In biochemistry, the Lineweaver-Burk plot (or double reciprocal plot) is a graphical representation of the Michaelis-Menten equation of enzyme kinetics, described by Hans Lineweaver and Dean Burk in 1934. [1] Another commonly-used plot in examining enzyme kinetics is the Lineweaver-Burk plot, in with the inverse of the reaction rate, \(1/r\), is plotted against the inverse of the substrate concentration \(1/\left[ \text{S} \right]\). Rearranging Equation \(\ref{Eq13.26}\),. Figure 13.12: Linweaver-Burk plot and regression equation for the data.

LineweaverBurk Plot Biochemistry, Enzyme Mcat
The Lineweaver-Burk plot (or double reciprocal plot) is a graphical representation of the Lineweaver-Burk equation of enzyme kinetics, described by Hans Lineweaver and Dean Burk in 1934. This plot is a derivation of the Michaelis-Menten equation and is represented as: Table of Contents Figure 4.9.1: Line-Weaver Burk Plot. For a Lineweaver-Burk, the manipulation is using the reciprocal of the values of both the velocity and the substrate concentration. The inverted values are then plotted on a graph as 1 / V vs. 1 / [ S ]. Because of these inversions, Lineweaver-Burk plots are commonly referred to as 'double-reciprocal' plots. Lineweaver Burk plots show that the Vmax was calculated at 9 nmoles per mg per 30 min, or 1.3 nmoles per pineal per 30 min. From: Serotonin and Behavior, 1973 Add to Mendeley About this page Molecular Aspects of Inhibitor Interaction with PDE4 Siegfried B. Christensen,. Theodore J. Torphy, in Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors, 1996 5 4 Problem To determine the V max from a Lineweaver-Burk plot you would: A Multiply the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept by -1. B Multiply the reciprocal of the y-axis intercept by -1. C Take the reciprocal of the x-axis intercept. D
PPT Chapter 6 Enzymes PowerPoint Presentation ID5143485
double reciprocal plot (e.g., Lineweaver-Burk plot discussed below;. Figure 13.12: Linweaver-Burk plot and regression equation for the data in Example 13.6.-diphenyl oxidase. The following data are for the oxidation of catechol (the substrate) to o-quinone by the enzyme o-diphenyl oxidase. The reaction is followed by monitoring the. Lineweaver-Burke (the "double reciprocal" plot) The Michaelis-Menten equation can be rearranged by taking the reciprocal, to yield: If X = 1/[S] and Y=1/V then this is a linear equation with a slope of K m /V max and a Y intercept of 1/V max; Figure 6.2.3: 1/S and1/V. affect the plots. A comparison between the two graphic representations direct is illustrated here with two "bad" data points (see Fig. 8.16, WWBH). •The same data points are plotted on adjacent Lineweaver-Burk in the left graph of this figure. Two features of the direct linear plot are immediately evident by comparison. The Lineweaver-Burk equation calculator computes the inverse of the initial velocity of an enzyme inhibited reaction INSTRUCTIONS: Enter the following: (Vmax) Maximum Velocity of Reaction in moles/(Liter⋅Seconds) [S] Concentration of Substrate [Km] Michaelis-Menten Constant Inverse Velocity (1/V0): The calculator returns the inverse velocity in seconds-liters per mole (s·L/mol) The Math.

LineweaverBurk Equation Theory and Derivation YouTube
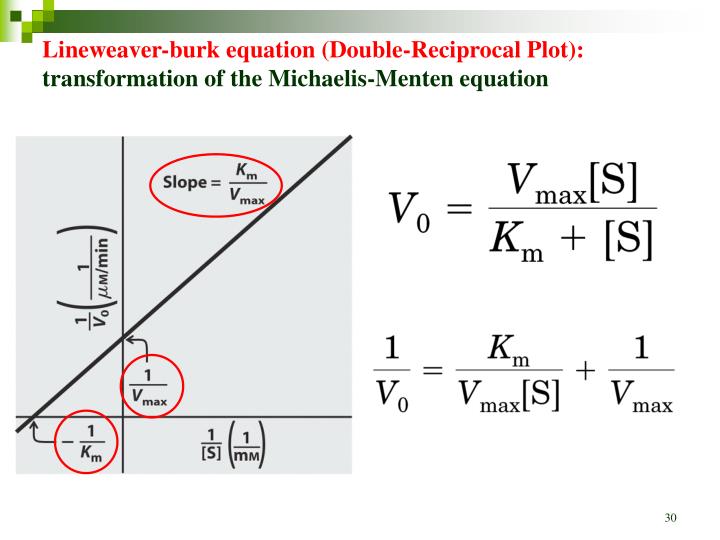
In Lineweaver Burk plots, the slope is equal to KM / Vmax, the x-intercept is equal to -1 / KM, and the y-intercept is equal to 1 / Vmax . The Lineweaver Burk plot is a graphical representation of enzyme kinetics. A. Data fit by nonlinear regression to a hyperbola. B. Data fit to a Lineweaver-Burk reciprocal plot. The gray line shows the fit obtained after omitting the point at the lowest substrate concentration. C. Data fit using the Eadie-Hofstee equation. In each figure, the equation and the resulting k cat and K m values are displayed.
The double reciprocal plot (Lineweaver Burk plot) offers a great way to visualize the inhibition. In the presence of I, just Vm will decrease. Therefore, -1/Km, the x-intercept will stay the same, and \(1/V_m\) will get more positive.. An equation, shown in the diagram above can be derived which shows the effect of the noncompetitive. Lineweaver-Burk analysis is one method of linearizing substrate-velocity data so as to determine the kinetic constants Km and Vmax. One creates a secondary, reciprocal plot: 1/velocity vs. 1/ [substrate].

Lineweaver Burk plot. The data on Xaxis indicate the 1/substrate while... Download Scientific
Lineweaver-Burk Plots. The Michaelis-Menten equation is useful in other ways, too. If we take its inverse, we get a new relationship. That's useful because it's really an expression for a straight line. If we plot 1/v against 1/[S], we get a straight line. The slope is K m /V max and the y intercept is 1/V max. Lineweaver-Burk plot gives a. Lineweaver-Burk plot with data points derived from double-reciprocal transformation, but we'll superimpose a line based upon nonlinear regression analysis, so that it reflects the best possible estimates of K m and V max. A different secondary plot, such as Hanes-Woolf or Eadie-Scatchard, is just as easy to create with Prism.



