When a company issues Class A and Class B shares of stock, it can define these shares almost entirely as it pleases. It can give Class B shares three votes each, or it can say that Class A stock receives half of Class B. So long as the definitions do not violate a shareholder's legal rights, the company can set these terms as it pleases. Corporate charters - not the law or the courts - define the difference between the classes of stock, often designated as Class A, B and C. Understanding how various classes of stock.
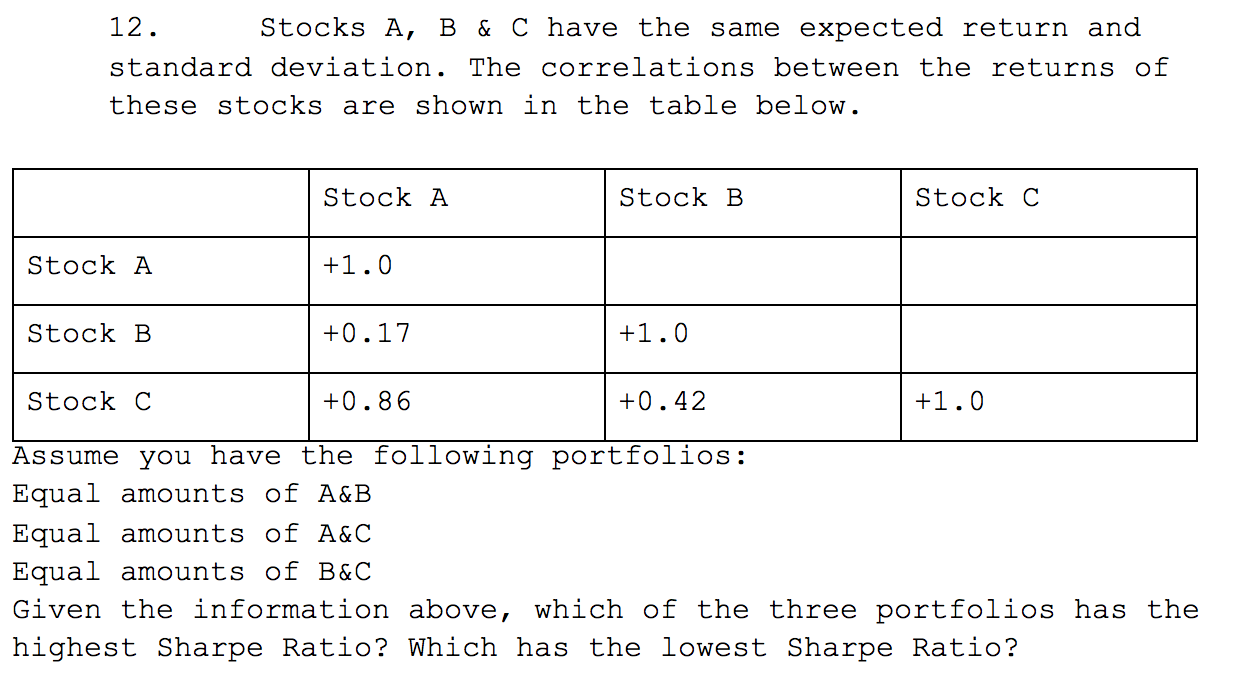
Solved 12. Stocks A, B & C have the same expected return and
• Class C shares can refer to shares given to employees or alternate share classes available to public investors, with varying restrictions and voting rights. Why Companies Have Different Types of Stock Shares When a company goes public, they are selling portions of their company, known as stocks, to shareholders. Class A shares refer to a classification of common stock that was traditionally accompanied by more voting rights than Class B shares. Traditional Class A shares are not sold to the public. Class A Shares vs. Class B Shares: An Overview The difference between Class A shares and Class B shares of a company's stock usually comes down to the number of voting rights assigned to the. Schwab Equity Ratings Schwab Equity Ratings use a scale of A, B, C, D, and F, and are assigned to approximately 3,000 U.S.-traded stocks. Schwab Equity Ratings use a scale of A, B, C, D, and F, and are assigned to approximately 3,000 U.S.-traded stocks.
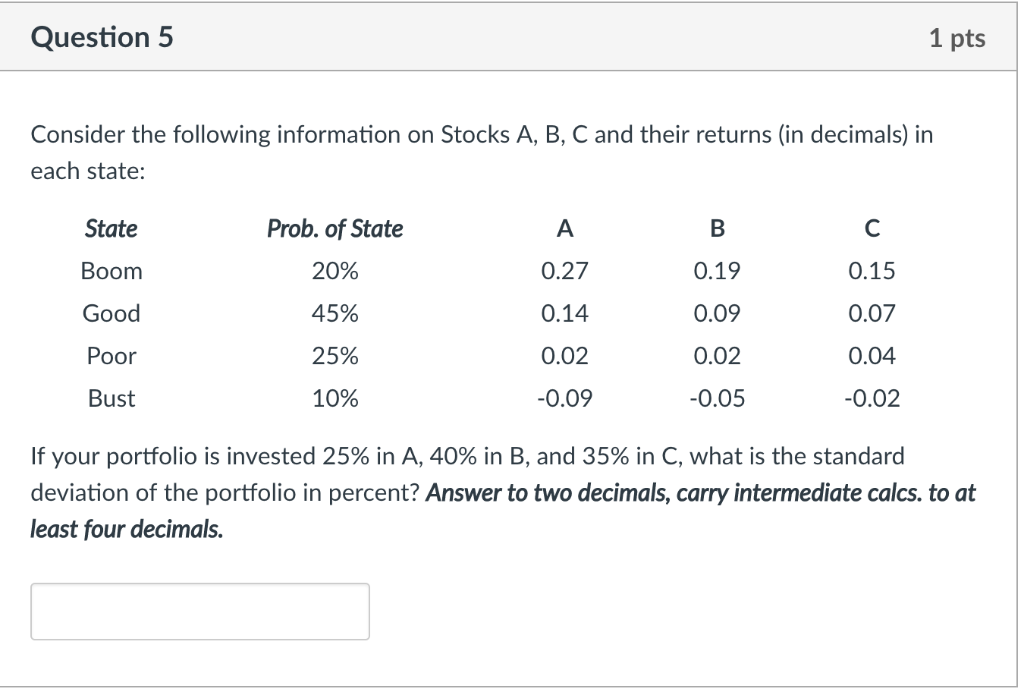
Solved Consider the following information on Stocks A, B, C
If the company must liquidate its assets, Class B shareholders have priority over Class A shareholders. Class C shares may be Executive Stock, which is given to the top management of the company as part of their compensation package. Each Class C share has 10 votes. Class C shareholders receive the same access to dividends and assets as Class A. A 50-to-1 stock split in 2010 sent the ratio to 1/1,500 th, which means each share of a Class A common stock was convertible at any time to 1,500 shares of Class B common stock. What Is Series A, B, and C Funding? Series A, B, and C are funding rounds that generally follow "seed funding" and "angel investing," providing outside investors the opportunity to. Fortunately, the back-end load declines gradually while you hold the fund, and eventually the load goes all the way down to zero. However, one drawback of B share funds is that they usually have something called a "12b-1 fee," which increases the expenses of the fund. 12b-1 fees are paid out of mutual fund or ETF assets to cover the costs of distribution (marketing and selling mutual fund.

Solved Consider the following information for Stocks A, B,
The downside is that Class B shares don't have a high control. The voting power and price doesn't necessarily have to be in proportion. For example, Class A shares could cost around $3,000 and receive 100 votes. On the other hand, Class B shares may cost up to $120 with just a single vote. Tickers GOOG and GOOGL both represent shares of Alphabet common stock, but they are two distinct share classes that have slightly different prices and attributes. Most publicly traded stocks.
Ditto for the B, C, D and F grades. The stocks that's the highest A may look very different than a stocks that is the lowest A (almost a B). Stock selection (even within all the A-rated stocks), how tight you place your stops, when and how you enter the trade will all affect your results. Class A and B shares are aimed at long-term investors, whereas Class C shares are for beginning investors who aim for short-term gains and may have less money to invest. Class C shares, especially.
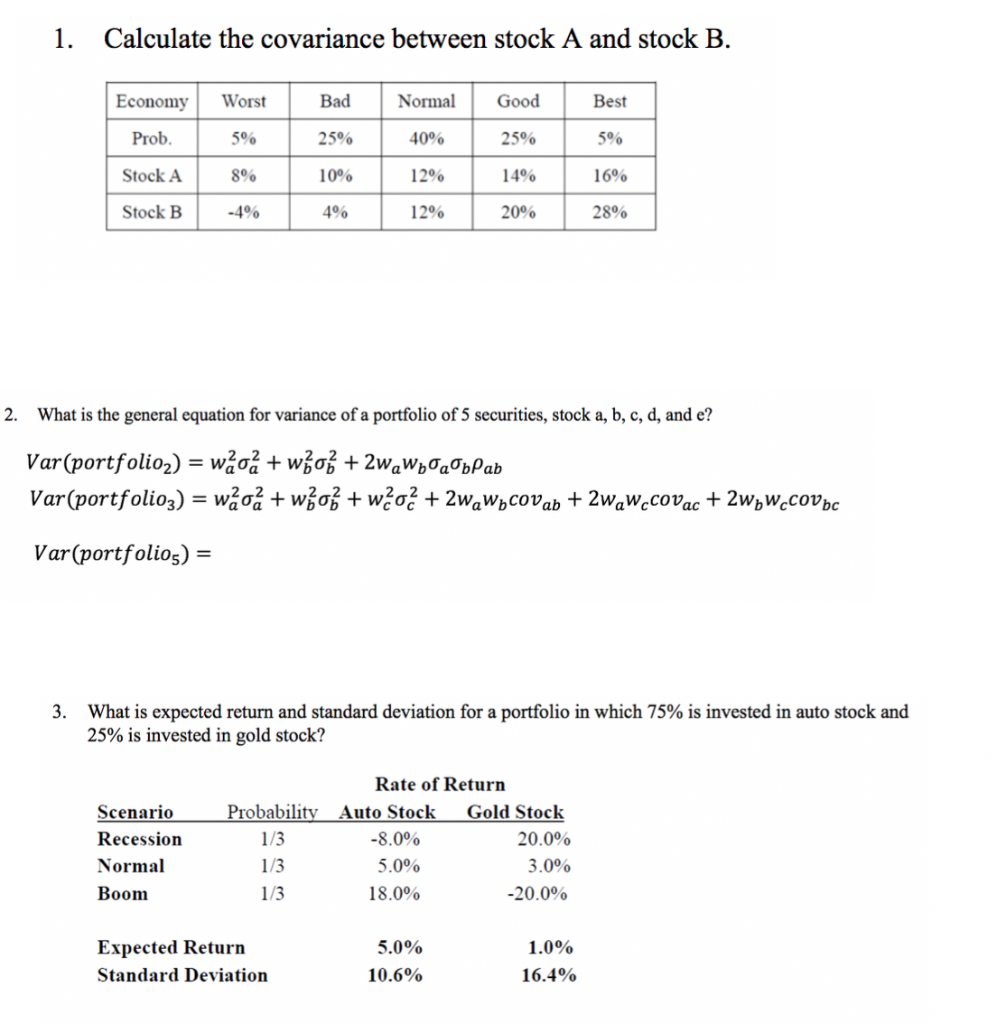
Solved Calculate the covariance between stock A and stock B
Google's parent company, Alphabet, announced a 20-for-1 stock split in February 2022. The split took effect on July 15, 2022. GOOG GOOG shares are the company's Class C shares. Class C shares. A stock market crash is a sudden, steep drop in stock prices that occurs over a short period and may take years to recover. Various factors, such as a financial crisis, geopolitical turmoil, or a sudden change in investor sentiment, can trigger crashes. Some of the most notable stock market crashes in history include: The Black Tuesday crash of.




