One of Chladni's best-known achievements was inventing a technique to show the various modes of vibration on a rigid surface, known as Chladni figuresChladni patterns due to the various shapes or patterns created by various modes. Chladni perfected these initial experiments by Hooke (using mostly sand this time) and introduced them systematically in his 1787 book, providing a significant contribution to the understanding of acoustic phenomena and how musical instruments functioned. Such patterns are now commonly termed "Chladni figures". Text by Adam Green.
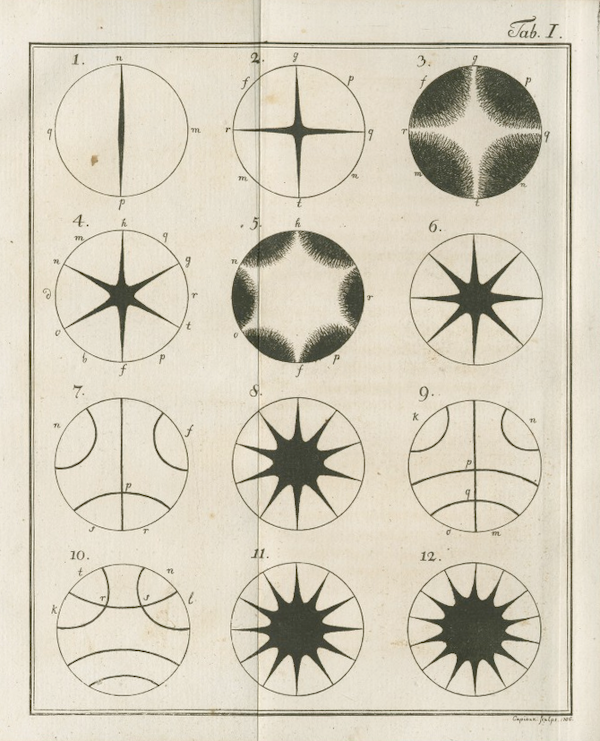
Chladni Figures (1787) The Public Domain Review
Les figures de Chladni sont les motifs géométriques que forme une poudre N 1 sur une plaque en vibration. Elles sont ainsi nommées en l'honneur du savant allemand Ernst Chladni . Les figures de Chladni dépendent de la fréquence de vibration de la plaque. Chladni Figures: Amazing Resonance Experiment By Brian Malow on June 13, 2013 When I first saw this video I thought it was fake. Perhaps an April Fool's joke. But, not only is it real, it is a. Chladni figures are wavy lines produced by scattered salt or sand on an elastic material of a given shape possibly constrained at the edges or at a point in the center and forced to vibrate with a violin bow The modes of vibration can be identified because these small particles end up in the places of zero vibration which happens at those parts. Charles Taylor recreates the famous Chadni figures and shows how vibrating plates are used to make music in various instruments.Watch the full third lecture.

A Chladni figure, created by placing grains of sand on a flat board, then playing sound through
Chladni Plate. This instrument was used in an Ohio high school and probably dates from the late 19th or early 20th centuries. The replication of classic experiments was a common way to teach science at this time, and Chladni's figures were considered to be both instructive and beautiful. To "play" this instrument, first sprinkle a thin. Chladni plates, invented by the physicist, musician and musical instrument maker Ernst Chladni (1756-1827) in the late 18th century, are used to demonstrate the complex patterns of standing wave vibrations that can occur in two-dimensional objects. Beautiful patterns of sand (Chladni figures) are formed on black thin metal plates as a result of standing waves (Figure 1). Materials Function generator + banana cables Mechanical vibrator Large aluminum square and circular plates with threaded rod through the center Sand Demonstration Figure 2 The Chladni figures of new resonant modes reveal morphologies with a nodal point at the driving position which is always an antinode in the isotropic plates. Full size image. Figure 8.
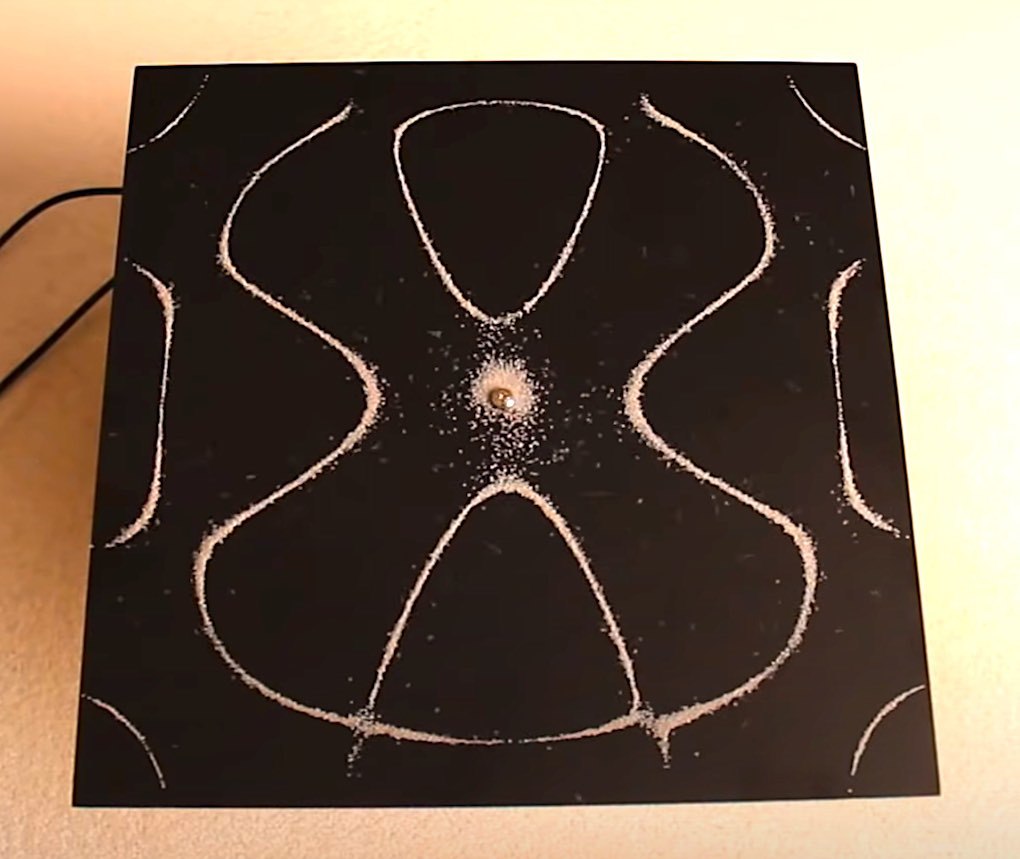

Chladni Figures The Resonance Experiment That Still Amazes LaptrinhX
Figure 2: Application and modern adaption of Chladni figures. Physical and Mathematical Background In an experimental physical setup, Chladni figures can be produced by inducing oscillation on some plate. The physical formulation of damped oscillation of a string is given by the following differential equation m @2 @2t h(x;t)+d @ @t h(x;t)+kh. Chladni patterns are one of the most fascinating physics demonstrations. They can be produced very easily using commercially available apparatus based on metallic plates attached to a mechanical driver, similar to a loudspeaker without the membrane, and a signal generator. The figures are observed using sand sprinkled on the surface of the plate.
Introduction. Chladni sound figures of vibrating plates which greatly impressed Napoleon in 18 th century 1 have inspired many essential research in modern physics such as quantum chaos 2, self-organization of granular media 3, 4, microscale acoustofluidics 5, 6, and pattern formation 7, 8.Due to its advantages of robustness, low cost, easier observation, and high replicability, the historic. Abstract and Figures. In his 1802 book "Acoustics", Ernst Florens Friedrich Chladni describes how to visualize different vibration modes using sand, a metal plate, and a violin bow. We will.

Ernst Chladni IDIS
Results from this study show the Chladni figures that form at different frequencies. As shown below, the patterns formed at 610 Hz vary greatly from the patterns formed at 3815 Hz. The analysis of sound waves at the different frequencies of a Chladni plate can be applied to other design projects involving the physical effects of sound. Named for Ernst Chladni, these figures represent nodal patterns formed by vibrating surfaces. Traditionally, these are formed placing fine particles on a surface, like a sheet of metal that is set vibrating (a violin bow against an edge of the metal plate is one popular method). The particles settle in the areas of the surface that have the.




