The transistor voltage regulator works based on the principle of using a variable resistor in the form of a transistor. This transistor adjusts its resistance in response to changes in input voltage or load conditions, thus maintaining a steady output voltage. A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. It may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages.

National Semiconductor LM317K Variable Voltage Regulator TO3 Transistor OMA064A Rich Electronics
Variable Voltage Regulator using Transistor This adjustable voltage regulator circuit uses a transistor, Zener diode, and potentiometer to produce a regulated output in the range 0 V to 8.5 V (at 0.5-amps max). The input voltage should be in the range 12 V to 16 V. Pass Element: The pass element (e.g. a transistor) acts as a variable resistance and drops the excess voltage across it. The output voltage is obtained at one terminal of the pass element. Figure 1: Variable Voltage Regulator Block Diagram Figure 1 shows the block diagram of a simple variable voltage regulator. 1. Zener Controlled Transistor Voltage Regulator A zener controlled voltage regulator is used when the efficiency of a regulated power supply becomes very low due to high current. There are two kinds of zener controlled transistor voltage regulators. Zener Controlled Transistor Series Voltage Regulator A voltage regulator with a transistor usually consists of a bipolar junction transistor (bjt) with high current handling capability in an emitter follower configuration, driven by zener diode and resistor potential divider (PD) network. We first use a Zener diode and resistor across the input rail to make a PD that provides a regulated output.
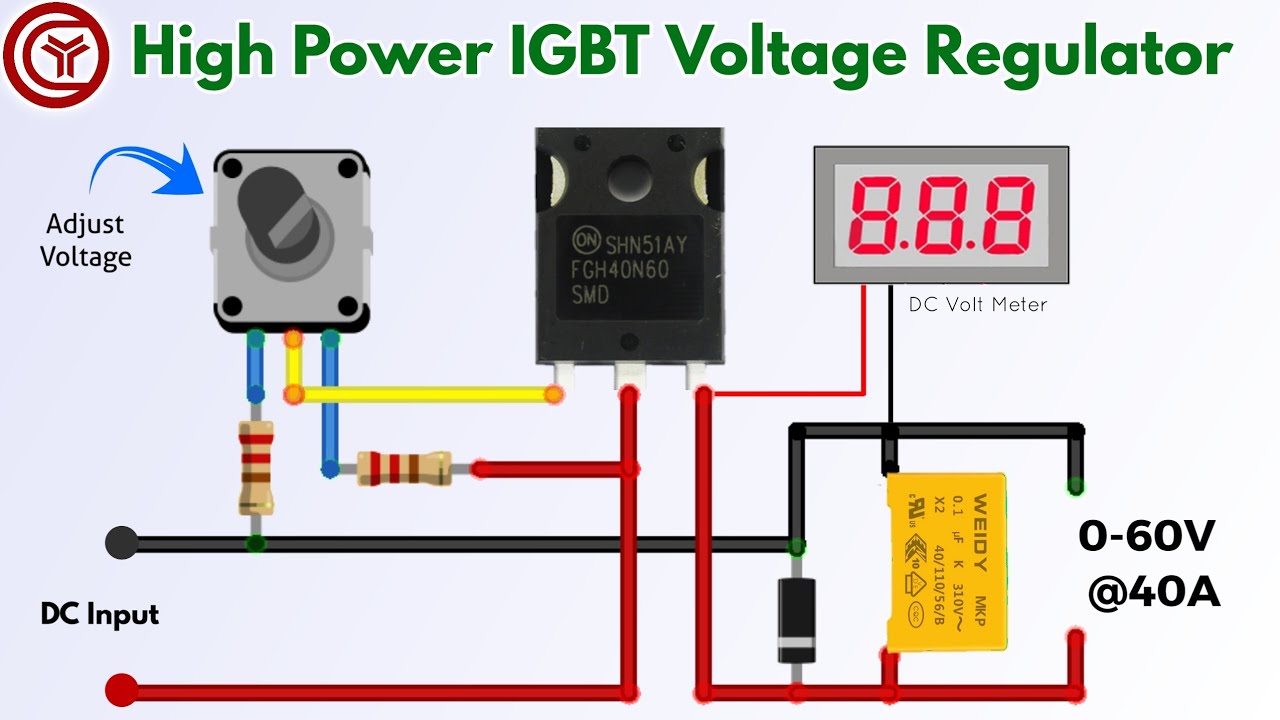
060v adjustable voltage regulator using single IGBT Transistor YouTube
A voltage regulator circuit using an op amp, emitter follower transistor, and Zener diode, is simple to draw from memory if you understand the working principle.. In addition, if you make R 1 a variable resistor, then the output voltage could be varied for a large range of voltages. For this op amp circuit, we use the operational amplifier. A regulator is an important device when it comes to power electronics as it controls the power output. Need for a Regulator For a Power supply to produce a constant output voltage, irrespective of the input voltage variations or the load current variations, there is a need for a voltage regulator. Low Dropout Voltage Regulator (LDO) The LDO act as a variable resistor that is placed between input power source and the load in order to drop and control the voltage applied to the load. Compared to DC‐DC switching regulators, LDOs are: Of continuous operation. Easier to use. A high-stability voltage regulator (VR) is proposed in this paper, which integrates transient enhancement and overcurrent protection (OCP). Taken into consideration the performance and area advantages of low-voltage devices, most control parts of proposed VR are supplied by the regulated output voltage, which forms self-power technique (SPT) with power supply rejection (PSR) boosting. Besides.

LM317T IC Adjustable Voltage Regulator FET Transistor Buy LM317T IC Adjustable Voltage
Practical Simplest Zener Regulator The most basic regulator employs a two-terminal device such as a zener diode with the characteristic of keeping a constant voltage across it. Figure 1 below depicts the basic circuit. Zener diodes could be connected in series in any configuration for achieving even higher voltages. Variable Voltage, Current Power Supply Circuit Using Transistor 2N3055 Last Updated on May 13, 2022 by Swagatam 290 Comments In this post we learn how to make a simple variable power supply circuit using transistor 2N3055 and some other passive components. It includes variable voltage and variable current feature, fully adjustable.
Transistor (Q1) - It helps to modify the resistance of the circuit to maintain voltage constant. Its terminals are Base, emitter and collector. The Zener diode is connected to the base of the transistor, and input is given at the collector side. The load is connected to the emitter. Let VBE be the base-emitter voltage. LM723 Voltage Regulator Features. It is an adjustable voltage regulator which operates in both positive or negative supply operation. Voltage can be adjusted from 2V to 37V. The maximum input voltage is 40V. Output current is 150mA without an external pass transistor. It can be increased to 10A by adding transistors externally.
Zener Diode as Voltage Regulator your electrical guide
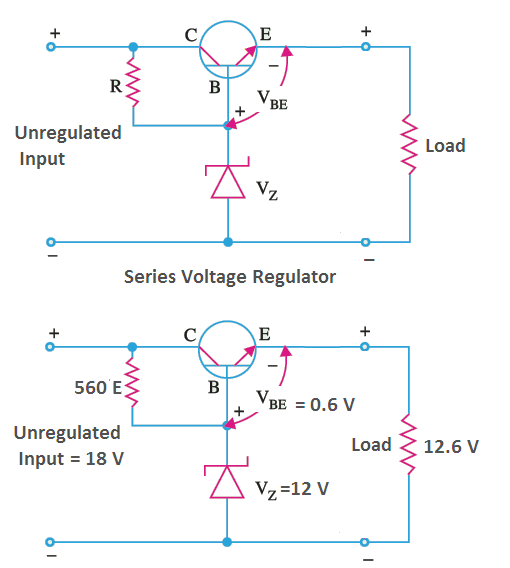
Here Zener diode provides the reference voltage. The transistor series voltage regulator working is when the voltage at the transistor's base voltage is held to the stable voltage across the diode. For instance, if Zener voltage is 8V, the transistor's base voltage will stay approximately 8V. Therefore, Vout = VZ - VBE. The Transistor Series Voltage Regulator Theory is explained as follows. From the circuit of Figure, we can observe that the feedback voltage V F, is the voltage developed across the part of the potential divider P & Q.If we represent that resistance by R f, the feed back fraction will be, R f /(R f + R a) where R a is the part of the potential divider R & P as shown in figure.



