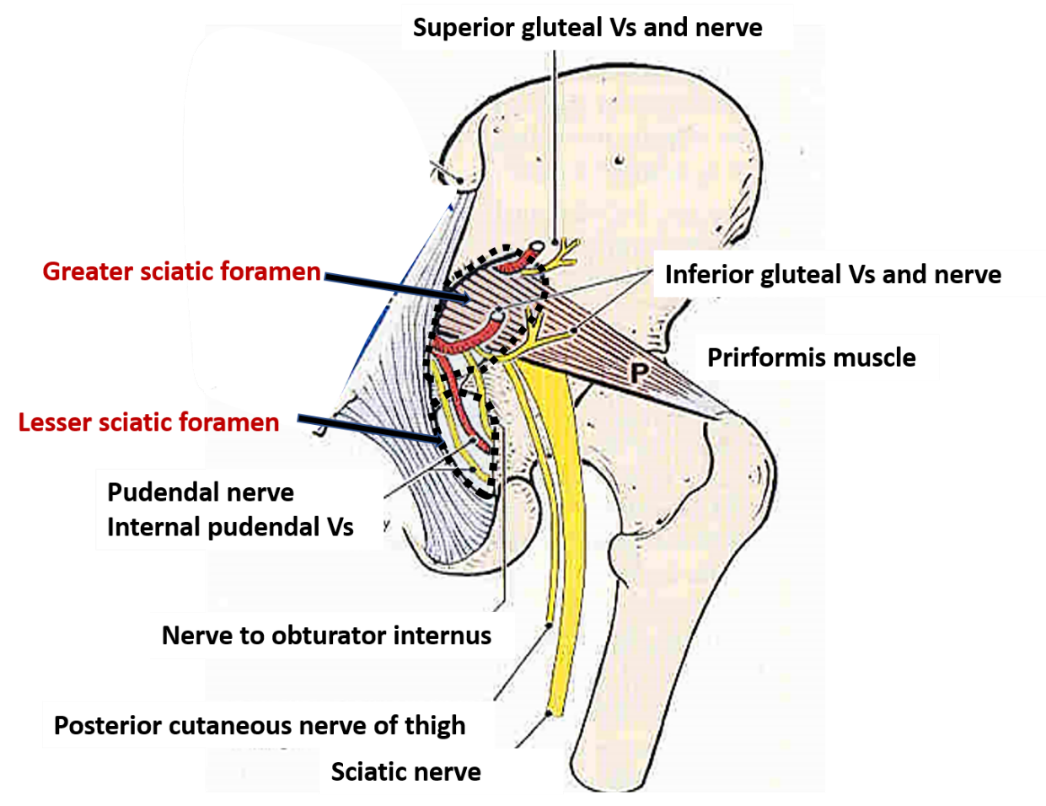
The greater and lesser sciatic foramina are two openings in the posterior aspect of the pelvis. The greater sciatic foramen is larger and is separated from the lesser sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the greater sciatic foramen and lesser sciatic foramen - their borders and contents. The greater sciatic foramen is a large osteoligamentous foramen within the pelvis that is a major conduit of neurovascular structures from the pelvis to the lower limb.The greater sciatic foramen is separated from the smaller lesser sciatic foramen below by the sacrospinous ligament.. Gross anatomy Boundaries. In a clockwise fashion, its boundaries include:
Greater, Lesser Sciatic Foramen , Structures passing through them , Anatomy QA
Greater sciatic foramen. The greater sciatic foramen is an opening ( foramen) in the posterior human pelvis. It is formed by the sacrotuberous and sacrospinous ligaments. The piriformis muscle passes through the foramen and occupies most of its volume. The greater sciatic foramen is wider in women than in men. Sciatica is a type of nerve pain, which is usually a burning, stabbing or shooting feeling. It radiates from your buttock down the back of your leg. It often gets worse when you walk, cough, strain on the toilet or go up stairs. Most people only have symptoms in one leg. You may also feel lower back pain. You might notice pins and needles. Greater sciatic foramen: an opening bounded by the posterior border of the iliac bone anterosuperiorly,. Lesser sciatic foramen: an opening bounded by the ischial body anteriorly, spine of the ischium and sacrospinous ligament superiorly, and the sacrotuberous ligament posteriorly. Its contents include the tendon of obturator. The sciatic nerve emerges from the greater sciatic foramen below the piriformis. It divides into the (medial) tibial and (lateral) common fibular divisions. The septum of Compton-Cruveilhier separates the two divisions. The tibial division innervates the posterior half of the adductor magnus, the semitendinosus, the semimembranosus.

Greater Sciatic Foramen Anatomy Lecture for Medical Students USMLE Step 1 YouTube
The greater sciatic foramen is a complete opening found along the posterior border of the hip bone or ilium. It is formed by the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments in the lateral wall of the pelvis, which transform the incomplete greater sciatic notch into a full-fledged foramen.The greater sciatic foramen is bounded by several structures:The antero-superior boundary is formed by the. This article reviews the relevant anatomy, imaging features on computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and management of common processes involving the sciatic foramen. The anatomy of the sciatic foramen is complex and provides an important conduit between the pelvis, gluteus, and lower extremity. This paper reviewed the anatomy, common pathologies, and imaging features of this region. a dorsal surface that is continuous superiorly with the iliac gluteal surface and inferiorly forms the large ischial tuberosity, which is palpable, usually 5 cm lateral to midline and 5 cm superior to the gluteal skin fold. the posterior border contains the inferior portion of the greater sciatic notch and the lesser sciatic notch, which are. Anatomy. The sciatic foramen is an opening in the posterior pelvis that is divided into greater and lesser sciatic foramina by two ligaments: the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligaments. The sacrospinous ligament is a triangular liga-ment that originates from the lateral cortex of the sacrum and the coccyx.

Illustration of anatomic landmarks of the greater and lesser sciatic... Download Scientific
The superior opening is the greater sciatic foramen. This large opening is formed by the greater sciatic notch of the hip bone, the sacrum, and the sacrospinous ligament. The smaller, more inferior lesser sciatic foramen is formed by the lesser sciatic notch of the hip bone, together with the sacrospinous and sacrotuberous ligaments. when the sciatic nerve bifurcates prior to exiting the greater sciatic foramen, the piriformis is frequently pierced by the common peroneal (fibular) nerve; An accessory piriformis muscle, which is really accessory muscle slip(s), has been rarely described with considerable variability 5:
The superior gluteal nerve leaves the pelvis via the greater sciatic foramen, entering the gluteal region superiorly to the piriformis muscle. It is accompanied by the superior gluteal artery and vein for much of its course. Roots: L4, L5, S1. Motor Functions: Innervates the gluteus minimus, gluteus medius and tensor fascia lata. The inferior gluteal artery supplies the superior and inferior gemelli muscles. The inferior gluteal artery arises from the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery before passing between the second and third sacral segments of the sacral plexus and exiting the greater sciatic foramen under the piriformis to supply the gemelli muscles.

STRUCTURES PASSING THROUGH THE GREATER SCIATIC FORAMEN. MNEMONIC DEVICE YouTube
It is the attachment site for the sacrospinous ligament. Immediately below the ischial spine is a small 'C' shaped concavity known as the lesser sciatic notch, which is the anterior border of lesser sciatic foramen. This foramen is posteriorly bounded by the sacrotuberous ligament and anteriorly by the sacrospinous ligament. The sciatic nerve exiting the greater sciatic foramen along the superior surface of the piriformis muscle (E) The nerve may also divide proximally, where the nerve or a division of the nerve may pass through the belly of the muscle, through its tendons or between the part of a congenitally bifid muscle.




