Koch's triangle, named after the German pathologist Walter Koch, [1] is an anatomical area located in the superficial paraseptal endocardium of the right atrium, which its boundaries are the coronary sinus orifice, tendon of Todaro, and septal leaflet of the right atrioventricular valve. [2] The triangle of Koch is defined by the following structures within the right atrium: (1) The ostium of the coronary sinus, posteriorly; (2) the anterior portion of the tricuspid valve annulus; and (3) the tendon of Todaro (a tendinous structure connecting the valve of the inferior vena cava ostium to the central fibrous body), posteriorly.
Triangle of Koch All About Cardiovascular System and Disorders
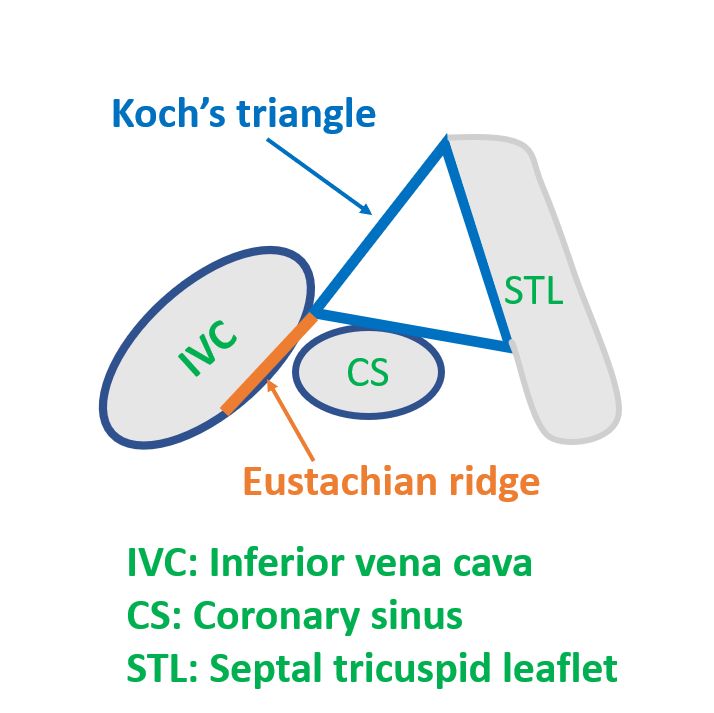
Triangle of Koch is situated on the right atrial aspect of the inter-atrial septum. It is bounded by the septal tricuspid leaflet, tendon of Todaro and the coronary sinus. The atrioventricular node is located at the apex of this triangle [1]. The initial description of the triangle was by Walter Koch in 1909 [2]. The triangle of Koch or Koch's triangle is an important landmark for atrioventricular catheter ablation procedures for the localization of the atrioventricular node. Gross anatomy The coronary sinus originates from the confluence of the oblique vein (of Marshall) of left atrium and the great cardiac vein, and receives the small and middle cardiac veins, and the posterior vein of the left ventricle as tributaries. This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the coronary sinus. Contents Anatomy and course This anatomic region is also commonly referred to as the triangle of Koch. The sinoatrial nodal artery supplies blood to the sinoatrial node, it branches off the right coronary artery in 60% of cases, whereas in 40% of cases, it comes from the left circumflex coronary artery. The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal branch of the.
Everything About The Triangle of Koch (Human Cardiac Anatomy) Medrenaline
This anatomic region is also commonly referred to as the triangle of Koch. The blood supply to the AV node is from the AV nodal branch of the right coronary artery (90%) or the left circumflex artery (10%) depending on the right or left dominant blood supply to the heart. The first septal perforator of the left anterior descending artery also. Synonyms: Triangle of Koch, Tendon of valve of inferior vena cava The atrioventricular node is an oblique, oval-shaped collection of cells located in the wall of the posteroinferior region of the interatrial septum, close to the coronary sinus. Triangle of Koch. Triangle of Koch with the compact atrioventricular (AV) node and its inferior and superior extensions. Contributed by Spyridon Koulouris, MD. Modified from Shereen. A comprehensive review of the anatomical variations in the right atrium and their clinical significance. Koch's triangle, named after the German pathologist Walter Koch, is an anatomical area located in the superficial paraseptal endocardium of the right atrium, which its boundaries are the coronary sinus orifice, tendon of Todaro, and septal leaflet of the right atrioventricular valve.

Highresolution mapping of the triangle of Koch Spatial heterogeneity of fast pathway
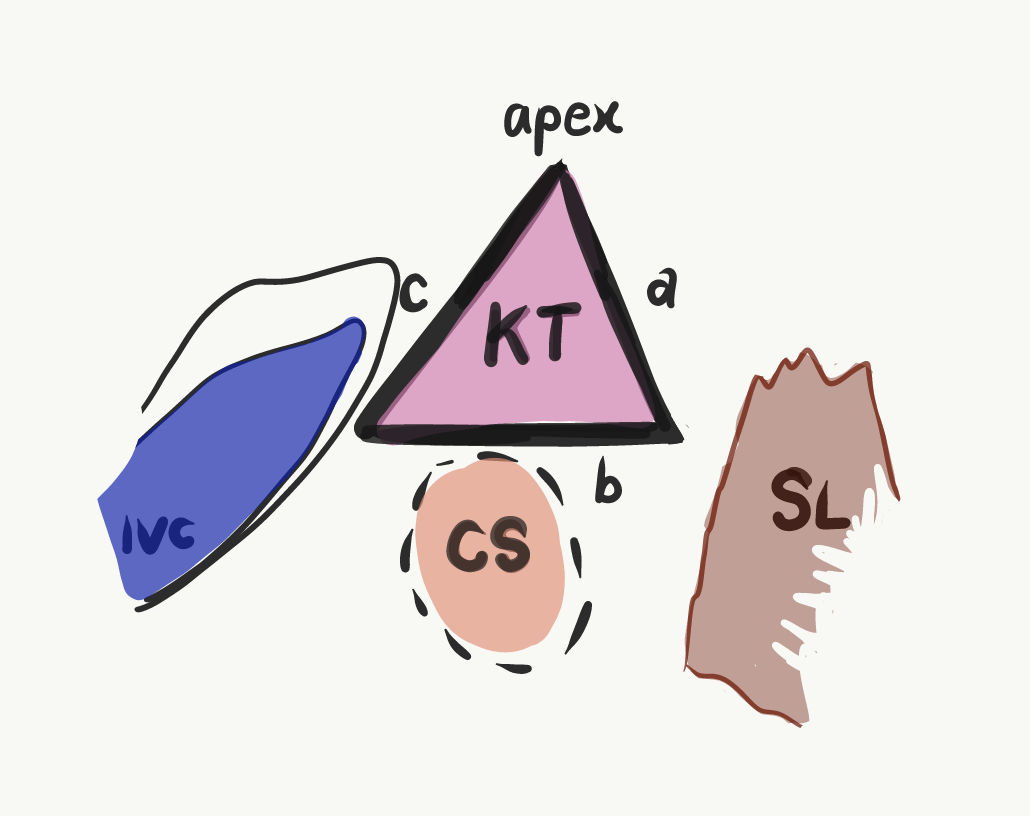
The Triangle of Koch is one of the important anatomical areas, it is located in the right atrium of the human heart, to be specific in the superficial paraseptal endocardium of the right atrium. The triangle of Koch is the target of ablation for atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia, septal and paraseptal accessory pathways, and atypical forms of atrial flutter (32,33). The size of the triangle of Koch varies in different individuals, with a mean height of 26 mm ± 8 .
The mean value of the Koch's triangle area was 151.5 ± 55.8 mm 2. The 95th percentile of triangle's height (the distance from the apex to the coronary sinus) was 21.8 mm. Conclusion Mean values and proportions of triangle's sides and angles were presented. Koch's triangle showed considerable individual variations in size. Introduction: There is growing use of the Todaro tendon and triangle of Koch as anatomic icons for invasive cardiac electrophysiologists. Reasons exist to doubt this validity. Methods and results: Histologic sections were prepared from 96 anatomically normal human hearts. The study area extended from the crista supraventricularis to the eustachian valve and included the AV node and His bundle.

Highresolution mapping of the triangle of Koch Spatial heterogeneity of fast pathway
ANATOMY - the Triangle of Koch is comprised of superficial structures located in the low right atrium. Defined by three anatomical borders: Septal leaflet of the tricuspid annulus Tendon of Todaro, the apex of the Triangle, anterior structure ( His bundle catheter placement) Morphometry of the triangle of Koch and position of the coronary sinus opening in cadaveric fetal hearts - PMC Journal List Indian Heart J v.69 (1); Jan-Feb 2017 PMC5319009 As a library, NLM provides access to scientific literature.




