Joint mobilization and traction are manual therapy techniques that are slow, passive movements of articulating surfaces. 5 They are used to regain normal active joint range of motion (ROM), restore normal passive motions that occur about a joint, reposition or realign a joint, regain a normal distribution of forces and stresses about a joint, or. Tractions' main goals are to control pain from muscle spasm, reduce fractures maintaining anatomical reduction, and to prevent and correct deformity. An effective traction will provide a pulling force on the body by ensuring a good grip on the injured limb that is adequate and secure.

Traction Supination Comment Muscler son Dos avec la Traction Supination
The elbow complex consists of humeroulnar and humeroradial joints. For the complete range of motion for elbow flexion and extension, accessory motions of valgus and varus are essential. The technique for each of the joints is described. Elbow mobilization is proved to be effective in post-traumatic or post-operative elbow injury cases. [1] Pronator quadratus Supinator Biceps brachii Brachioradialis Clinical points Anterior interosseus nerve syndrome Erb's palsy Musculocutaneous nerve palsy Monteggia fracture Galeazzi fracture Sources + Show all Bones and joints Pronation and supination are movements that occur at the radioulnar joints. Most of the extensor-supinator muscles and the flexor-pronator muscles cross both the elbow and wrist joints, so their excursion at the elbow will be impacted by wrist and forearm positions. Figure 80-3 . The biceps length test. A, Elbow extension is passively measured with the shoulder in neutral (no tension on proximal portion of biceps). Upper extremity osteopathy - Knowledge @ AMBOSS The flexibility of the upper extremity results in a wide range of movements across the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints, which often leads to excessive and directionally awkward stress. The upper.
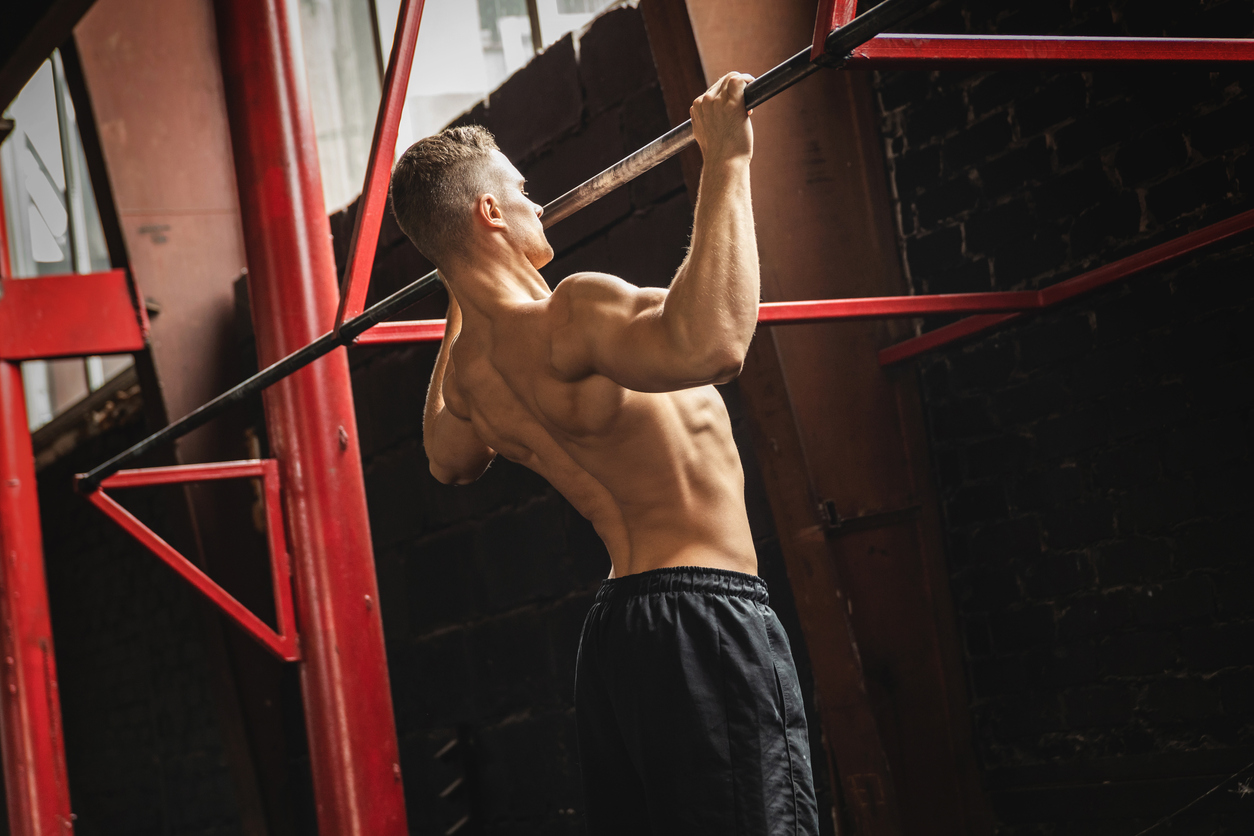

Les Tractions Les Meilleurs Exercices Pour Muscler Le Haut Du Corps Blog Eric Favre Sport
mobilization treatment principles. Oscillations • Oscillations or prolonged hold at mid-range. 60-120/min stimulates type I. 1-5 sets of 5-60 sec mechanoreceptors. generally used to treat pain • Oscillations or prolonged hod at end range stimulates type II. passively abduct arm to maximal degree, then release and ask patient to slowly lower to side. inability to perform controlled lowering is a positive test usually lose control around 100 ° note that pain can cause a false positive result. Shoulder - Rotator Cuff. Weakness may be due to pain and/or muscle tear. treatment of a femoral fracture; overbody or lateral skeletal traction. allows elbow motion while maintaining alignment of a humeral fracture. Traction can overcome muscle spasm. associated with bone or joint disease. An example is Buck traction, which is sometimes recommended for patients with hip injuries. Pronator teres muscle arises by two heads named after their origin sites. The humeral head (superficial head) originates from the medial supracondylar ridge of humerus, located superior to the medial epicondyle of humerus and inferior to the attachment of brachialis muscle. The ulnar head (deep head) originates from the coronoid process of ulna. This area is located between the attachments of.
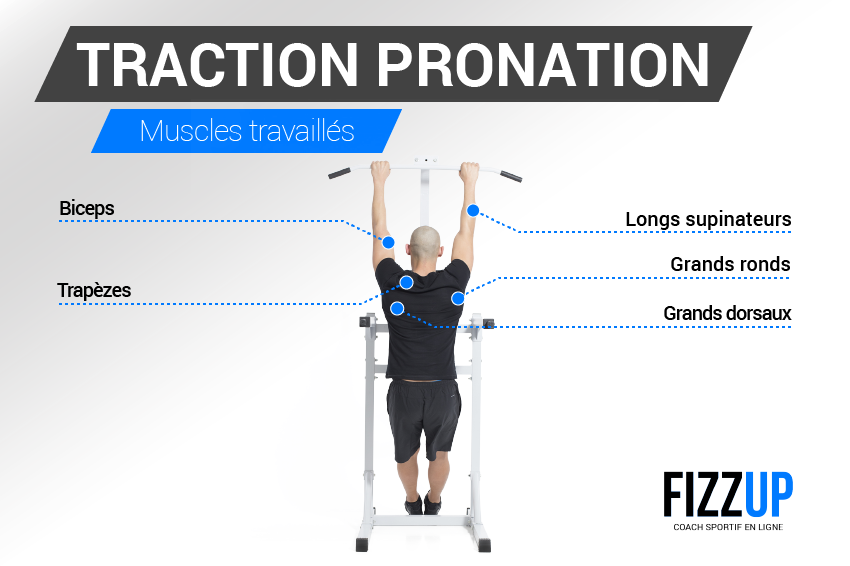
Tractions pronation trapèzes et dos musclés FizzUp
A muscle contracture is a permanent shortening of a muscle or of periarticular tissue [ 1] that is usually secondary to prolonged hypertonic contraction in a concentrated muscle area. Spasticity and contracture are often associated in a variety of nervous system diseases: brachial plexus lesions related to neonatal palsy or adult trauma Repetitive exertion in supination/pronation could increase the risk of forearm diseases due to fatigue. Kinesio taping (KT) is a physical therapy technique that decreases muscle tone and musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) risk. Many assumptions about taping have been made and several studies have considered the taping applications; however, the effect of KT on strength and fatigue of the forearm.
The flexor pronator muscles (FPMs) have been reported to act as dynamic stabilizers against valgus forces in overhead-throwing athletes. Several studies have demonstrated the anatomic, biomechanical, and clinical effects of the FPMs.. to decrease the traction force on the MUCL and lower the risk of elbow throwing injury. There are several. Contents 1 - Pronation traction 2 - Supination Traction 3 - Wide grip traction 4 - Tight grip pull 5 - Mixed grip traction 6 - Power steering 7 - Ballasted traction 8 - Muscle up 9 - One arm pull Conclusion 1 - Pronation traction The pronation traction (or pull-up) is the basic version of this exercise.
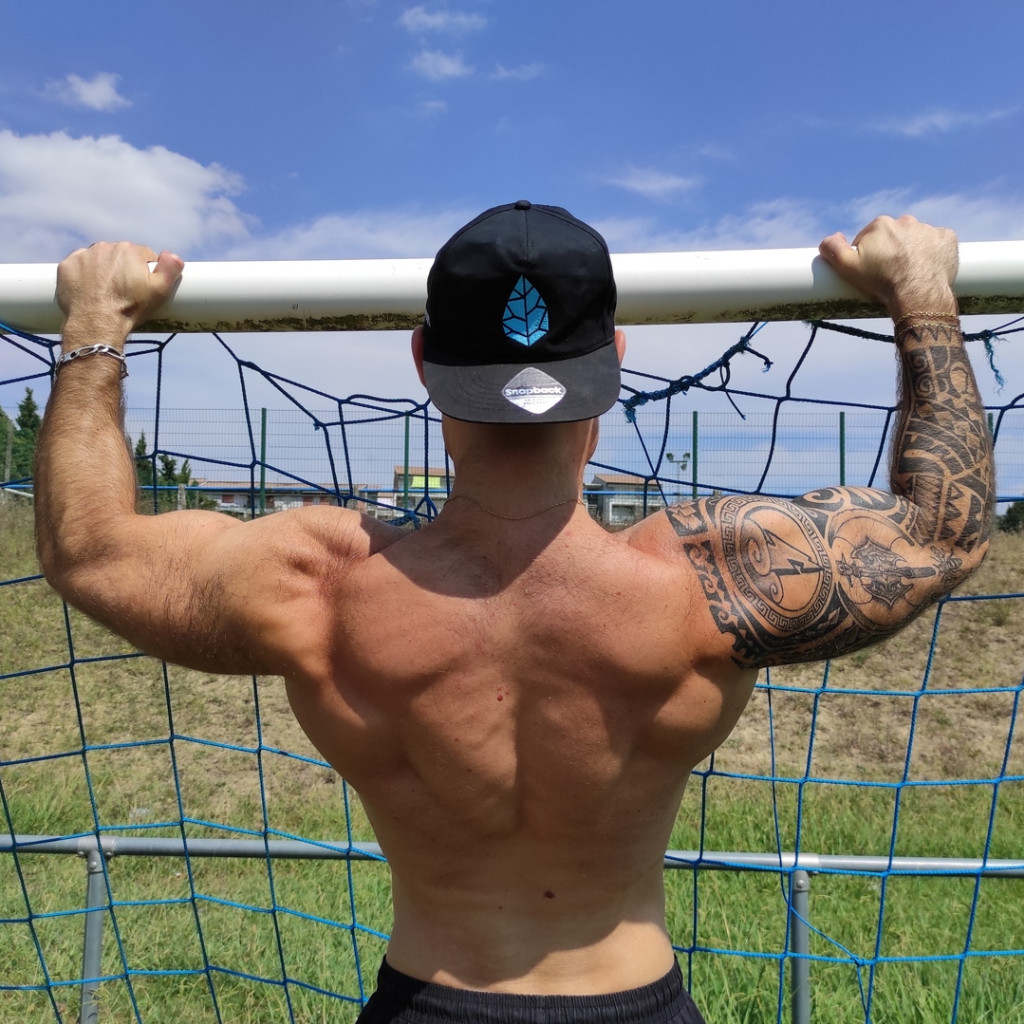

Traction pronation, comment progresser sans douleurs
Pronation allows you to use the supinator, pronator and forearm muscles. Therefore, thanks to the anatomy of the hand muscles and tendons, you can work in different ways. Here are the different outlets: Pronation It refers to the movement and position of the arm that corresponds to the palm of the hand facing the ground (hand pronation). Les tractions en pronation sont un exercice de base, poly-articulaire, sollicitant principalement les muscles du dos : grand dorsal, grand rond, rhomboïdes et trapèzes, notamment les portions moyennes et inférieures. Secondairement, le biceps brachial, le brachial et le brachio-radial.




