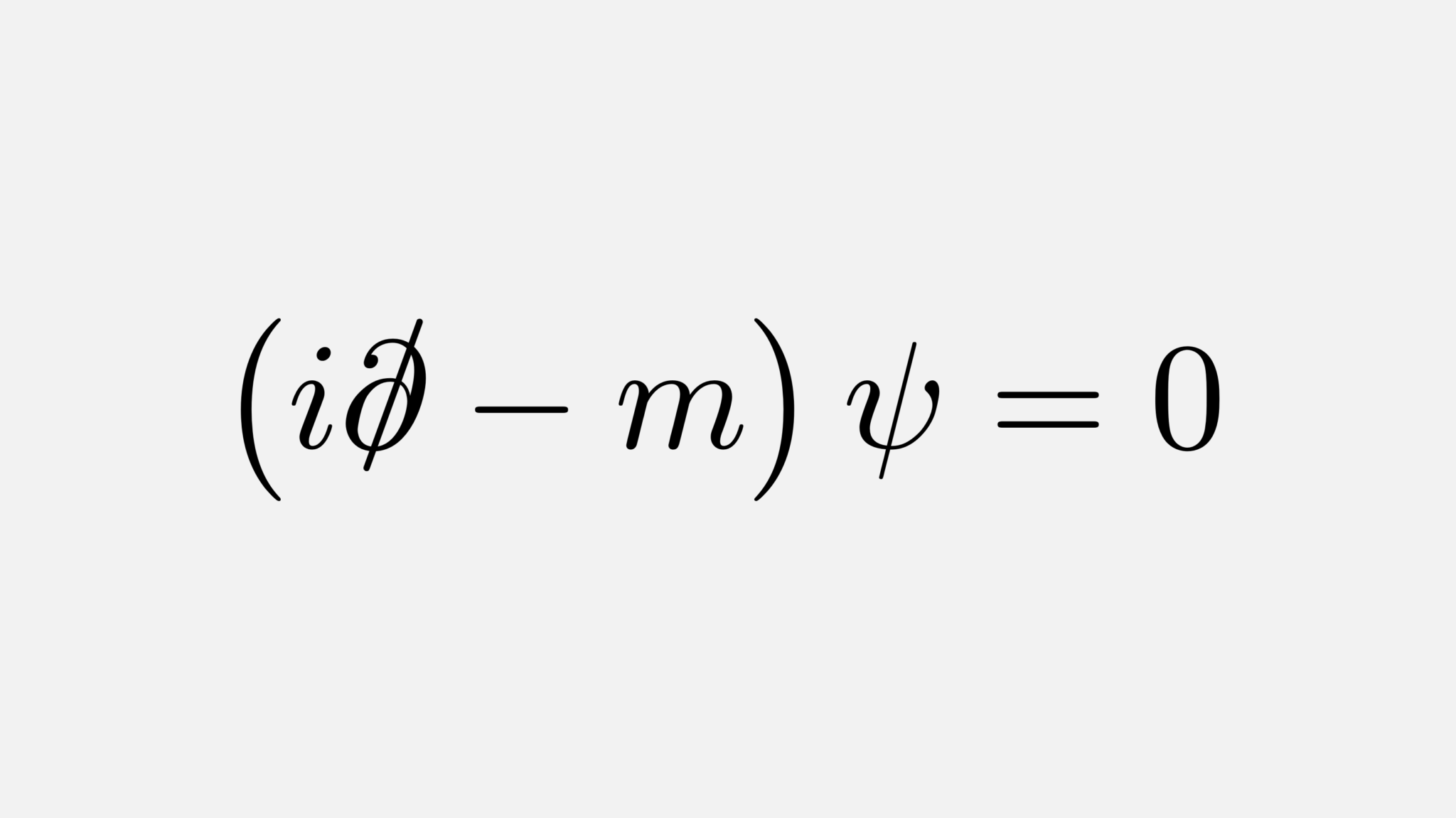In particle physics, the Dirac equation is a relativistic wave equation derived by British physicist Paul Dirac in 1928. In its free form, or including electromagnetic interactions, it describes all spin- 1⁄2 massive particles, called "Dirac particles", such as electrons and quarks for which parity is a symmetry. British theoretical physicist Paul Dirac was one of the most significant figures in the early days of quantum physics, who along with Erwin Schrödinger won the Nobel Prize for physics in 1933.
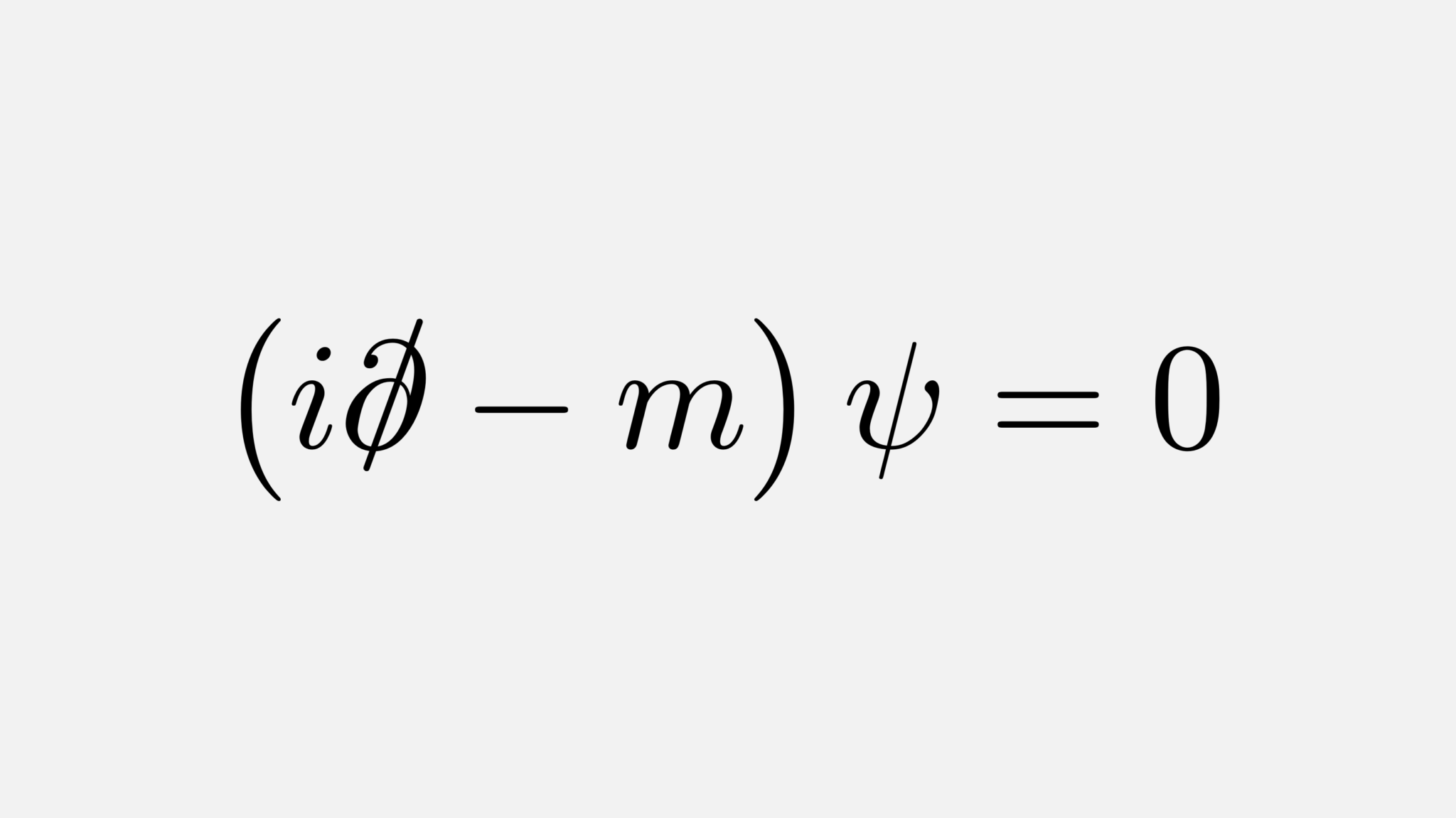
L’Equation de Paul DIRAC
History Feature Paul Dirac: the purest soul in physics 01 Feb 1998 Paul Dirac published the first of his papers on "The Quantum Theory of the Electron" seventy years ago this month. The Dirac equation, derived in those papers, is one of the most important equations in physics, says Michael Berry Genius at work. Dirac's equation is a relativistic wave equation explaining that parity inversion (sign inversion of spatial coordinates) is symmetrical for all half-spin electrons and quarks. The equation was first explained in 1928 by P. A. M. Dirac. The equation is used to predict the existence of antiparticles. Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac OM FRS [6] ( / dɪˈræk /; 8 August 1902 - 20 October 1984) was an English mathematical and theoretical physicist who is considered to be one of the founders of quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. [7] [8] He is credited with laying the foundations of quantum field theory. The Dirac Hamiltonian. So far, we have been using \(p^2/2m\)-type Hamiltonians, which are limited to describing non-relativistic particles.In 1928, Paul Dirac formulated a Hamiltonian that can describe electrons moving close to the speed of light, thus successfully combining quantum theory with special relativity.

The Dirac Equation In Ten Different Coordinate Systems YouTube
In 1927, Paul Dirac sought to reconcile these theories and intro-duced the Dirac equation to describe relativitistic quantum mechanics. Paul Dirac (1902-1984) The objective of this course was to deepen our understanding of quantum eld theory, one of the. The Dirac Equation has to be relativistic, and so a logical place to start our derivation is equation (1). If you're wondering where equation (1) comes from, it's quite simple.. The Dirac Equation Our goal is to find the analog of the Schrödinger equation for relativistic spin one-half particles,however, There was no explanation of the gyromagnetic ratio of 2. the Schrödinger-Pauli Hamiltonianwhich contains the dot product of the Pauli matrices with the momentum operator. These equations needed to be adapted to Einstein's theory of relativity, however. In 1928 Paul Dirac formulated a fully relativistic quantum theory. The equation gave solutions that he interpreted as being caused by a particle equivalent to the electron, but with a positive charge. This particle, the positron, was later confirmed through.

Solutions of the Dirac Equation with Gravitational plus Exponential Potential
For a free electron, the Dirac equation predicts the Zitterbewegung to have an amplitude of the order of the Compton wavelength, RZB ≈ 10 -12 m, and a frequency of ωZB ≈ 10 21 Hz, and the. The Dirac equation. Paul Dirac developed a theory that combined quantum mechanics, used to describe the subatomic world, with Einstein's special relativity, which says nothing travels faster.
Paul Adrien Maurice Dirac Born: August 8, 1902, Bristol, Gloucestershire, England Died: October 20, 1984, Tallahassee, Florida, U.S. (aged 82) Awards And Honors: Copley Medal (1952) Nobel Prize (1933) Notable Works: "The Principles of Quantum Mechanics" Subjects Of Study: Dirac equation Fermi-Dirac statistics approximation electron quantum August 8 is the birth anniversary of Paul Dirac (1902-1984), a significant theoretical physicist who is recognized for his revolutionary contributions to quantum field theory and quantum mechanics.
Solution of Dirac Equation YouTube
The differential operator introduced by Dirac in his study of the quantum theory of the electron has turned out to be of fundamental importance both for physics and for mathematics. Essentially the operator is a formal square-root of the wave operator or, with a different signature, of the Laplacian. In this lecture I will attempt to survey its. The Dirac equation is a combination many discoveries and innovations that were occurring at the beginning of the 20th century. The equation helps to relate the wave function of an electron to the curvature of spacetime. In order to do this, both the Planck constant(h) and the Shrodinger equation are referenced.