Narentanians (S) Online historical atlas showing a map of Europe at the end of each century from year 1 to year 2000: Complete Map of Europe in Year 800. Map information sources. 800 AD Charlemagne- Emperor Of The West- Charlemagne was crowned Emperor of the West by Pope Leo III on December 25th — Christmas Day — in St. Peters Church. Pope Leo allowed Charlemagne to clear himself of a series of charges. The coronation of Charlemagne represented an irrevocable breach between Constantinople.
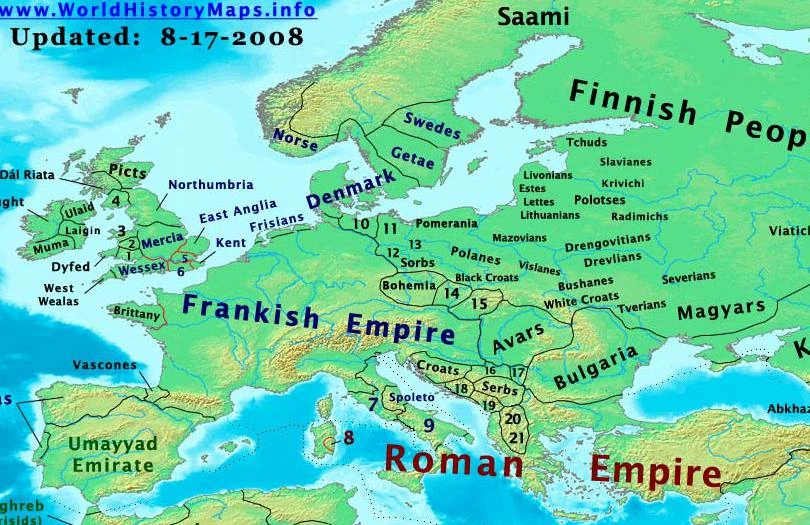
Image Europe800ad.jpg Wiki Atlas of World History Wiki FANDOM powered by Wikia
World History 800-900 AD. 800 AD Charlemagne- Emperor Of The West - Charlemagne was crowned Emperor of the West by Pope Leo III on December 25th -- Christmas Day -- in St. Peters Church. Pope Leo allowed Charlemagne to clear himself of a series of charges. The coronation of Charlemagne represented an irrevocable breach between Constantinople. Europe by cartographer Abraham Ortelius in 1595. The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD 500), the Middle Ages (AD 500 to AD 1500), and the modern era (since AD 1500).. The first early European modern humans appear in the fossil record about 48,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic Era. The time between the 8th and 11th centuries (c. 800-1000) is assigned to the early Middle Ages generally, even by those who extend. For almost a thousand years, Rome was the most politically important, richest and largest city in Europe. Around 100 AD, it had a population of about 450,000,. History of Europe - Medieval, Feudalism, Crusades: The period of European history extending from about 500 to 1400-1500 ce is traditionally known as the Middle Ages. The term was first used by 15th-century scholars to designate the period between their own time and the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The period is often considered to have its own internal divisions: either early and late.

Europe in 800 AD Maps on the Web
The Iron Age was a time of dramatic change for the people of Britain and Europe. Iron replaced bronze as the material used to make tools and weapons, while religion, art, daily life, economics and politics changed dramatically. The story of these civilisations (known to the Greeks and Romans as Britons, Celts, Germans and Iberians) and their. Shutterstock. Life as a Viking in 800 AD was about more than making a living at home and surviving to see the next day. According to The History Association, that was the year that kicked off the Viking Age, and by 1150, around 200,000 Vikings had said goodbye to their homeland and set off into the world. 800. Year 800 ( DCCC) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar, the 800th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 800th year of the 1st millennium, the 100th and last year of the 8th century, and the 1st year of the 800s decade. The most recent millennium of European political history was wrought with war and conquest. Borders shifted; empires rose and fell. In the video above we see Europe's evolution from 1000 A.D. to.

Historical map of Europe in the year 800 AD Historical maps Pinterest
East-Anglia. Powys. Northumbria. Gwynedd. Strathclyde. Califate of Baghdad. Kingdom of the Danes. Gwent. Historical Atlas of Europe, complete history map of Europe in year 800 showing the major states: Eastern Roman Empire, Emirate of Cordoba, Kingdom of Maghreb, Bulgarian Khanate, Papal States, Khanate of the Khazars and Asturias and Galicia. Europe is the world's second-smallest continent in terms of area, covering about 10,400,000 square kilometres (4,010,000 sq mi) or 2.0% of the Earth's surface. The only continent smaller than Europe is Australia. In terms of population, it is the third-largest continent (after Asia and Africa) with a population of some 710,000,000 or about 11%.
The Viking Raids, a.d. 800-1150OverviewThe Vikings, or Norsemen, of Scandinavia, were the dominant sea power in Europe from about a.d. 800 to 1150, exploring the coastlines of Europe, the British Isles, and North Africa. Source for information on The Viking Raids, A.D. 800-1150: Science and Its Times: Understanding the Social Significance of Scientific Discovery dictionary. History of Europe - Migration, Population, Ethnicity: For the continent as a whole, the population growth under way by 1500 continued over the "long" 16th century until the second or third decade of the 17th century. A recent estimate by the American historian Jan De Vries set Europe's population (excluding Russia and the Ottoman Empire) at 61.6 million in 1500, 70.2 million in 1550, and.

Short History of Europe
"Little is known of the early part of this period in Scandinavia and eastern Europe. Against the hardship of climate and topography, people in both regions establish a way of life but interact little with the centers of civilization to the south and west. By the late eighth century, however, bands of Scandinavians are active throughout Europe, raiding wealthy monasteries and sailing as far. Since the late nineteenth century, the central European Iron Age has been divided into two sequential periods named after important archaeological sites. The earlier period (c. 800-480 b.c.) is known as the Hallstatt period. The later period (c. 480-1 b.c.) is known as the La Tène period and is characterized by a very distinctive style of.



