In German, there are four different forms or categories (cases), called Fälle or Kasus. Two of these cases are the nominative and the accusative. der Nominativ: The subject is always in the nominative case. The articles take the form: der/ein, die/eine, das/ein, die/-. der Akkusativ: Most objects are in the accusative case. The German Cases. Right, let's get stuck into the heart of the German language, the cases. There are four cases in the German language: nominative, accusative, dative and genitive. The cases are an important part of German grammar as they are responsible for the endings of adjectives, indefinite articles and when to use which personal pronoun.
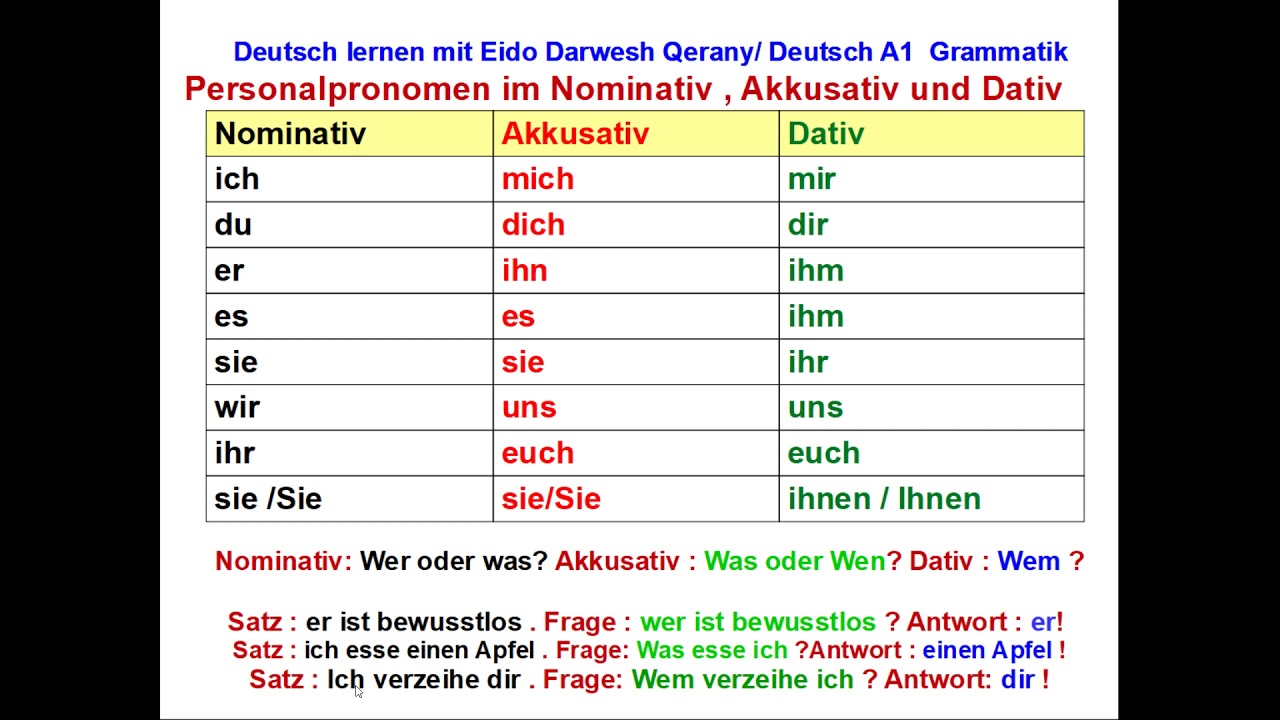
Nominativ, Akkusativ , Dativ تعليم اللغة الالمانية الدرس السادس قواعد YouTube
the subject (Nominativ) does the direct object (Akkusativ) related to the indirect object (Dativ) examples: Den Brief, kannst du (ihn) (mir) bringen, kannst du (ihn) (mir) schreiben? Verbs with Genitiv: rarely used, usage sounds a bit stiltet, often written language, point out to a reason or origin, have often also an Akkusativ version: The Dative Case (Der Dativ or Der Wemfall) The dative case is a vital element of communicating in German. In English, the dative case is known as the indirect object. Unlike the accusative, which only changes with the masculine gender, the dative changes in all genders and even in the plural. The pronouns also change correspondingly. The adjective endings - en, - e, and - es correspond to the articles den , die, and das respectively (masc., fem., and neuter). Once you notice the parallel and the agreement of the letters n , e , s with den , die , das, it makes the process a little clearer. Many German learners find the DATIVE (indirect object) case to be intimidating, but. Is the verb a dative verb? If so, the object will be in the dative. 4. If none of the other conditions apply, then you need to determine which noun in the sentence is the subject, and put that in nominative. Then look for a direct object (put in accusative) and indirect object (put in dative).

Nominativ / Akkusativ / Dativ Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (2) A2 Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (3) B1 Personalpronomen - Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ (4) B1; A1 Beginner A2 Elementary B1 Intermediate B2 Upper intermediate C1 Advanced. Grammar Tenses Verbs Verb Conjugator Nouns and Articles Pronouns. 3. Is the verb a dative verb? If so, the object will be in the dative. 4. If none of the other conditions apply, then you need to determine which noun in the sentence is the subject, and put that in nominative. Then look for a direct object (put in accusative) and indirect object (put in dative). The four German cases are nominative, accusative, dative, and genitive. The nominative case is used for sentence subjects. The subject is the person or thing that does the action. For example, in the sentence, "the girl kicks the ball", "the girl" is the subject. The accusative case is for direct objects. The Nominative Case (Nominativ) is the Basic form of the Noun and describes the Subject of the sentence (the Person or Thing that is acting or being talked about).. Akkusativ (Accusative) Dativ (Dative) Genitiv (Genitive) The following things need to be adjusted (declined) based on the case:
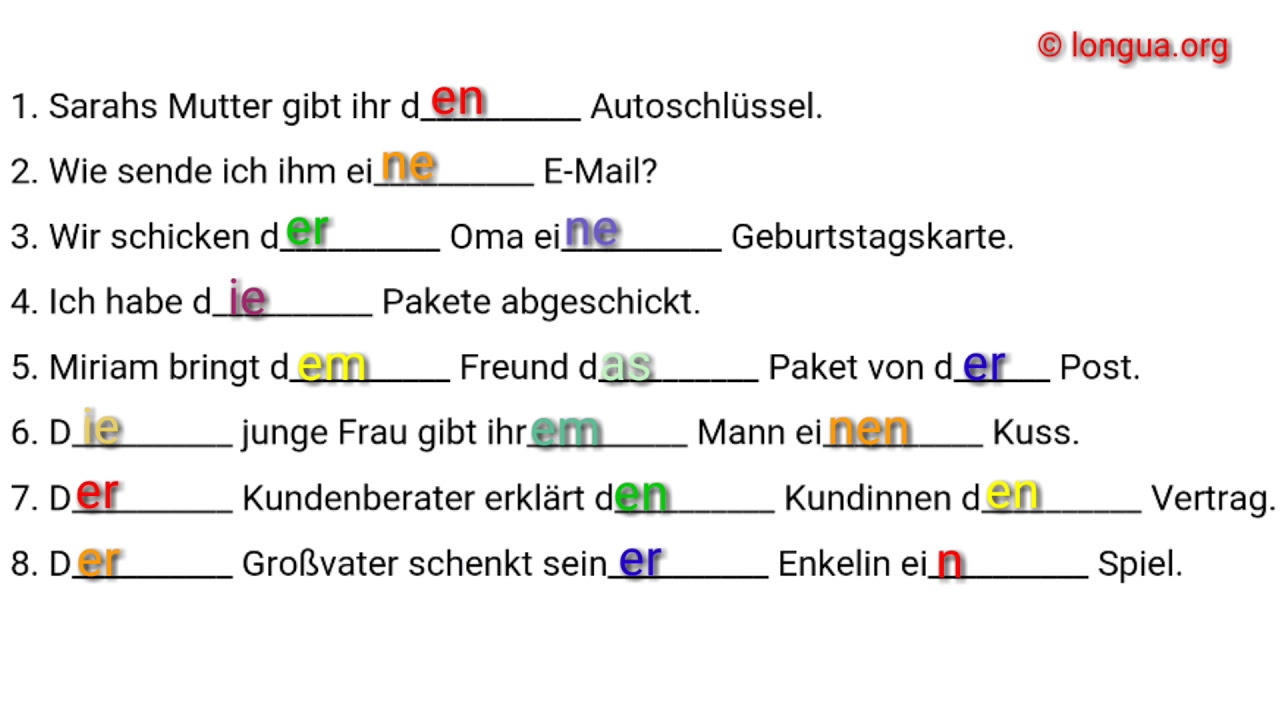
A1, A2, B1 Übungen Deutsch lernen Nominativ, Akkusativ, Dativ Artikel, der, die, das, den
German has "only" 4 cases: Nominative (Nominativ) Accusative (Akkusativ) Dative (Dativ) Genitive (Genitiv) Other languages have a way more! Hungarian: 18 cases. Finish: 15 cases. So take it positive and appreciate that you only have to learn four cases. The Basics - Nominativ, Akkusativ oder Dativ? (Oder Genitiv?) To be able to follow this step-by-step guide you should have gone through all of the following topics already: The 4 German Cases (Nominative, Accusative, Dative und Genitive) Prepositions; Verbs with Complements; This guide is a summary of all the rules in a way that is easy to put.
We'll demystify the four cases with German preposition charts and other essential tools. Stay tuned to learn about: The nominative case, which focuses on the subject of a sentence. The accusative case, which deals with the direct object. The dative case, which highlights the indirect object. The genitive case, which shows possession and other. But in the first sentence, the man ("he") is nominative, whereas in the second sentence, the man (now "him") is accusative. The change in cases from nominative to accusative means that the pronoun referring to the man changes. Let's look at this in a bit more detail now, so that you can figure out the difference between the German.

SOLUTION Th nominativ akkusativ dativ Studypool
Relativpronomen - Nominativ/Akkusativ/Dativ (1) B1 Relativpronomen - Nominativ/Akkusativ/Dativ (2) B1 Relativpronomen - alle (1) C1 Relativpronomen - alle (2) C1; A1 Beginner A2 Elementary B1 Intermediate B2 Upper intermediate C1 Advanced. Grammar Tenses Verbs Verb Conjugator Nouns and Articles Pronouns. Akkusativ The accusative case. As you may have heard before, there are 4 grammar cases in German: nominative (Nominativ), accusative (Akkusativ), dative (Dativ) ,and genitive (Genitiv). Even though English does not have declensions, German cases have some correspondences with our English grammar features.




