9 Answers Sorted by: 397 Declaring a static variable in Java, means that there will be only one copy, no matter how many objects of the class are created. The variable will be accessible even with no Objects created at all. However, threads may have locally cached values of it. Java and the JVM provide many ways to control memory order, and the volatile keyword is one of them. This tutorial focuses on Java's foundational but often misunderstood concept, the volatile keyword. First, we'll start with some background about how the underlying computer architecture works, and then we'll get familiar with memory order in Java.

Java volatile keyword explained by example,Volatile in java,java volatile vs static,JSR133
What Is a volatile Variable? Unlike other variables, volatile variables are written to and read from the main memory. The CPU does not cache the value of a volatile variable. Let's see how to declare a volatile variable: static volatile int count = 0; 3. Properties of volatile Variables 1. Overview In this tutorial, we'll explore the static keyword of the Java language in detail. We'll find out how we can apply the static keyword to variables, methods, blocks, and nested classes, and what difference it makes. Further reading: The "final" Keyword in Java asking a static variable value is also going to be one value for all threads, then why should we go for volatile? I found following example : Photo by Paul Summers on Unsplash. The Java language specification defines volatile as follows:. In the Java programming language, threads are allowed to access shared variables. To ensure that.
What is Volatile Variable in Java? When to Use it? Example Java67
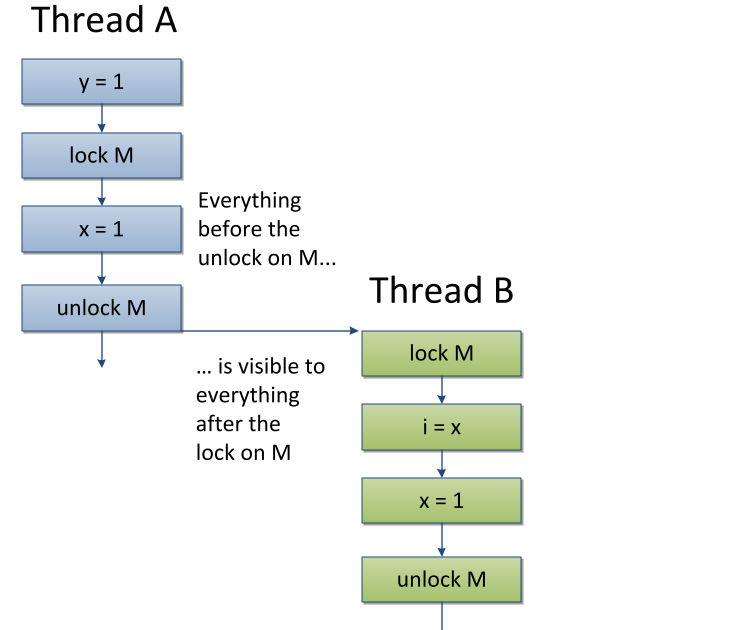
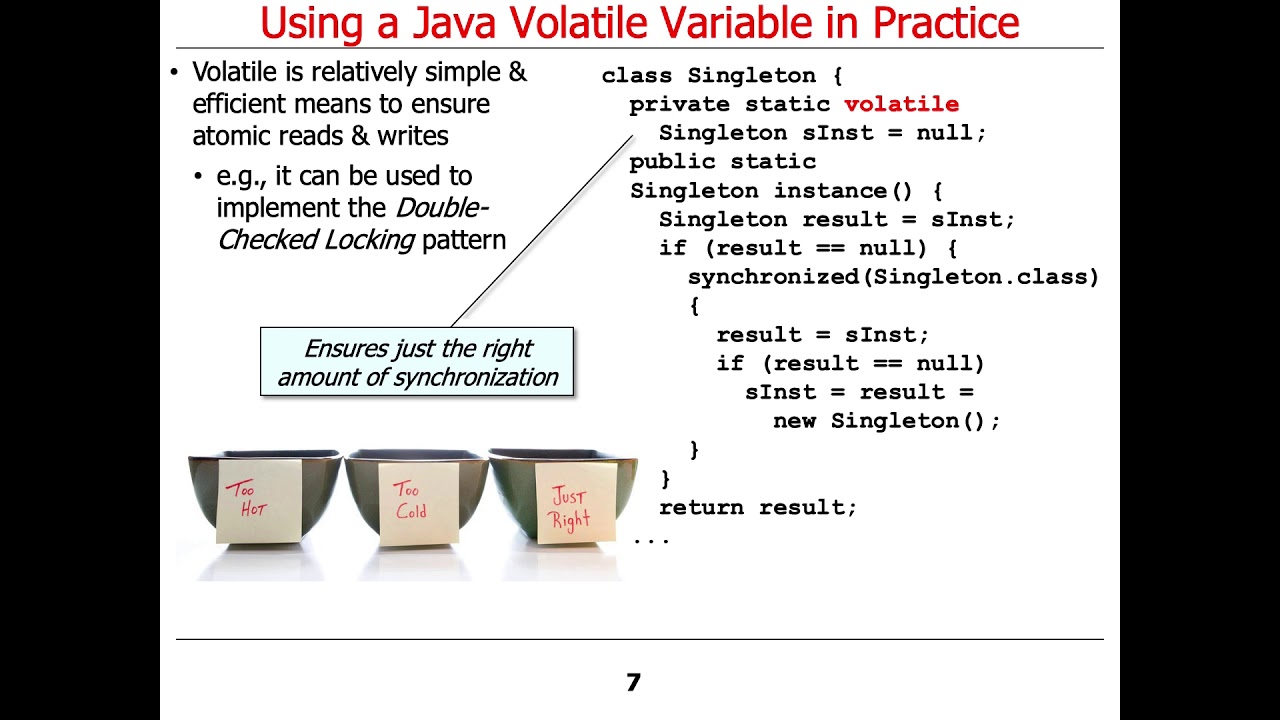
The volatile Keyword. The volatile keyword marks a variable as, well, volatile. By doing so, the JVM guarantees that each write operation's result isn't written in the local memory but rather in the main memory. This means that any thread in the environment can access the shared variable with the newest, up-to-date value without any worry. A Non-Intuative Volatile Feature. volatile on the singletons INSTANCE field is recommended whenever the singleton contains mutable state and is created using the double-checked locking idiom. So. Short answer: volatile is a keyword we can apply to a field to ensure that when one thread writes a value to that field, the value written is "immediately available" to any thread that. To see the constant pool, use the javap class file disassembler included in the JDK. Running javap with the verbose -v option prints a wealth of detail about the class, including the constant pool and the bytecode for all the methods. Running javap -v Hello.class, I get a listing of 83 lines.

Java Static Method, Static Variable and Block with Example JAVA Programming JAVA Tutorial
public class VolatileTest { private static final Logger LOGGER = MyLoggerFactory.getSimplestLogger (); private static volatile int MY_INT = 0; public static void main (String [] args) { volatile transient native 1. static: The static keyword means that the entity to which it is applied is available outside any particular instance of the class. That means the static methods or the attributes are a part of the class and not an object. The memory is allocated to such an attribute or method at the time of class loading.
Volatile keyword is used to modify the value of a variable by different threads. It is also used to make classes thread safe. It means that multiple threads can use a method and instance of the classes at the same time without any problem. The volatile keyword can be used either with primitive type or objects. The Java volatile keyword is used to mark a Java variable as "being stored in main memory". More precisely that means, that every read of a volatile variable will be read from the computer's main memory, and not from the CPU registers, and that every write to a volatile variable will be written to main memory, and not just to the CPU registers.
Java Volatile Variables Example Application YouTube
Volatile vs Static in Java Declaring a static variable in Java, means that there will be only one copy, no matter how many objects of the class are created. The variable will be accessible even with no Objects created at all. However, threads may have locally cached values of it. When we make the variable volatile the values are always read from the main memory and written to the main memory so it is visible to other threads. volatile long someLongValue = 0L; void assign (long value) {. someLongValue = value; // Writes are made to main memory. }




