A servo motor is defined as an electric motor that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, speed, and torque. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback and a controller that regulates the motor's movement according to a desired setpoint. The servo motor is an electric motor, which enables continuous determination of precise positions, speeds and torque via control electronics (servo controller).

What is a servo motor? How it works & application
A servomotor (or servo motor or simply servo) [1] is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration in a mechanical system. [1] [2] It constitutes part of a servomechanism, and consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. A servomotor (or servo motor) is a rotary or linear actuator that allows precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a position feedback sensor. Servo motors are used in applications such as robotics, CNC machinery, or automated manufacturing. noun ser· vo· mo· tor ˈsər-vō-ˌmō-tər : a power-driven mechanism that supplements a primary control operated by a comparatively feeble force (as in a servomechanism) Examples of servomotor in a Sentence Recent Examples on the Web Our test car also suffered from an incessantly whirring servomotor. The servo motor is a closed-loop mechanism that incorporates positional feedback in order to control the rotational or linear speed and position. The motor is controlled with an electric signal, either analog or digital, which determines the amount of movement which represents the final command position for the shaft.
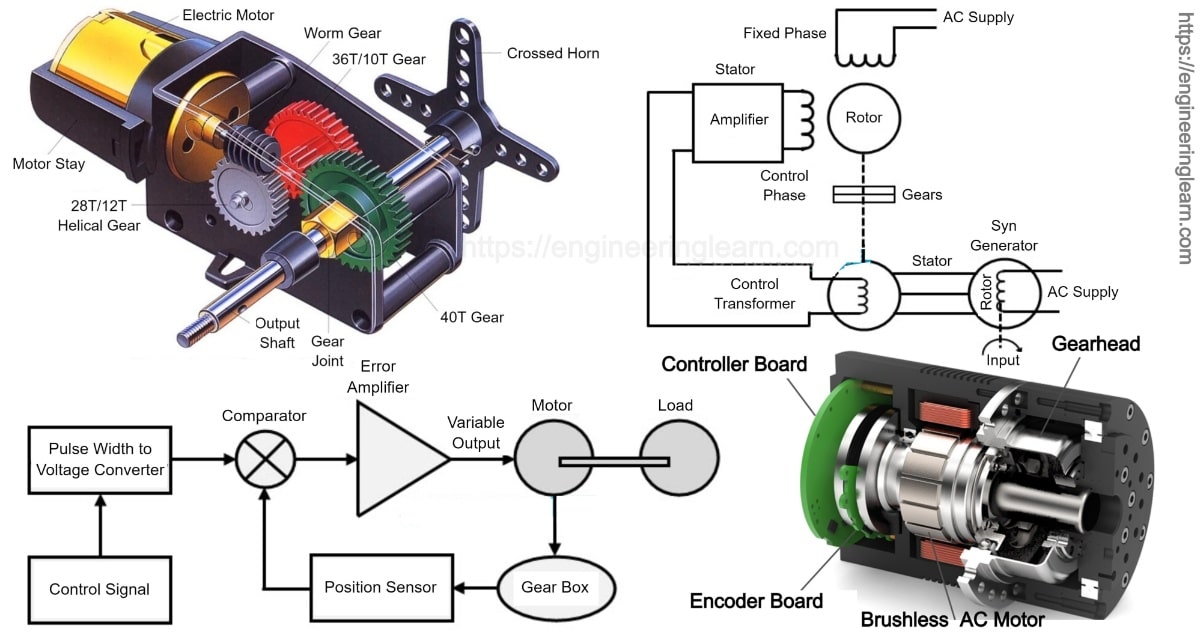
Servomotor Working Principle Engineering Learner
A servo motor is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular position. It consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a servo drive to complete the system. The drive uses the feedback sensor to precisely control the position, speed or velocity of the motor. How Does a Servo Motor Work? In mechanical and control engineering, a servomechanism (also called servo system, or simply servo) is a control system for the position and its time derivatives, such as velocity, of a mechanical system. It often includes a servomotor, and uses closed-loop control to reduce steady-state error and improve dynamic response. [1] A servomotor is a structural unit of a servo system and is used with a servo drive. The servomotor includes the motor that drives the load and a position detection component, such as an encoder. The servo motor is the motor used for servo system. The so-called servo system is a control system that acts according to the instructions. It can compare the actual state of the system with the corresponding state of the instructions, and use the comparison result for further control. Servo motors include direct current motors (with brush and.
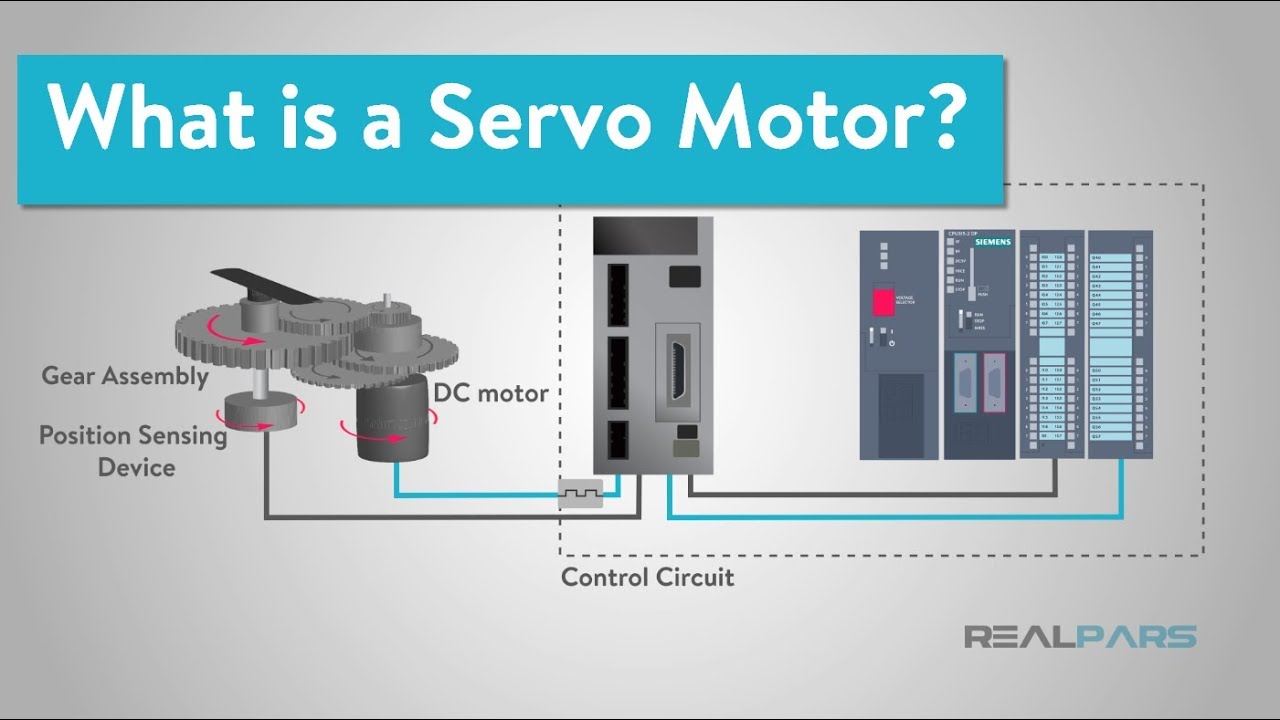
What is a Servo Motor and How it Works? YouTube
A servo motor is a type of motor that can rotate with great precision. Normally this type of motor consists of a control circuit that provides feedback on the current position of the motor shaft, this feedback allows the servo motors to rotate with great precision. The term "servo" refers to the control mechanism. In terms of technology, the mechanism that performs control is called the "master" and the mechanism being controlled is called the "slave." Both terms, "servo" and "slave" derive from "servus", the Latin word for slave.
Definition of Servo Motor: A servo motor is defined as a linear or rotary type of actuator that provides fast precision position control for closed-loop position control applications. As compared to large industrial electric motors, servo motors are not useful for continuous energy conversion. What is a servo motor? Servo motors (or servos) are self-contained electric devices (see Figure 1 below) that rotate or push parts of a machine with great precision. Servos are found in many places: from toys to home electronics to cars and airplanes.
Servo Motor Types, Construction, Working, Controlling & Applications
A servo motor is a rotary actuator or motor that allows for a precise control in terms of angular position, acceleration and velocity, capabilities that a regular motor does not have. It makes use of a regular motor and pairs it with a sensor for position feedback. Servo motors work on servo mechanism that uses position feedback to control the speed and final position of the motor. Internally, a servo motor combines a motor, feedback circuit, controller and other electronic circuit. It uses encoder or speed sensor to provide speed feedback and position. This feedback signal is compared with input command.




