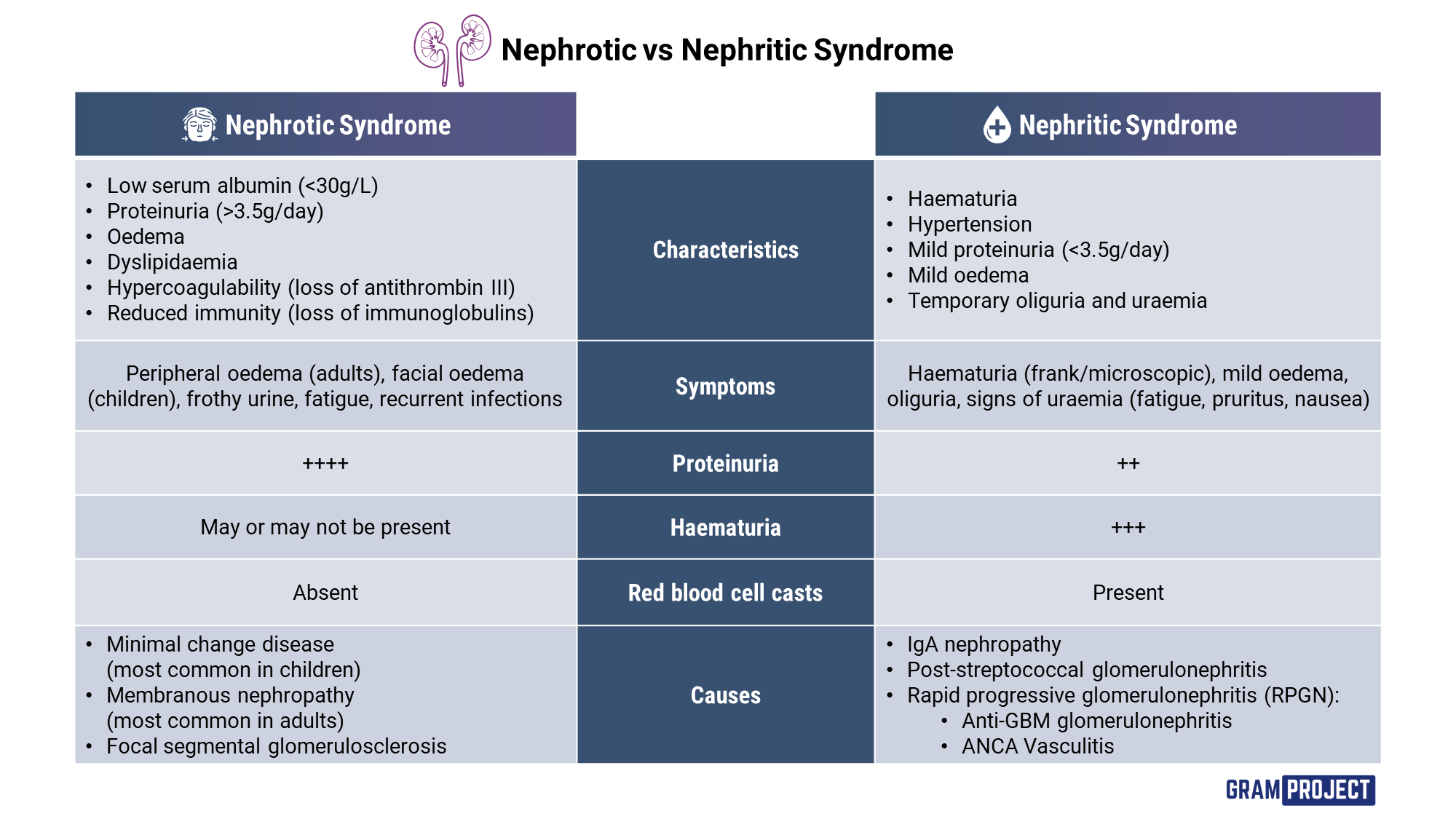
Nephrotic syndrome is a condition involving the loss of significant volumes of protein via the kidneys (proteinuria) which results in hypoalbuminaemia. The definition of nephrotic syndrome includes both massive proteinuria (≥3.5 g/day) and hypoalbuminaemia (serum albumin ≤30 g/L). 1 Clinical features Nephritic syndrome is characterized by inflammation of the glomeruli (glomerulonephritis) and renal dysfunction. The most common cause is immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy, also known as Berger's disease, but other causes include postinfectious glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis.

What is the difference between Nephritic and Nephrotic syndrome MedStudier YouTube
Nephrotic ( neff-rot-ick) syndrome is a condition in which your kidneys release an excessive amount of protein (proteinuria) in your urine (pee). Nephrotic syndrome usually results from a problem with your kidneys' filters (glomeruli). Glomeruli ( glo-mare-yoo-lye) are tiny blood vessels in your kidneys. Nephrotic Syndrome versus Nephritic Syndrome. In: Lerma EV, Berns JS, Nissenson AR. Lerma E.V., & Berns J.S., & Nissenson A.R. (Eds.),Eds. Edgar V. Lerma, et al.eds. CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment: Nephrology & Hypertension. McGraw Hill; 2009. Accessed January 11, 2024. https://accessmedicine.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=372§ionid=39961161 Nephrotic syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes your body to pass too much protein in your urine. Nephrotic syndrome is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in your kidneys that filter waste and excess water from your blood. Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is a clinical syndrome defined by massive proteinuria responsible for hypoalbuminemia, with resulting hyperlipidemia, edema, and various complications. It is caused by increased permeability through the damaged basement membrane in the renal glomerulus, especially infectious or thrombo-embolic.

No Time for Kidneying Around Nephritic vs Nephrotic Syndromes maidoodles Nursing school
Nephrotic syndrome may occur when the filtering units of the kidney are damaged. This damage allows protein normally kept in the plasma to leak into the urine in large amounts, which reduces the amount of protein in your blood. Preview A 5-year-old girl comes to the pediatrician's office because of edema in her lower legs, ankles, and feet. The edema is less apparent in the morning and worsens throughout the day. The patient's mother states that the patient had suffered from an upper respiratory infection the previous week. Nephrotic vs Nephritic Syndrome: How to Spot the Difference Perspective > The Curbsiders COMMENTARY Nephrotic vs Nephritic Syndrome: How to Spot the Difference Matthew F. Watto, MD;. nephritic syndrome (low-level proteinuria , microhematuria , oliguria , and hypertension ) or nephrotic syndrome (high-level proteinuria and generalized edema

Nephritic vs Nephrotic Syndrome Step 1 If the patient GrepMed
Tests and procedures used to diagnose nephrotic syndrome include: Urine tests. A urinalysis can reveal abnormalities in your urine, such as large amounts of protein. You might be asked to collect urine samples over 24 hours. Blood tests. A blood test can show low levels of the protein albumin and often decreased levels of blood protein overall. Nephrotic syndrome results from damage to the kidneys' glomeruli. These are the tiny blood vessels that filter waste and excess water from the blood and send them to the bladder as urine. Your glomeruli keep protein in the body. When they are damaged, protein leaks into the urine. Healthy kidneys allow less than 1 gram of protein to spill into.
The nephritic syndrome can be due to acute proliferative glomerulonephritis (postinfectious and infection associated), crescentic glomerulonephritis, and proliferative lupus glomerulonephritis. In children, the most common cause of acute glomerulonephritis is post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. [1] Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms indicating damage to the glomerular filtration barrier. It is characterized by massive proteinuria ( > 3.5 g/24 hours ), hypoalbuminemia, and edema. In adults, the most common causes of nephrotic syndrome include focal segmental glomerulosclerosis ( FSGS) and membranous nephropathy.
Nephrotic Vs Nephritic Syndromes Rebel Em Emergency Medicine Blog kulturaupice
1. Hematuria 2. Oliguria 3. Azotemia 4. Hypertension How do you make these lists hang together in a way that you can remember? First, let's take nephrotic syndrome. The thing to remember for this one is massive proteinuria. You might do this by remembering that nephrotic and protein both have an "o"Â in them. Summary. Nephrotic syndrome is defined as the presence of proteinuria (>3.5 g/24 hours), hypoalbuminemia (<3.0 g/dL), and peripheral edema. Hyperlipidemia and thrombotic disease are also frequently seen. Despite heavy proteinuria and lipiduria, the urine contains few cells or casts. This is in contrast to nephritic syndrome, which is typically.




