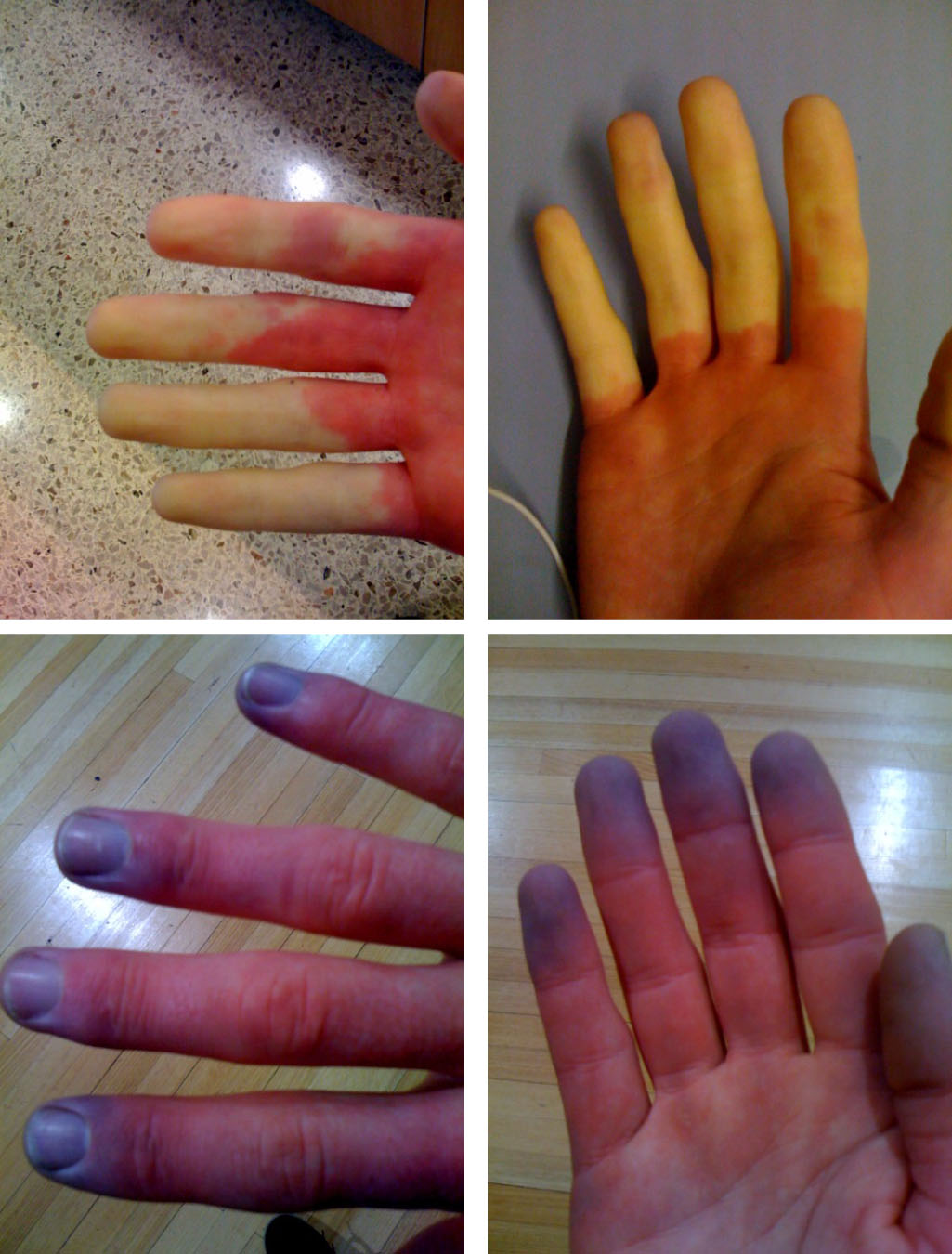
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. [1] Typically, the fingers, and less commonly, the toes, are involved. [1] Rarely, the nose, ears, nipples, or lips are affected. [1] Raynaud's (pronounced ray-nodes) syndrome is a disorder that affects small blood vessels in your fingers and toes. It may also affect blood vessels in your nose, lips or ear lobes. Raynaud's causes you to have episodic spasms, called vasospastic attacks, in response to cold temperatures or stress.

Renaud Syndrom / Maladie de Raynaud — Wikipédia
departments Overview Raynaud's (ray-NOSE) disease causes some areas of the body — such as fingers and toes — to feel numb and cold in response to cold temperatures or stress. In Raynaud's disease, smaller arteries that supply blood to the skin narrow. This limits blood flow to affected areas, which is called vasospasm. Raynaud's phenomenon Raynaud's phenomenon is frequently the first manifestation of CREST/lcSSc, preceding other symptoms by years. Stress and cold temperature induce an exaggerated vasoconstriction of the small arteries, arterioles, and thermoregulatory vessels of the skin of the digits. Sjögren syndrome or Sjögren's syndrome ( SjS, SS) is a long-term autoimmune disease that affects the body's moisture-producing glands ( lacrimal and salivary ), [4] and often seriously affects other organ systems, such as the lungs, kidneys, and nervous system. [8] Raynaud's Symptoms. You might notice: Cold fingers and toes. Your skin might turn white or blue when it's cold or when you're stressed. As you warm up, it could turn red. Your fingers and.

5 dolog, amiről felismerheti a Raynaudszindrómás beteget!
Raynaud's syndrome is a condition in which a person's fingers, and sometimes toes, turn blue and/or white upon exposure to cold, and then bright red upon rewarming. These symptoms— caused by the constriction of small blood vessels in the hands or feet—can last for seconds to hours, but most often last around 15 minutes. Medicines used to treat people with Raynaud's disease may include: Calcium channel blockers. These drugs relax and open small blood vessels in the hands and feet. These drugs also can help heal sores on fingers or toes. Examples include nifedipine (Procardia), amlodipine (Norvasc), felodipine and isradipine. Vasodilators. Raynaud phenomenon can be categorized as either primary or secondary. [1][2][3] In response to cold temperatures, the body adapts by restricting blood flow to the skin. This is done as a thermoregulating mechanism to prevent further loss of body heat and to sustain the core body temperature. In Raynaud phenomenon, blood-flow restriction occurs. A Raynaud-szindróma egy olyan tünetegyüttes, amelynél a végtagokban (leginkább az ujjak végein, de változatos kiterjedésben) keringészavar áll be. Ennek következtében az ujjak vége ellilul, előtte azonban éles határokkal kifehéredik, a bőr feszül és fáj.
Raynaud's Phenomenon Cause Symptoms Diagnosis and Treatment
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders in the current classification, with the latest type discovered in 2018. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic. A Raynaud-jelenség (RP) az arteriolák stressz hatására létrejövő reverzibilis, görcsszerű összehúzódása. Maurice Raynaud írta le először, 1862-ben. Leggyakrabban ujjakon, az orron, nyelven vagy fülön fordul elő. Az esetek többségénél sápadtság kíséri, amelyet fokozottabb cianózis követ és a bőr kivörösödése kísér a hiperaemia következményeként.
A Raynaud-betegség terápiájában az értágító hatású szájon át szedhető és kúraszerűen infúzió formájában adható kezelés mellett hatásos a szén-dioxid terápia, vagyis a mofetta kezelés. Ez értágító hatása révén kifejezetten előnyös Raynaud-betegségben. Raynaud phenomenon is a condition in which the body's normal response to cold or emotional stress is exaggerated, resulting in abnormal spasms (vasospasms) in small blood vessels called arterioles. The disorder mainly affects the fingers but can also involve the ears, nose, nipples, knees, or toes. The vasospasms reduce blood circulation.

Raynaudszindróma gyógytornász válaszol Gyógytornászom.hu
Primer Raynaud-szindróma esetén a tünetek önállóan fordulnak elő, a secunder Raynaud-szindróma esetében a panaszok más kórkép részeként jelentkeznek. A tünetek mindkét esetben a véráramlás zavarával függnek össze - magyarázza a különbségeket és a hasonlóságokat dr. Smajda Zsuzsanna immunológus, az Immunközpont orvosa. A Raynaud-szindróma egy olyan állapot, amikor az ujjak, a lábujjak, a fül vagy az orr vérárama nem teljesen ép, esetleg ezekben egyáltalán nem történik keringés. Ez akkor fordul elő, amikor a kezekben vagy lábakban lévő erek összehúzódnak, amennyiben szűület történik azt vazospasmusnak nevezzük. A szindrómát kísérheti más emögött meghúzódó tünetek.




