WHAT IS CELL MEMBRANE ? The cell membrane (also called the plasma membraneplasma membrane or plasmalemmaplasmalemma) is a biological membrane separating the interior of a cell from the outside environment It appears in thin sections with the electron microscope as a triple-layered structure about 7.5-10 nanometers thick Term coined by C. Membrane functions Membrane structure Membrane fluidity Membrane Structure & Function Membranes serve a wide variety of functions Barriers to separate cells from environment (plasma membrane) and one compartment from another (organelle membranes) Transport - Passive, active, and vesicular transport Sites for enzyme systems, e.g. a) ATP.
PPT Cell Membrane Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4587218
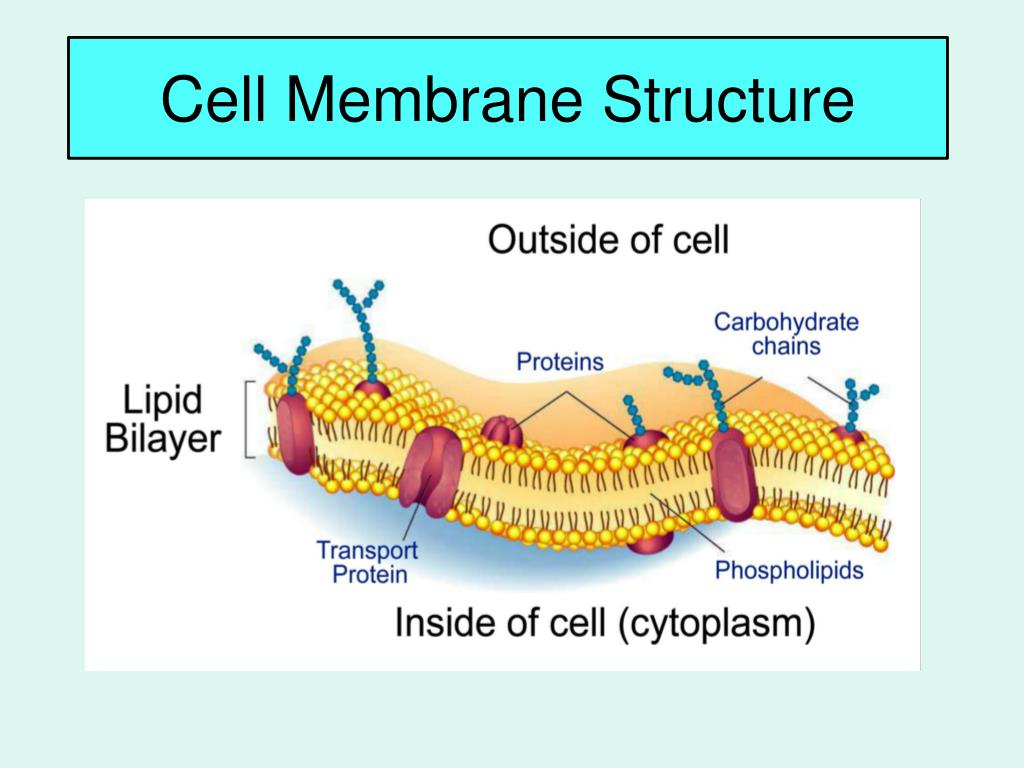
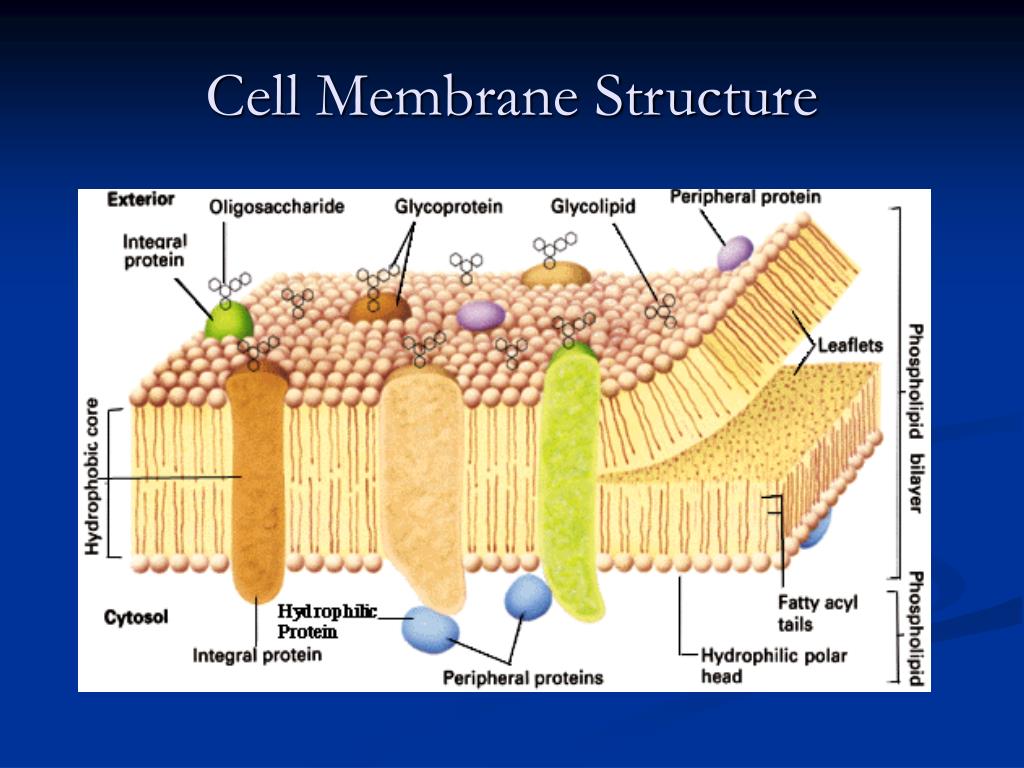
The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins, and, in animal cells, cholesterol. The amount of cholesterol in animal plasma membranes regulates the fluidity of the membrane and changes based on the temperature of the cell's environment. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles. In this way, it is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several. Chapter 4: Cell Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane: Thin barrier separating inside of cell (cytoplasm) from outside environment Function: Isolate cell's contents from outside environment Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell Communicate with other cells Microfilaments or other elements of the cytoskeleton may be bonded to membrane proteins, a function that helps maintain cell shape and stabilizes the location of certain membrane proteins. Proteins that adhere to the ECM can coordinate extracellular and intracellular changes (see Figure 6.29). (d) (e) (f) Glyco- protein Figure 7.9. 19.
PPT Cell Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID436575
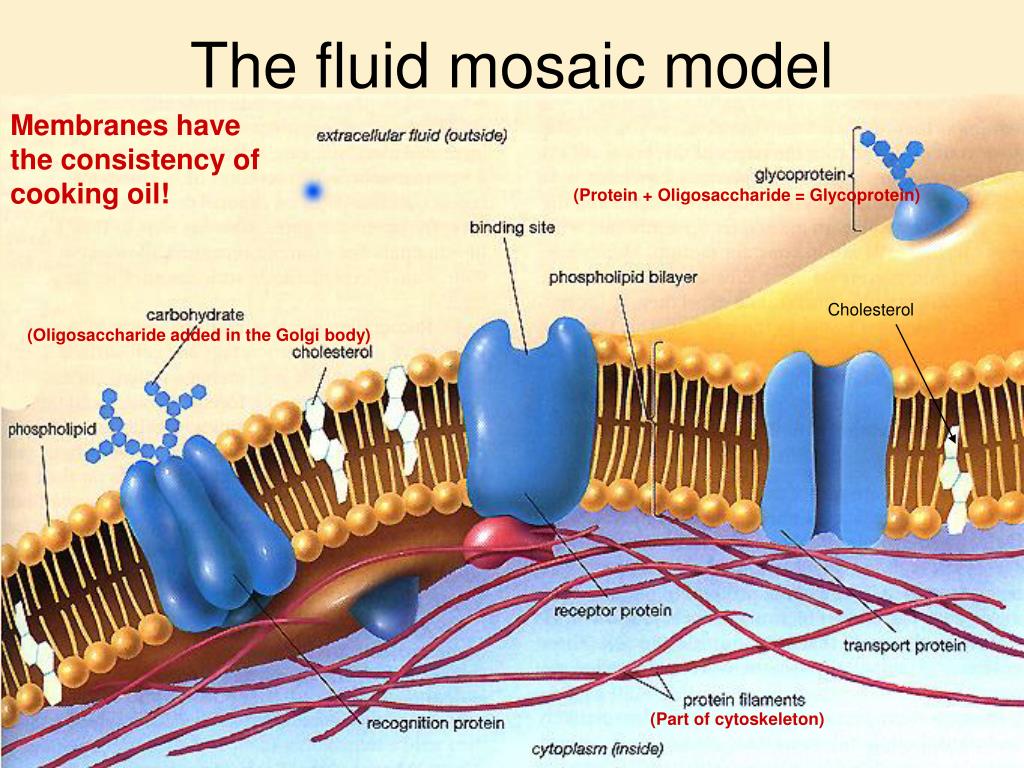
Biologists use a fluid mosaic model to describe a membrane. The kinky tails of many phospholipids, along with cholesterol, found in animal cell membranes, keep the molecules from packing tightly. Thus, the membrane remains fluid, and its components can drift about like party-goers elbowing their way through a crowded room. Bethesda, MD 20894 HHS Vulnerability Disclosure Special proteins inserted in cellular membranes create pores that permit the passage of molecules across them. The bacterial protein shown here uses the energy from light (photons) to activate the pumping of protons across the plasma membrane. Under physiological conditions, membranes are more fluid-like than gel-like. must be fluid for proper function Organisms Can Adjust the Membrane Composition Membrane fluidity is determined mainly by the fatty acid composition and melting point. More fluid membranes require shorter and more unsaturated fatty acids. The fracture plane often follows the hydrophobic interior of a membrane, splitting the phospholipid bilayer into two separated layers. The membrane proteins go wholly with one of the layers. Extracellular layer Cytoplasmic layer APPLICATION A cell membrane can be split into its two layers, revealing the ultrastructure of the membrane's interior.
PPT Membrane Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID825867
PowerPoint Presentation. BCOR 011 Lecture 9: Cell membrane structure Sept 19, 2005 major functions of membrane proteins Proteins embedded and floating in a sea of phospholipids Integral Membrane proteins Membrane proteins and lipids Are synthesized in the ER and Golgi apparatus Evidence for integral membrane proteins: Freeze-Fracture Electron. The Plasma Membrane (Structure & Function) Dr. Tapan Kr. Dutta Panskura Banamali College fHistory of the Plasma Membrane 1665: Robert Hooke 1895: Charles Overton - composed of lipids 1900-1920's: must be a phospholipid 1925: E. Gorter and G. Grendel - phospholipid bilayer 1935: J.R. Danielli and H. Davson - proteins also part, proposed the.
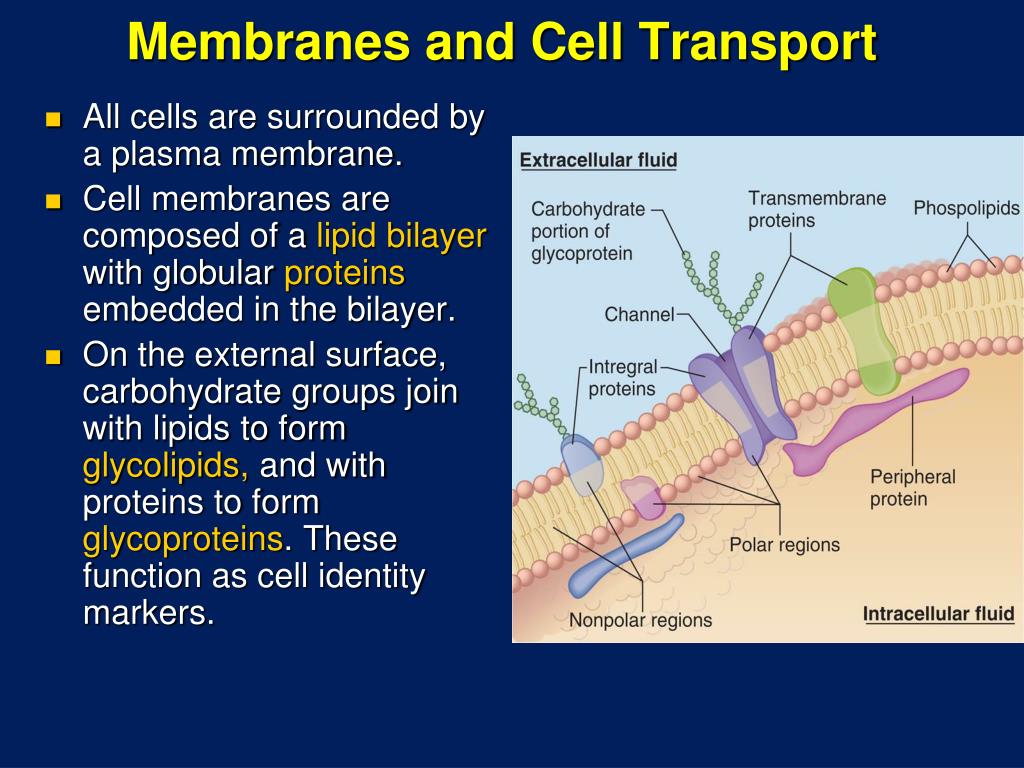
May 25, 2012 620 likes | 1.37k Views Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Function. Membranes organize the chemical activities of cells. The outer plasma membrane forms a boundary between a living cell and its surroundings Exhibits selective permeability Controls traffic of molecules in and out. Membrane Function. Download Presentation Cell Membrane Structure and Function. Membranes and Cell Transport. All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. Cell membranes are composed of a lipid bilayer with globular proteins embedded in the bilayer. Download Presentation membrane protein passive transport processes atp enzymes signal receptor surface molecules cholesterol nonpolar tails
PPT The Cell Membrane PowerPoint Presentation ID501873
Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Structure and Function. Cells must contain a cell membrane, cytoplasm and genetic material. The cell membrane is the EDGE, "boundary of life", while the cytoplasm is the site of all the reactions of life and the genetic material is the information required for life. 736 views • 21 slides membrane, in biology, the thin layer that forms the outer boundary of a living cell or of an internal cell compartment. The outer boundary is the plasma membrane, and the compartments enclosed by internal membranes are called organelles.Biological membranes have three primary functions: (1) they keep toxic substances out of the cell; (2) they contain receptors and channels that allow specific.




