Golgi's method is a silver staining technique that is used to visualize nervous tissue under light microscopy. The method was discovered by Camillo Golgi, an Italian physician and scientist, who published the first picture made with the technique in 1873. [1] Golgi staining is a classical technique based on a deposition of metal precipitate in a random set of neurons. Despite their versatility, Golgi methods have limitations that largely precluded.
Structure of a Neuron Owlcation
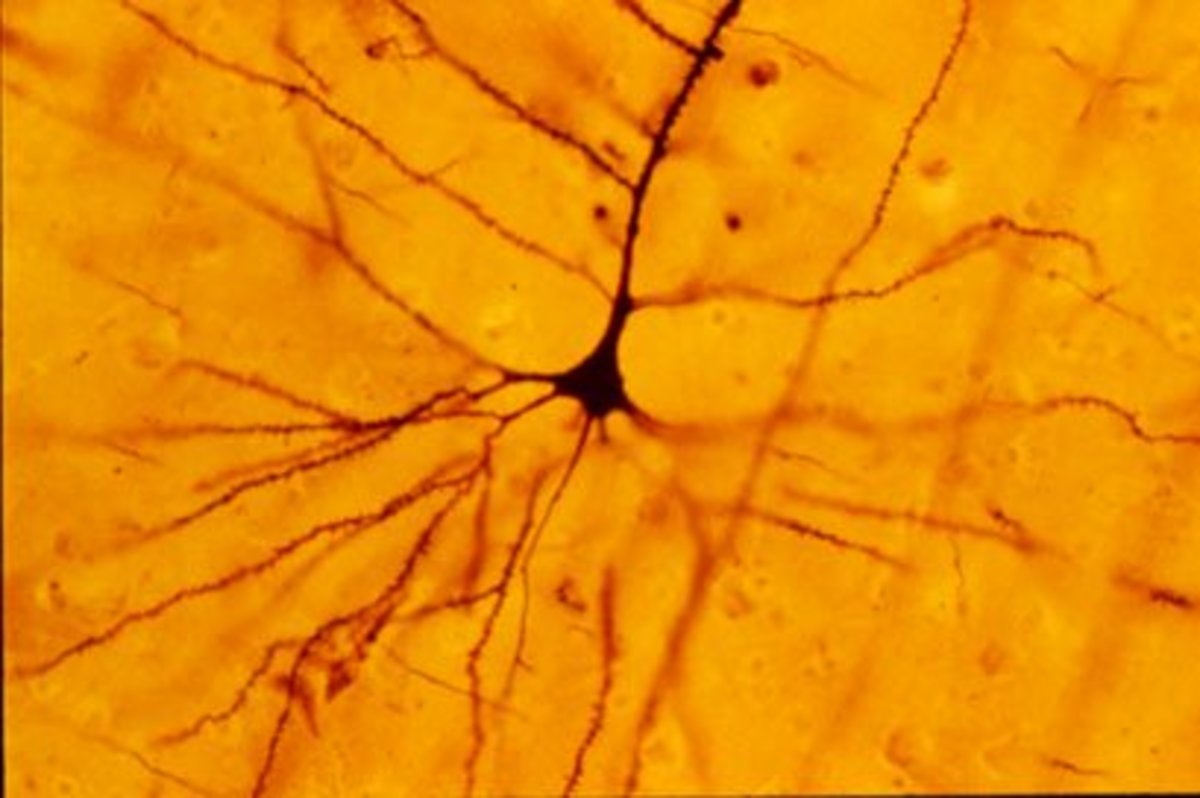
Golgi needed a staining technique to reveal neurons in their entire, undamaged form to confirm his reticular theory. Reticular theory stated that the entire nervous system was a continuous network of cells without gaps or synapses in between the cells. Golgi used his stain to characterize the structure of different types of neurons and discovered a new cell organelle, the Golgi Apparatus. Scientists still use the Golgi stain today, more than 170 years after its advent. Under the microscope, scientists can see details as fine as dendritic spines on Golgi-stained neurons. About the Author The Golgi stain has an important place in the history of neuroscience. In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, Santiago Ramón y Cajal used this technique for his seminal studies of the cellular morphology of the nervous system. Golgi Staining A major advancement in the study of neuronal morphology came about in the late 1800s.

Photomicrographs of Golgistained neurons in primary motor (AC,F,G)... Download Scientific
Silver impregnation identification of Golgi bodies was discovered in owl optic nerve. Staining reagents since the late 1800s were widely used across all disciplines and for nerve tissue and became a key contributor to advancement in nerve-related research. Discovered already by Golgi ( 1873 ), the non-invasive Golgi staining method is far from out-of-date, and it facilitates an analysis of neuronal morphology with axonal and dendritic arborization and spines through visualization of only a low percentage of neurons (1-3%). Golgi staining allows for the analysis of neuronal arborisations and connections and is considered a powerful tool in basic and clinical neuroscience. The fundamental rules for improving neuronal staining using the method are not fully understood; both intrinsic and extrinsic factors may control the staining process. PMID: 11624294 10.1076/jhin.8.2.132.1847 The black reaction, invented in 1873 by Camillo Golgi (1843-1926, was the first technique to reveal neurons in their entirety, i.e. with all their processes. This important development passed unnoticed at first and only received wide international attention after a long delay.

Representative images of Golgistained pyramidal neurons in hippocampal... Download Scientific
Golgi staining involves impregnation of neurons with metals and can stain the whole neuron, including the soma (Simons and Woolsey, 1984; Patrick and Anderson, 1995; Gibb and Kolb, 1998 ), axon (Faherty et al., 2003; Marín-Padilla et al., 2003 ), and dendrites (Zhang et al., 2011; Koyama et al., 2013; Levine et al., 2013 ). Highlights We describe a simple modification of the Golgi-Cox method to differentially stain neurons and glia. If the rat brain or brain tissue block was exposed to a fixative at any stage, glial cells were stained, whereas in its absence neurons were stained. Same brain (different portions) may be used for differential staining of neurons and glia. Staining was achieved in less than 48 h.
Golgi staining was first discovered by Camillo Golgi in 1873, called the "black reaction," and to this day remains a reliable method to assess neuronal cytoarchitecture.. (PSD95) for postsynaptic terminals (or dendritic spines). These do not, however, offer the unique advantage of Golgi in staining the entire neuron structure including. The Golgi-Cox method has been one of the most effective techniques for studying the morphology of neuronal dendrites and dendritic spines. However, the reliability and time-consuming process of Golgi-Cox staining have been major obstacles to the widespread application of this technique. To overcome.

Photomicrographs of Golgistained mouse cortical neurons from slices.... Download Scientific
The neuron doctrine was based on two contributions; Golgi's stain and Cajal's histological studies. The neuron doctrine was named and popularized by Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz [ 3 ], who coined the name neuron to refer to the nerve cell. The early background: nerve fibres and nerve cells During the years, Golgi technique has undergone many modifications, enhancements and refinements, in order to attain the maximal visualization of neurons and neuronal processes, the minimal precipitations and the reasonable abbreviation of the total time that required for the procedure (Zhang et al., 2003).




