Hopefully you guys find it useful too. Prissy PRILs get all A's (Ace inhibitors) e.g. lisinopril, monopril. CAL PINES for his girlfriend (calcium channel blockers) Amodopine, felodopine. The SARTAN (sultan) ARBitrarialy (ARB- Angiiotensin II Receptor Blocker) beats his camel e.g Losartan. Of course there are exceptions, but it was still very. Beta Blockers Classification Mnemonics: How to remember in 2 minutesCardioselective drugs:EsmololNebivololBisoprololBetaxololAcebutolol AtenololMetoprolol Ce.

Cardioselective BetaBlockers Mnemonic
Beta Blocker Medications. The drug list for beta blockers is extensive, making it challenging to remember the mechanism of action and pharmacology of each one. Some beta blocker medications are selective for beta-1 receptors, while other beta blockers are non-selective for beta-1 and beta-2 receptors. Atenolol Bispoprolol Betaxolol Celiprolol Esmolol Metoprolol Nebivolol Nebivolol = NO donor Beta blockers with 1st letter from O to Z are Non-selective: Pindolol Propanolol Sotalol Timolol Both alpha and beta blockers: Labetalol, Bucindolol, Carvedilol Beta blockers with Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) or parital agonists Nadolol (Corgard). Nebivolol (Bystolic). Propranolol (Inderal LA, InnoPran XL). When beta blockers are used Beta blockers are not recommended as a first treatment if you have only high blood pressure. Beta blockers are not usually used for high blood pressure unless other medicines, such as diuretics, have not worked well. Published on November 14, 2022 Key takeaways: Beta blockers are medications used to treat high blood pressure and other heart-related conditions. Other uses include treating glaucoma and preventing migraines. There are two groups of beta blockers: selective and non-selective. Selective beta blockers specifically target your heart.

How to remember Cardio Selective Beta Blockers Phartoonz
Health Library / Treatments & Procedures / Beta-blockers Beta-blockers Beta-blockers are a class of medicines most commonly used for problems involving your heart and your circulatory system. They also are sometimes used to treat conditions related to your brain and nervous system. Beta-blockers, as a class of drugs, are primarily used to treat cardiovascular diseases and other conditions. Beta-blockers are indicated and have FDA approval for the treatment of tachycardia, hypertension, myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, essential tremor, aortic dissection, portal hypertension, glaucoma, migraine. migraine. anxiety disorders. hyperthyroidism. tremors. Doctors typically turn to beta-blockers for high blood pressure when other medications, such as diuretics, aren't working or have too many. Beta blockers work mainly by slowing down the heart. They do this by blocking the action of hormones like adrenaline.. If you forget to take a dose of your beta blocker, take it as soon as you remember, unless it is nearly time for your next dose. In this case, just leave out the missed dose and take your next dose as normal..
Betablockers Mnemonics
Beta-blockers can cause some side effects. Dizziness, lightheadedness, feeling faint. Beta-blockers will slow your heart rate (pulse) and lower your blood pressure. If you are dizzy or feel like you might faint, sit or lie down right away. Get up slowly to give your blood vessels time to adjust. Drowsiness or fatigue. Simple and short presentation for classification of beta blockers. Easy to memorize and distinguish the different beta blockers into various types based on c.
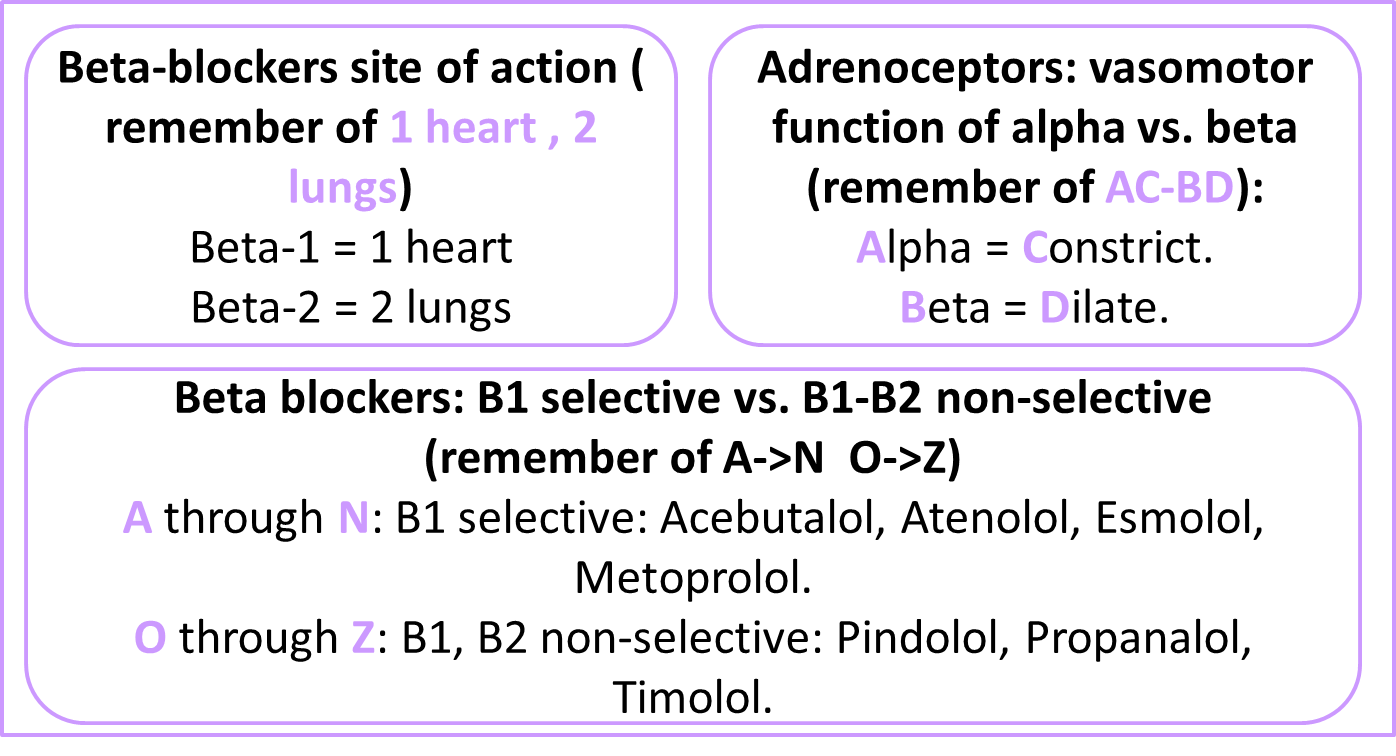
Fortunately, the following tricks work wonders. • Class I Antiarrhythmics are the sodium channel blockers, and these are further classified as Class IA, IB, and IC. To remember these, try Double Quarter Pounder, Lettuce Mayo, Fries Please. Broken down, it looks like this: 1. Class IA = D isopyramide, Q uinidine, and P rocainamide 2. Here are some useful mnemonics to remember the beta-blockers. Beta-blockers site of action ( remember 1 heart , 2 lungs) Beta-1 = 1 heart Beta-2 = 2 lungs Adrenoceptors: vasomotor function of alpha vs. beta (remember ABCD): Alpha = Constrict. Beta = Dilate. Beta blockers: B1 selective vs. B1-B2 non-selective (remember A->N O->Z)

Medicowesome Uses of alpha and beta blockers
Often, we get lucky and the drug class hints at the mechanism of action such as calcium channel blockers, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, etc. but this may not always be the case. Check out some tips and tricks on how to remember the MOA of some other common medications below:⠀ Bisoprolol. Bisoprolol is a selective beta blocker that's used to treat high blood pressure. It's also a preferred beta blocker for heart failure, although this is an off-label use. Bisoprolol only comes in a tablet form. Compared to other beta blockers, bisoprolol stays in the body for a much longer period of time. 7.




