The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. In ancient Roman times there were two main types of Latin script, capital letters and cursive. There were also varieties of writing that mixed capitals and cursive or semicursive letters; Latin uncial script developed from such a mixed form in the 3rd century ce.
/GettyImages-852354592-5c71dc9846e0fb0001f87ce0.jpg)
Letters of the Latin Alphabet Tracing Language History
This is one version of the Ancient Latin alphabet. Many of the letters have serveral different shapes in different inscriptions and texts. Latin was original written either from right to left, left to right, or alternating between those two directions (boustrophedon). By the 5th or 4th century BC it was normally written from left to right. Duenos inscription, dated to the 6th century BC, shows the earliest known forms of the Old Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world. [1] It is the standard script of the English language and is often referred to simply as "the alphabet" in English. The Latin alphabet originally had 21 letters in the first century BCE, but then, as the Romans became Hellenized, they added two letters at the end of the alphabet, a Y for the Greek upsilon, and a Z for the Greek zeta, which then had no equivalent in the Latin language. Latin was the language of the area known as Latium (modern Lazio), and Rome was one of the towns of Latium. The earliest known inscriptions in Latin date from the 6th century BC and were written using an alphabet adapted from the Etruscan alphabet. Rome gradually expanded its influence over other parts of Italy and then over other parts of Europe.
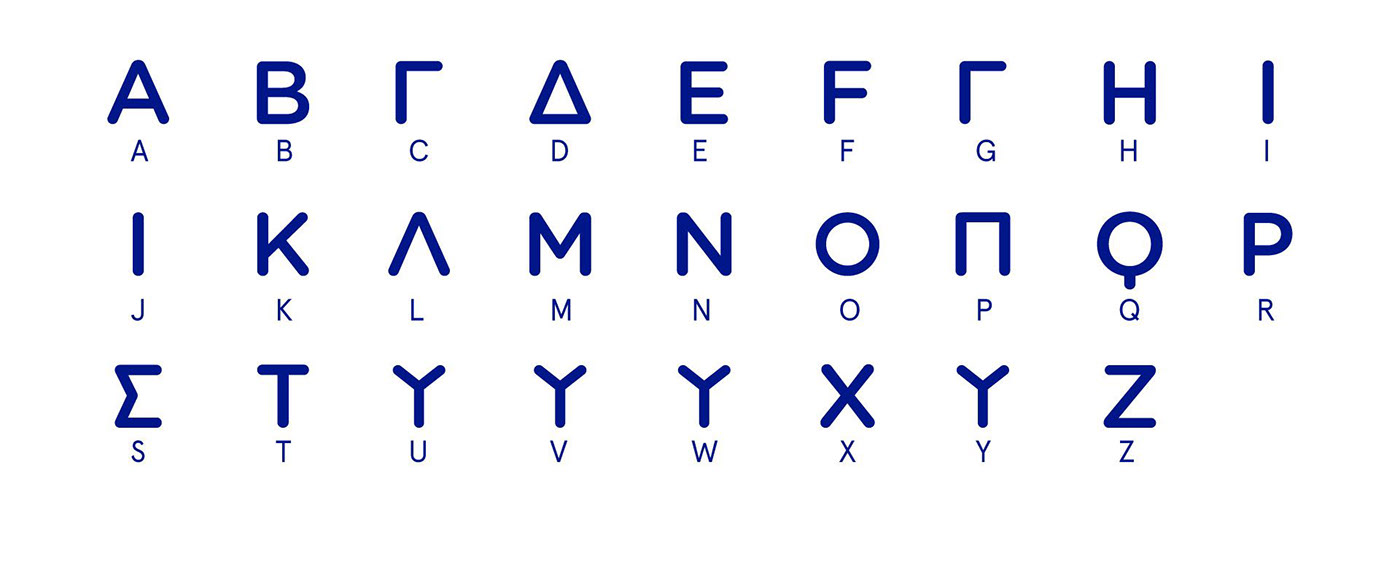
The History of the Latin Alphabet on Behance
Greek alphabet on an ancient black figure vessel. There is a digamma but no ksi or omega. The letter phi upright in the photograph is missing a stroke and looks like the omicron Ο, but on the other side of the bottom it is a full Φ. Etruscan writing, the beginning of the writing with the Latin alphabet. The Latin alphabet, also known as the Roman alphabet, is the collection of letters originally used by the ancient Romans to write the Latin language. As already mentioned, the original Etruscan alphabet consisted of 26 letters, of which the Romans adopted only 21. They did not retain the three Greek aspirate letters ( theta, phi, and chi) in the alphabet because there were no corresponding Latin sounds but did employ them to represent the numbers 100, 1,000, and 50. The A to Z of Alphabet Origins and the Most Ancient Written Languages; Egyptian Hieroglyphs: The Language of the Gods; Similarly, the Bronze Age Mesopotamians wrote their Sumerian language using cuneiform pictographs on clay tablets. In both Egypt and Mesopotamia, the written language played a number of different roles from the cultic to the profane.
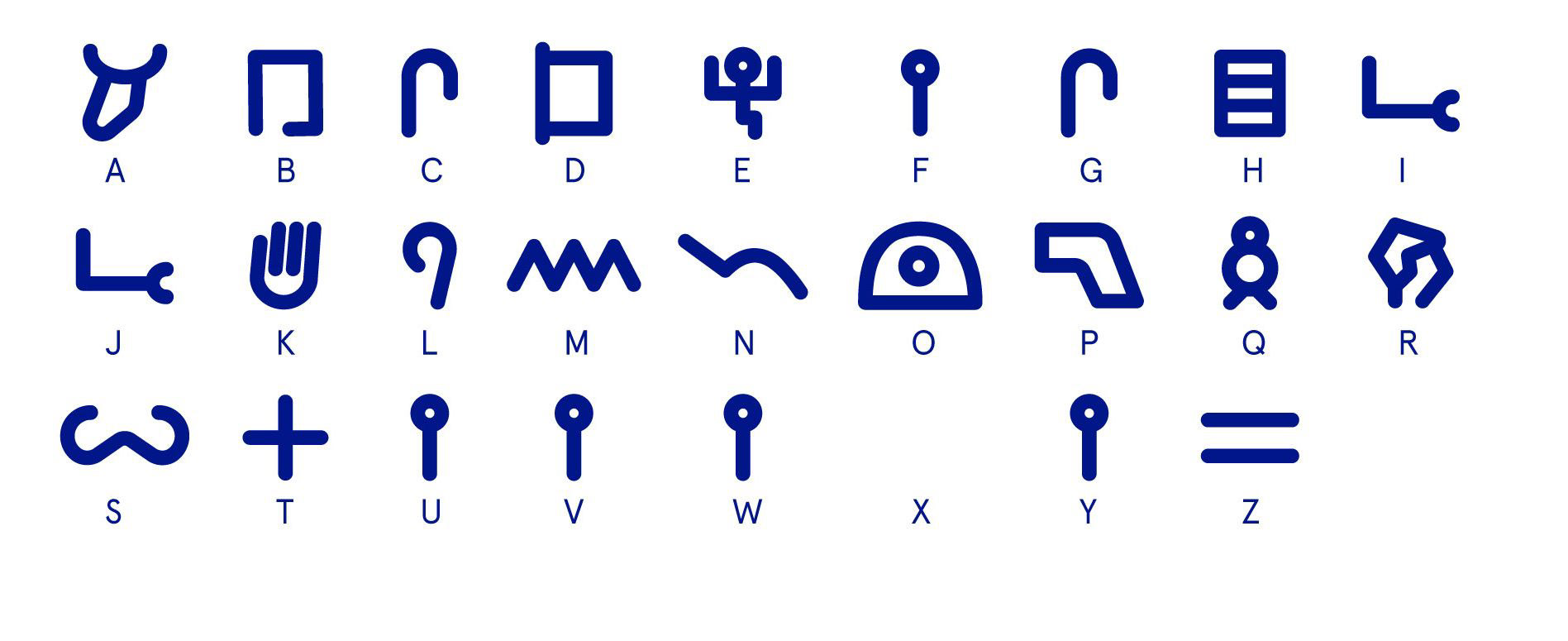
The History of the Latin Alphabet on Behance
L'alphabet latin, comme la majorité de ceux issus de l' alphabet grec, est bicaméral : on utilise deux graphies pour chaque graphème (ou lettre ), l'une dite bas de casse ou minuscule, l'autre capitale ou majuscule. Dans la majorité des cas, chaque lettre possède les deux variantes. The Latin alphabet was not invented from scratch, on the contrary, it was the result of thousands of years of evolution, assimilation and improvements. The writing of upper and lower case characters was also influenced and modified many times before eventually be the system we use today. "Each letter of the alphabet is a steadfast loyal.
latin alphabet Phoenician 4shares The Latin script, one of the most widely used scripts today, is believed to be derived from the Greek Chalcidian alphabet, with a strong lineage connecting it to some of the greatest ancient civilizations. The Latin alphabet is undoubtedly the world's most recognizable form of written language, whose history goes back in time to the eras of ancient Greek and Roman dominance of the entire Western world.

FileLatin Letters.jpg Wikimedia Commons
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern Italy ( Magna Graecia ). The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscans, and subsequently their. Classical Latin alphabet. The Classical Latin alphabet developed by the 3rd century BC. The version shown below was used for monumental inscriptions, and is known as Roman Square Capitals (capitalis quadrata) or Elegant Capitals (capitalis elegans).During the classical revival, which started in the 18th century, the letter forms of the Classical Latin alphabet, were reintroduced to the.
/GettyImages-852354592-5c71dc9846e0fb0001f87ce0.jpg)



