a master branch that points to the last commit you made. Every time you commit, the master branch pointer moves forward automatically. Note

GIT Branch and its Operations. An Easy Understanding Digital Varys
The "branch" command helps you create, delete, and list branches. It's the go-to command when it comes to managing any aspect of your branches - no matter if in your local repository or on your remotes. Important Options -v -a Provides more information about all your branches. Prior to creating new branches, we want to see all the branches that exist. We can view all existing branches by typing the following: git branch -a. Adding the "-a" to the end of our command tells GIT that we want to see all branches that exist, including ones that we do not have in our local workspace. The git branch command does more than just create and delete branches. If you run it with no arguments, you get a simple listing of your current branches: $ git branch iss53 * master testing Notice the * character that prefixes the master branch: it indicates the branch that you currently have checked out (i.e., the branch that HEAD points to). Remote Branches Remote references are references (pointers) in your remote repositories, including branches, tags, and so on. You can get a full list of remote references explicitly with git ls-remote
, or git remote show for remote branches as well as more information. 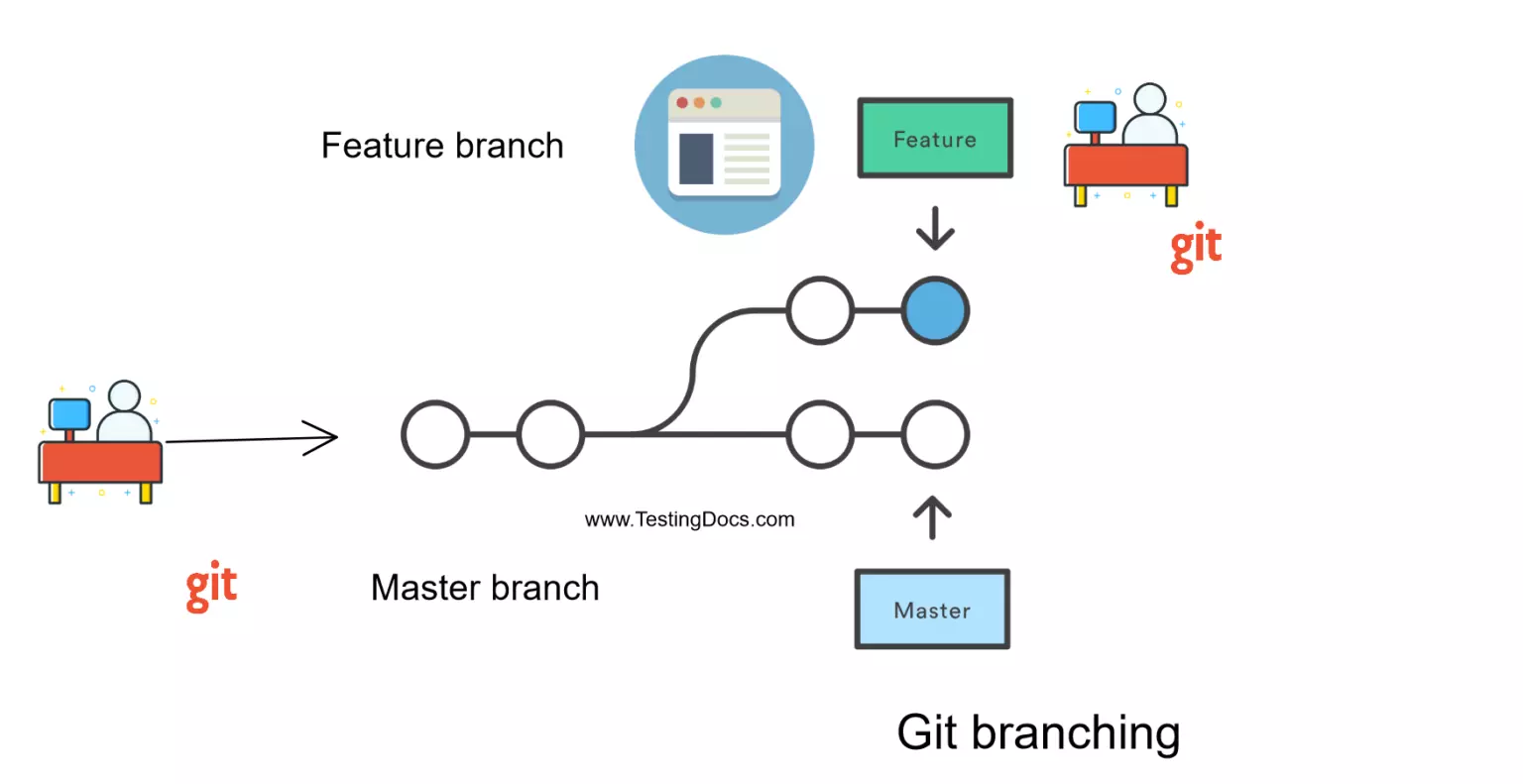
Create a Git Branch
How to create branches How to rename branches How to switch branches How to publish branches How to track branches How to delete branches How to merge branches How to rebase branches How to compare branches How to Create a Branch in Git Before you can work with branches, you need to have some in your repository. Git Branching and Merging: A Step-By-Step Guide In previous articles, you learned "How to Revert a Commit in Git" (a PowerShell Git tutorial) and "How to Merge in Git: Remote and Local Git Repositories Tutorial." You can…
Jul 26, 2023 Edward S. 3min Read How to Use a Git Branch Git is a tool used by developers to manage version control of their applications. It is highly popular and used by many important projects such as GNOME and others. It is also a fairly efficient application. creating new local branches deleting existing local or remote branches listing local and/or remote branches listing branches that e.g. haven't been merged yet Learn More Learn more about the git branch command 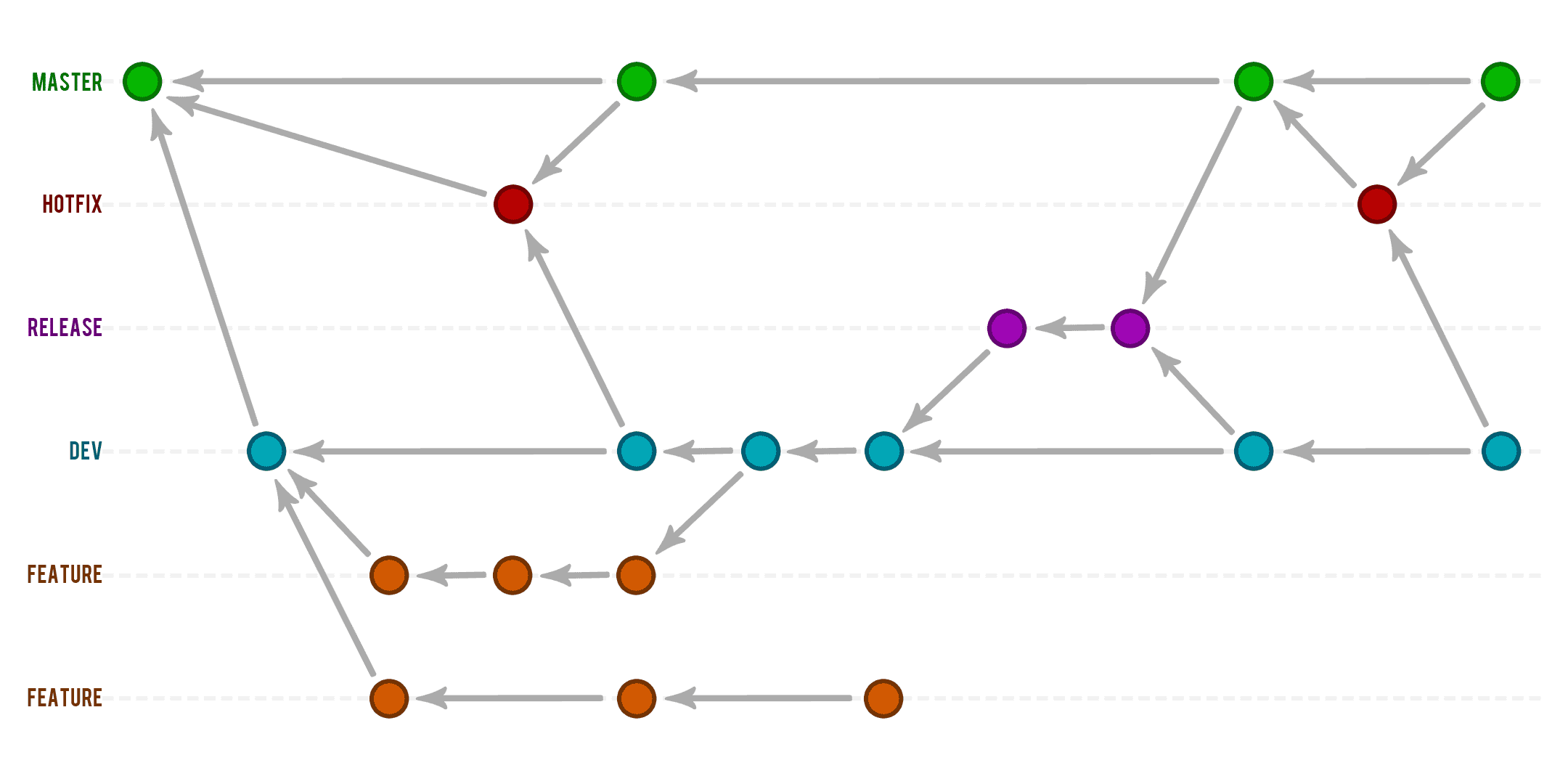
GIT Branching & Release Strategy Geoff Ford
If the branch already exists on the remote, the 'git push' command can be used. Merging branches involves ensuring the working tree is clean, checking out the branch to merge into another and then running the 'git merge my-branch-name' command. Branches can be deleted using 'git push origin --delete my-branch-name' for remote branches and 'git. 7 Answers Sorted by: 361 git checkout -b BRANCH_NAME creates a new branch and checks out the new branch while git branch BRANCH_NAME creates a new branch but leaves you on the same branch. In other words git checkout -b BRANCH_NAME does the following for you.




