The R2 quantifies the degree of any linear correlation between Yobs and Ypred, while for the goodness-of-fit evaluation only one specific linear correlation should be taken into consideration: Yobs = 1· Ypred + 0 (i.e., the 1:1 line). [8] [9] Definitions Gravitation Gravitation is the attraction between objects that have mass. Newton's law states: The gravitational attraction force between two point masses is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of their separation distance.

Line graph of the number of coupled r 1 , r 2 values for which the... Download Scientific Diagram
Published on April 22, 2022 by Shaun Turney . Revised on June 22, 2023. The coefficient of determination is a number between 0 and 1 that measures how well a statistical model predicts an outcome. The coefficient of determination is often written as R2, which is pronounced as "r squared." In the real world, the inverse square law (squared distance law) I ~ 1/ r2 is always an idealization because it assumes exactly equal sound intensity or acoustic intensity I as sound energy propagation in all directions. If there are reflective surfaces in the sound field, About Transcript A finite geometric series can be solved using the formula a (1-rⁿ)/ (1-r). Sal demonstrates how to derive a formula for the sum of the first 'n' terms of such a series, emphasizing the importance of understanding the number of terms being summed. Questions Tips & Thanks Want to join the conversation? Sort by: Top Voted averynash Calculus Simplify (1-r^2)/ (1-r) 1 − r2 1 − r 1 - r 2 1 - r Simplify the numerator. Tap for more steps. (1+r)(1− r) 1−r ( 1 + r) ( 1 - r) 1 - r Cancel the common factor of 1−r 1 - r. Tap for more steps. 1+r 1 + r

1 R2, R
The distance square in the Newton's law of universal gravitation is really a square? (7 answers) Closed 9 years ago. Is there something intrinsic about the structure of space that gravity is proportional to 1/r^2 instead of, for example, 1/r^2.143 ? What makes the exponent turn out to be a nice even number? newtonian-gravity Share Cite Components Coefficient a The first nine terms of geometric series 1 + r + r2 + r3. drawn as functions (colored in the order red, green, blue, red, green, blue,.) within the range | r | < 1. The closed form geometric series 1 / (1 - r) is the black dashed line. The geometric series a + ar + ar2 + ar3 +. is written in expanded form. [1] Free integral calculator - solve indefinite, definite and multiple integrals with all the steps. Type in any integral to get the solution, steps and graph Compute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals. For math, science, nutrition, history.

Question What is does the (R) in this photo mean? chemistry
Popular Problems Algebra Factor r^2+2r+1 r2 + 2r + 1 r 2 + 2 r + 1 Rewrite 1 1 as 12 1 2. r2 + 2r+12 r 2 + 2 r + 1 2 Check that the middle term is two times the product of the numbers being squared in the first term and third term. 2r = 2⋅r ⋅1 2 r = 2 ⋅ r ⋅ 1 Rewrite the polynomial. r2 + 2⋅r⋅1+12 r 2 + 2 ⋅ r ⋅ 1 + 1 2 Calculus Evaluate the Integral integral of 1/ (r^2) with respect to r ∫ 1 r2 dr ∫ 1 r 2 d r Apply basic rules of exponents. Tap for more steps. ∫ r−2dr ∫ r - 2 d r By the Power Rule, the integral of r−2 r - 2 with respect to r r is −r−1 - r - 1. −r−1 +C - r - 1 + C Rewrite −r−1 +C - r - 1 + C as −1 r +C - 1 r + C. −1 r +C - 1 r + C
(y1-y_bar)^2 + (y2-y_bar)^2 + (y3-y_bar)^2 = (1-2)^2 + (2-2)^2 + (3-2)^2 = 2. this is going to be a very small fraction over here. 1 minus a very small fraction is going to be a number close to 1. So then, our R-squared will be close to 1, which tells us that a lot of the variation in y is described by the variation in x. Which makes sense. High School Math Solutions - Radical Equation Calculator. Radical equations are equations involving radicals of any order. We will show examples of square roots; higher. Read More. Save to Notebook! Sign in. Free solve for a variable calculator - solve the equation for different variables step-by-step.
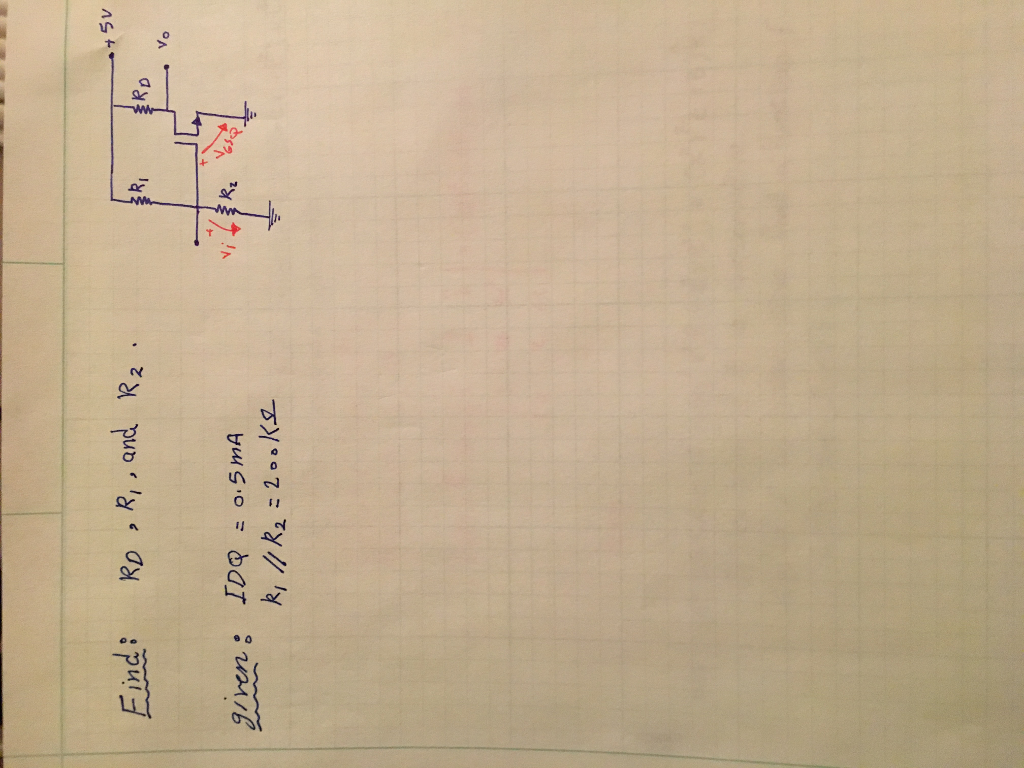
Solved Find R_D, R_1, and R_2 Given IDQ = 0.5 mA
Here are some basic characteristics of the measure: Since r 2 is a proportion, it is always a number between 0 and 1.; If r 2 = 1, all of the data points fall perfectly on the regression line. The predictor x accounts for all of the variation in y!; If r 2 = 0, the estimated regression line is perfectly horizontal. The predictor x accounts for none of the variation in y! You can find the gradient of $1/r$ more easily using the chain rule and the identity $\nabla r^2 = 2 \vec r$. In particular, $$\nabla \frac{1}{r} = \nabla \frac{1}{\sqrt{r^2}} =- \frac{1}{2 (r^2)^{3/2}} \nabla r^2 =-\frac{\vec r}{ r^3} = -\frac{\hat r}{r^2}$$ Finally, in evaluating the problem $\nabla \cdot \hat r$, you can use the product rule:



