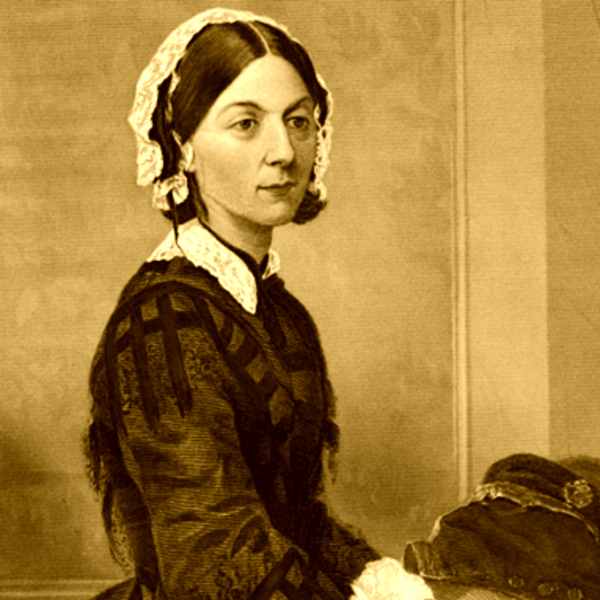Origin The effect is named for Florence Nightingale, a pioneer in the field of nursing in the second half of the 19th century. Due to her dedication to patient care, she was dubbed "The Lady with the Lamp" because of her habit of making rounds at night, previously not done. Her care would forever change the way hospitals treated patients. Stendhal syndrome, Stendhal's syndrome or Florence syndrome is a psychosomatic condition involving rapid heartbeat, fainting, confusion, and even hallucinations, [1] allegedly occurring when individuals become exposed to objects, artworks, or phenomena of great beauty. [2]
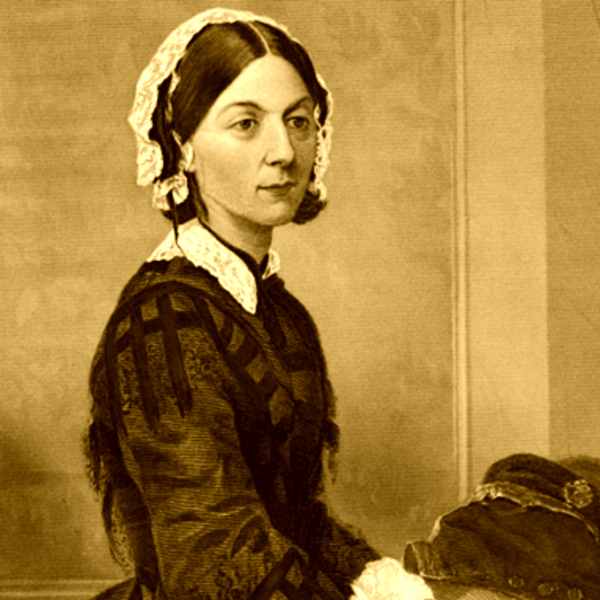
Florence Nightingale, pioneira da ciência na saúde Questão de Ciência
The Florence Nightingale Effect explains why caregivers sometimes develop romantic and/or sexual feelings for their patients. Also known as Nightingale Syndrome, it is sometimes used to explain why caregivers show empathy and compassion for patients, even if there aren't any romantic or sexual overtones. Recommended videos Powered by AnyClip The Florence Nightingale Effect (also referred to as Nightingale Syndrome) is a pop-culture reference to the real nurse, Florence Nightingale, who treated her patients with care and compassion. 25 October, 2017 The Florence Nightingale Syndrome is also referred to as the Florence Nightingale Effect 1 2 3. This syndrome happens when an individual caring for another individual develops romantic feelings for them. ; 12 May 1820 - 13 August 1910) was an English , statistician and the founder of modern . Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during the , in which she organised care for wounded soldiers at She significantly reduced death rates by improving hygiene and living standards.

The Life and Legacy of Florence Nightingale The Historic England Blog
The purpose of this article is threefold: (a) to discuss the facts that point to the cause of Nightingale's Crimean fever as brucellosis, (b) to show that her debilitating illness for 32 years (1855-1887) was compatible with the specific form of chronic brucellosis, and (c) to present new evidence that she was still having severe symptoms in Dec. Florence Nightingale (born May 12, 1820, Florence [Italy]—died August 13, 1910, London, England) British nurse, statistician, and social reformer who was the foundational philosopher of modern nursing. Nightingale was put in charge of nursing British and allied soldiers in Turkey during the Crimean War. Arrival at Scutari On 21 October 1854, Florence and her party of nurses left London. They crossed the Channel and travelled through France to Marseilles. From there they sailed to Constantinople (now Istanbul), arriving on 3 November. At Scutari, near Constantinople, the conditions were dire. Florence Nightingale (1820-1910), known as "The Lady With the Lamp," was a British nurse, social reformer and statistician best known as the founder of modern nursing. Her experiences as a nurse.

Biography of Florence Nightingale British nurse
In the summer of 1856 Florence Nightingale sailed home from war furious. As the nursing administrator of a sprawling British Army hospital network, she had witnessed thousands of sick soldiers. Exploring Nightingale's characteristics of EI such her confidence, determination, integrity and compassion, her teachings and beliefs can transcend time to mold successful nurses more than a century later. "The voice of a leader. It is as resounding as the heart it encourages, as far-reaching as the change it invokes.
The Florence Nightingale effect therefore represents a novel contribution to the literature as a new approach to understanding the role of recognizing suffering for positive occupational identities.. The burn-out syndrome in the day care setting. Child Care Q. 6 100-113. 10.1007/bf01554696 [Google Scholar] Maslach C., Schaufeli W. B. Famous Scientists Women's History Florence Nightingale Florence Nightingale was a trailblazing figure in nursing who greatly affected 19th- and 20th-century policies around proper medical.

A Crutch With Legs How Nightingale Syndrome Impacted My View of Dating by Dawn Johnson
Florence Nightingale ( Figure 1 ), the founder of modern nursing of professional nursing, was born in Florence, Italy, on 1820, in an English family; she was named of the city of her birth. Florence learned mathematics, language, philosophy and religion (all subjects that later influenced on her work) from her father ( 1 ). Figure 1. Florence Nightingale Syndrome refers to a concerning phenomenon where caregivers develop inappropriate romantic or sexual attraction to patients under their care. While not a recognized psychological condition, this controversial syndrome raises serious ethical questions and underscores the need for clear professional boundaries.